Abstract
Objective
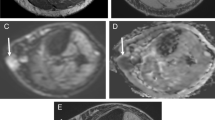
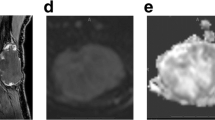
Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) provides essential information regarding tumor composition, such as cellularity and/or perfusion. DWI is helpful in distinguishing between malignant and benign lesions. Malignant intramuscular/soft tissue lesions consist of a wide spectrum of tumors that have different cell counts and matrix. It is presumed that these different tumors have different DWI findings and have different apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values. The aim of this study was to analyze DWI findings of different intramuscular malignancies in a multicentric study by using a standardized DWI protocol, and to compare the ADC values acquired.
Materials and methods
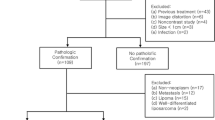
The data banks of four radiology departments were screened retrospectively for malignant intramuscular tumors. Only lesions that were investigated by MRI (with a 1.5-T scanner) using DWI (multishot EPI sequence with b values of 0 and 1,000 s/mm2) were included in the study. Overall, 51 patients (28 women, 23 men; mean age 58.8 ± 16.1 years) with 57 different malignant intramuscular lesions were collected. In every case apparent diffusion constant (ADC) maps were calculated. In 14 patients muscle lymphoma, 11 patients intramuscular metastases from different primary tumors, and in 26 cases several muscle sarcomas were identified.
Results
The mean ADC value of the estimated lesions was 1.24 ± 0.53 × 10−3 mm2s−1, median value, 1.11 × 10−3 mm2s−1, range, 0.54–2.9 × 10−3 mm2s−1. The mean ADC value in muscle metastases was 1.28 ± 0.24 × 10−3 mm2s−1, in muscle lymphoma 0.76 ± 0.14 × 10−3 mm2s−1, and in muscle sarcomas 1.82 ± 0.63 × 10−3 mm2s−1. Muscle lymphoma showed statistically significant lower ADC values in comparison to muscle metastases (p = 0.01) and muscle sarcoma (p = 0.001). There was no significant differences between ADC values in muscle metastases and sarcomas (p = 0.48). ADC values in muscle lymphoma were homogeneous with less inter-patient variability and were within a relatively close range. Muscle sarcomas had a broad range of ADC values.
Conclusion
Intramuscular malignant lesions had different ADC values on DWI. 22.8 % of the tumors analyzed had low ADC values, 26.3 % moderate, and 50.9 % high ADC values. Muscle lymphoma had statistically significantly lower ADC values in comparison to muscle metastases and sarcomas. Muscle sarcomas presented with a broad range of ADC values.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Subhawong TK, Durand DJ, Thawait GK, Jacobs MA, Fayad LM. Characterization of soft tissue masses: can quantitative diffusion weighted imaging reliably distinguish cysts from solid masses? Skeletal Radiol. 2013;42:1583–92.
Sasaki M, Eida S, Sumi M, Nakamura T. Apparent diffusion coefficient for sinonasal diseases: differentiation of benign and malignant lesions. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011;32:1256–62.
Fornasa F, Pinali L, Gasparini A, Toniolli E, Montemezzi S. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in focal breast lesions: analysis of 78 cases with pathological correlation. Radiol Med. 2011;116(2):264–75.
Driessen JP, Caldas-Magalhaes J, Janssen LM, et al. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in laryngeal and hypopharyngeal carcinoma: association between apparent diffusion coefficient and histologic findings. Radiology 2014;272(2):456–63.
Schnapauff D, Zeile M, Niederhagen MB, et al. Diffusion-weighted echo-planar magnetic resonance imaging for the assessment of tumor cellularity in patients with soft-tissue sarcomas. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009;29:1355–9.
Yamaguchi K, Schacht D, Nakazono T, Irie H, Abe H. Diffusion weighted images of metastatic as compared with nonmetastatic axillary lymph nodes in patients with newly diagnosed breast cancer. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2014; doi: 10.1002/jmri.24829.
Van Rijswijk CSP, Kunz P, Hogendoorn PC, et al. Diffusion-weighted MRI in the characterization of soft-tissue tumors. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2002;15:302–7.
Einarsdóttir H, Karlsson M, Wejde J, Bauer HC. Diffusion-weighted MRI of soft tissue tumours. Eur Radiol. 2004;14:959–63.
Genovese E, Canì A, Rizzo S, Angeretti MG, Leonardi A, Fugazzola C. Comparison between MRI with spin-echo echo-planar diffusion-weighted sequence (DWI) and histology in the diagnosis of soft-tissue tumours. Radiol Med. 2011;116(4):644–56.
Razek A, Nada N, Ghaniem M, Elkhamary S. Assessment of soft tissue tumours of the extremities with diffusion echoplanar MR imaging. Radiol Med. 2012;117(1):96–101.
Surov A, Behrmann C. Diffusion-weighted imaging of skeletal muscle lymphoma. Skeletal Radiol. 2014;43(7):899–903.
Nagata S, Nishimura H, Uchida M, et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging of soft tissue tumors: usefulness of the apparent diffusion coefficient for differential diagnosis. Radiat Med. 2008;26(5):287–95.
Oka K, Yakushiji T, Sato H, et al. Usefulness of diffusion-weighted imaging for differentiating between desmoid tumors and malignant soft tissue tumors. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2011;33(1):189–93.
Surov A, Fiedler E, Voigt W, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of intramuscular metastases. Skeletal Radiol. 2011;40:439–46.
Khoo MM, Tyler PA, Saifuddin A, Padhani AR. Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) in musculoskeletal MRI: a critical review. Skeletal Radiol. 2011;40:665–81.
Subhawong TK, Jacobs MA, Fayad LM. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging for characterizing musculoskeletal lesions. Radiographics. 2014;34(5):1163–77.
Subhawong TK, Jacobs MA, Fayad LM. Insights into quantitative diffusion-weighted MRI for musculoskeletal tumor imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2014;203(3):560–72.
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Surov, A., Nagata, S., Razek, A.A.A. et al. Comparison of ADC values in different malignancies of the skeletal musculature: a multicentric analysis. Skeletal Radiol 44, 995–1000 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-015-2141-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-015-2141-5