Abstract
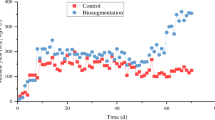
Ruminal microbiota (RM) were co-inoculated with anaerobic sludge (AS) at different ratios to study the digestion of rice straw in batch experiments. The CH4 yield reached 273.64 mL/g volatile solid (VS) at a co-inoculum ratio of 1:1. The xylanase and cellulase activities were 198.88–212.88 and 24.51–29.08 U/mL in co-inoculated samples, respectively, and were significantly different compared to the results for single inoculum (p < 0.05). Higher ratios of AS enhanced acetoclastic methanogenesis, and propionate accumulation could be the main reason for the longer lag phase observed in samples with a higher RM ratio. The microbial compositions were clearly altered after digestion. Fibrobacter, Ruminococcus and Butyrivibrio from the rumen did not settle in the co-inoculated system, whereas Clostridiales members became the main polysaccharide degraders. Microbial interactions involving hydrolytic bacteria and acetoclastic methanogens in the residue were considered to be significant for hydrolysis activities and methane production. Syntrophy involving propionate oxidizers with associated methanogens occurred in the liquid phase. Our findings provide a better understanding of the anaerobic digestion of rice straw that is driven by specific microbial populations.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (1995) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 19th edn. American Public Health Association, New York
Azman S, Khadem AF, van Lier JB, Zeeman G, Plugge CM (2015) Presence and role of anaerobic hydrolytic microbes in conversion of lignocellulosic biomass for biogas production. Crit Rev Env Sci Tec 45:2523–2564. doi:10.1080/10643389.2015.1053727
Chapleur O, Bize A, Serain T, Mazéas L, Bouchez T (2014) Co-inoculating ruminal content neither provides active hydrolytic microbes nor improves methanization of 13C-cellulose in batch digesters. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 87:616–629. doi:10.1111/1574-6941.12249
Chen Y, Cheng JJ, Creamer KS (2008) Inhibition of anaerobic digestion process: a review. Bioresour Technol 99:4044–4064. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2007.01.057
Dai X, Tian Y, Li J, Su X, Wang X, Zhao S, Liu L, Luo Y, Liu D, Zheng H, Wang J, Dong Z, Hu S, Huang L (2015) Metatranscriptomic analyses of plant cell wall polysaccharide degradation by microorganisms in the cow rumen. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:1375–1386. doi:10.1128/AEM.03682-14
Demirel B, Scherer P (2008) The roles of acetotrophic and hydrogenotrophic methanogens during anaerobic conversion of biomass to methane: a review. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 7:173–190. doi:10.1007/s11157-008-9131-1
Dodsworth JA, Blainey PC, Murugapiran SK, Swingley WD, Ross CA, Tringe SG, Chain PSG, Scholz MB, Lo CC, Raymond J, Quake SR, Hedlund BP (2013) Single-cell and metagenomic analyses indicate a fermentative and saccharolytic lifestyle for members of the OP9 lineage. Nat Commun 4:1854. doi:10.1038/ncomms2884
Finegold SM, Lawson PA, Vaisanen ML, Molitoris DR, Song Y, Liu C, Collins MD (2004) Anaerofustis stercorihominis gen. nov., sp. nov., from human feces. Anaerobe 10:41–45. doi:10.1016/j.anaerobe.2003.10.002
FitzGerald JA, Allen E, Wall DM, Jackson SA, Murphy JD, Dobson AD (2015) Methanosarcina play an important role in anaerobic co-digestion of the seaweed Ulva lactuca: taxonomy and predicted metabolism of functional microbial communities. PLoS One 10:e0142603. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0142603
Glissmann K, Conrad R (2000) Fermentation pattern of methanogenic degradation of rice straw in anoxic paddy soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 31:117–126. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6941.2000.tb00677.x
Gu Y, Chen X, Liu Z, Zhou X, Zhang Y (2014) Effect of inoculum sources on the anaerobic digestion of rice straw. Bioresour Technol 158:149–155. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2014.02.011
Han S, Liu Y, Zhang S, Luo G (2016) Reactor performances and microbial communities of biogas reactors: effects of inoculum sources. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:987–995. doi:10.1007/s00253-015-7062-7
Hatamoto M, Kaneshige M, Nakamura A, Yamaguchi T (2014) Bacteroides luti sp. nov., an anaerobic, cellulolytic and xylanolytic bacterium isolated from methanogenic sludge. Int J Syst Evol Micr 64:1770–1774. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.056630-0
Hu J, Arantes V, Saddler JN (2011) The enhancement of enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic substrates by the addition of accessory enzymes such as xylanase: is it an additive or synergistic effect? Biotechnol Biofuels 4:36. doi:10.1186/1754-6834-4-36
Hu ZH, Yu HQ (2005) Application of rumen microorganisms for enhanced anaerobic fermentation of corn stover. Process Biochem 7:2371–2377. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2004.09.021
Hu ZH, Yu HQ, Yue ZB, Harada H, Li YY (2007) Kinetic analysis of anaerobic digestion of cattail by rumen microbes in a modified UASB reactor. Biochem Eng J 37:219–225. doi:10.1016/j.bej.2007.04.013
Joblin KN (2005) Methanogenic archaea. In: Makkar HPS, McSweeney CS (eds) Methods in gut microbial ecology for ruminants. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 47–53
Kudo H, Cheng KJ, Costerton J (1987) Interactions between Treponema bryantii and cellulolytic bacteria in the in vitro degradation of straw cellulose. Can J Microbiol 33:244–248. doi:10.1139/cjas-2016-0032
Lee CS, Jung YT, Park S, Oh TK, Yoon JH (2010) Lysinibacillus xylanilyticus sp. nov., a xylan-degrading bacterium isolated from forest humus. Int J Syst Evol Micr 60:281–286. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.013367-0
Li J, Rui J, Pei Z, Sun X, Zhang S, Yan Z, Wang Y, Liu X, Zheng T, Li X (2014) Straw- and slurry-associated prokaryotic communities differ during co-fermentation of straw and swine manure. Appl Microbiol Biot 98:4771–4780. doi:10.1007/s00253-014-5629-3
Limam RD, Chouari R, Mazéas L, Wu TD, Li T, Grossin-debattista J, Guerquin-Kern JL, Saidi M, Landoulsi A, Sghir A, Bouchez T (2014) Members of the uncultured bacterial candidate division WWE1 are implicated in anaerobic digestion of cellulose. MicrobiologyOpen 3:157–167. doi:10.1002/mbo3.144
Liu FH, Wang SB, Zhang JS, Zhang J, Yan X, Zhou HK, Zhao GP, Zhou ZH (2009) The structure of the bacterial and archaeal community in a biogas digester as revealed by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and 16S rDNA sequencing analysis. J Appl Microbiol 106:952–966. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2008.04064.x
Liu X, Liu H, Chen Y, Du G, Chen J (2008) Effects of organic matter and initial carbon–nitrogen ratio on the bioconversion of volatile fatty acids from sewage sludge. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 83:1049–1055. doi:10.1002/jctb.1913
Müller N, Worm P, Schink B, Stams AJ, Plugge CM (2010) Syntrophic butyrate and propionate oxidation processes: from genomes to reaction mechanisms. Env Microbiol Rep 2:489–499. doi:10.1111/j.1758-2229.2010.00147.x
Miura Y, Okabe S (2008) Quantification of cell specific uptake activity of microbial products by uncultured Chloroflexi by microautoradiography combined with fluorescence in situ hybridization. Environ Sci Technol 42:7380–7386. doi:10.1021/es800566e
Monlau F, Barakat A, Trably E, Dumas C, Steyer JP, Carrère H (2013) Lignocellulosic materials into biohydrogen and biomethane: impact of structural features and pretreatment. Crit Rev Env Sci Tec 43:260–322. doi:10.1080/10643389.2011.604258
Morrison M, Pope PB, Denman SE, Mcsweeney CS (2009) Plant biomass degradation by gut microbiomes: more of the same or something new? Curr Opin Biotech 20:358–363. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2009.05.004
Mussoline W, Esposito G, Giordano A, Lens P (2013) The anaerobic digestion of rice straw: a review. Crit Rev Env Sci Tec 43:895–915. doi:10.1080/10643389.2011.627018
Nelson MC, Morrison HG, Benjamino J, Grim SL, Graf J (2014) Analysis, optimization and verification of Illumina-generated 16S rRNA gene amplicon surveys. PLoS One 9:e94249–e94249. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0094249
Nesbø CL, Kumaraswamy R, Dlutek M, Doolittle WF, Foght J (2010) Searching for mesophilic Thermotogales bacteria: “mesotogas” in the wild. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:4896–4900. doi:10.1128/AEM.02846-09
Nyonyo T, Shinkai T, Mitsumori M (2014) Improved culturability of cellulolytic rumen bacteria and phylogenetic diversity of culturable cellulolytic and xylanolytic bacteria newly isolated from the bovine rumen. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 88:528–537. doi:10.1111/1574-6941.12318
Qiu YL, Kuang XZ, Shi XS, Yuan XZ, Guo RB (2014) Paludibacter jiangxiensis sp. nov., a strictly anaerobic, propionate-producing bacterium isolated from rice paddy field. Arch Microbiol 196:149–155. doi:10.1007/s00203-013-0951-1
Romsaiyud A, Songkasiri W, Nopharatana A, Chaiprasert P (2009) Combination effect of pH and acetate on enzymatic cellulose hydrolysis. J Environ Sci 21(7):965–970. doi:10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62369-4
Sambusiti C, Rollini M, Ficara E, Musatti A, Manzoni M, Malpei F (2014) Enzymatic and metabolic activities of four anaerobic sludges and their impact on methane production from ensiled sorghum forage. Bioresour Technol 155:122–128. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2013.12.055
Shi J, Xu FQ, Wang ZJ, Stiverson JA, Yu ZT, Li YB (2014) Effects of microbial and non-microbial factors of liquid anaerobic digestion effluent as inoculum on solid-state anaerobic digestion of corn stover. Bioresour Technol 157:188–196. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2014.01.089
Song H, Clarke WP, Blackall LL (2005) Concurrent microscopic observations and activity measurements of cellulose hydrolyzing and methanogenic populations during the batch anaerobic digestion of crystalline cellulose. Biotechnol Bioeng 91:369–378. doi:10.1002/bit.20517
Sun L, Liu T, Müller B, Schnürer A (2016) The microbial community structure in industrial biogas plants influences the degradation rate of straw and cellulose in batch tests. Biotechnol Biofuels 9:128. doi:10.1186/s13068-016-0543-9
Sun L, Pope PB, Eijsink VGH, Schnürer A (2015) Characterization of microbial community structure during continuous anaerobic digestion of straw and cow manure. Microb Biotechnol 8:815–827. doi:10.1111/1751-7915.12298
Vartoukian SR, Palmer RM, Wade WG (2007) The division “Synergistes”. Anaerobe 13:99–106. doi:10.1016/j.anaerobe.2007.05.004
Wang H, Vuorela M, Keränen AL, Lehtinen TM, Lensu A, Lehtomäki A, Rintala J (2010) Development of microbial populations in the anaerobic hydrolysis of grass silage for methane production. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 72:496–506. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6941.2010.00850.x
Yang W, Beauchemin K, Rode L (2001) Effect of dietary factors on distribution and chemical composition of liquid- or solid-associated bacterial populations in the rumen of dairy cows. J Anim Sci 79:2736–2746. doi:10.2527/2001.79102736x
Yokoyama H, Wagner ID, Wiegel J (2010) Caldicoprobacter oshimai gen. nov., sp. nov., an anaerobic, xylanolytic, extremely thermophilic bacterium isolated from sheep faeces, and proposal of Caldicoprobacteraceae fam. nov. Int J Syst Evol Micr 60:67–71. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.011379-0
Yue ZB, Wang J, Liu XM, Yu HQ (2012) Comparison of rumen microorganism and digester sludge dominated anaerobic digestion processes for aquatic plants. Renew Energ 46:255–258. doi:10.1016/j.renene.2012.03.030
Yue ZB, Li WW, Yu HQ (2013) Application of rumen microorganisms for anaerobic bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour Technol 128:738–744. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2012.11.073
Zhang H, Zhang P, Ye J, Wu Y, Fang W, Gou X, Zeng G (2016) Improvement of methane production from rice straw with rumen fluid pretreatment: a feasibility study. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 113:9–16. doi:10.1016/j.ibiod.2016.03.022
Zhang KG, Song L, Dong XZ (2010) Proteiniclasticum ruminis gen. nov., sp. nov., a strictly anaerobic proteolytic bacterium isolated from yak rumen. Int J Syst Evol Micr 60:2221–2225. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.011759-0
Zwietering MH, Jongenburger I, Rombouts FM, Van’t Riet K (1990) Modeling of the bacterial growth curve. Appl Environ Microbiol 56(6): 1875-1881. doi:0099-2240/90/061875-07$02.00/0
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant numbers 21506076, 51678279, 21276114], the National Science and Technological Support of China [grant number 2014BAC25B01] and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities [grant number JUSRP11435].
The authors were also grateful to Enzyme Engineering Technology Center of Jiangsu for the help in rumen collection of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, Y., Huang, Z., Zhao, M. et al. Effects of co-inoculating rice straw with ruminal microbiota and anaerobic sludge: digestion performance and spatial distribution of microbial communities. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101, 5937–5948 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8332-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8332-3