Abstract
Objective
To investigate the potential inhibitory effects of uremic toxins on the major human hepatic drug-metabolising cytochrome P450 (CYP) and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) enzymes in vitro.
Methods
Benzyl alcohol, p-cresol, indoxyl sulfate, hippuric acid and a combination of the four uremic toxins were co-incubated with human liver microsomes and selective probe substrates for the major human drug-metabolising CYP and UGT enzymes. The percentage of enzyme inhibition was calculated by measuring the rates of probe metabolite formation in the absence and presence of the uremic toxins. Kinetics studies were conducted to evaluate the K i values and mechanism(s) of the inhibition of CYP2E1, CYP3A4, UGT1A1 and UGT1A9 by p-cresol.
Results
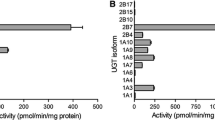
The individual uremic toxins inhibited CYP and UGT enzymes to a variable extent. p-Cresol was the most potent individual inhibitor, producing >50 % inhibition of CYP2E1, CYP3A4, UGT1A1, UGT1A9 and UGT2B7 at a concentration of 100 μM. The greatest inhibition was observed with UGT1A9. p-Cresol was shown to be an uncompetitive inhibitor of UGT1A9, with unbound K i values of 9.1 and 2.5 μM in the absence and presence of bovine serum albumin (BSA), respectively. K i values for p-cresol inhibition of human liver microsomal CYP2E1, CYP3A4 and UGT1A1 ranged from 43 to 89 μM. A combination of the four uremic toxins produced >50 % decreases in the activities of CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2E1, CYP3A4, UGT1A1, UGT1A9 and UGT2B7.
Conclusions
Uremic toxins may contribute to decreases in drug hepatic clearance in individuals with kidney disease by inhibition of hepatic drug-metabolising enzymes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davies DF, Shock NW (1950) Age changes in glomerular filtration rate, effective renal plasma flow, and tubular excretory capacity in adult males. J Clin Invest 29:496–507
Rowe JW, Andres R, Tobin JD, Norris AH, Shock NW (1976) The effect of age on creatinine clearance in men: a cross-sectional and longitudinal study. J Gerontol 31:155–163
Kirch W, Ramsch KD, Duhrsen U, Ohnhaus EE (1984) Clinical pharmacokinetics of nimodipine in normal and impaired renal-function. Int J Clin Pharmacol Res 4:381–384
Mooy J, Schols M, Baak M, Hooff M, Muytjens A, Rahn KH (1985) Pharmacokinetics of verapamil in patients with renal failure. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 28:405–410
Anderson S, Brenner BM (1986) Effects of aging on the renal glomerulus. Am J Med 80:435–442
Dowling TC, Briglia AE, Fink JC, Hanes DS, Light PD, Stackiewicz L et al (2003) Characterization of hepatic cytochrome P4503A activity in patients with end-stage renal disease. Clin Pharmacol Ther 73:427–434
Sun H, Frassetto L, Benet LZ (2006) Effects of renal failure on drug transport and metabolism. Pharmacol Ther 109:1–11
Bianchetti G, Graziani G, Brancaccio D, Morganti A, Leonetti G, Manfrin M et al (1976) Pharmacokinetics and effects of propranolol in terminal uraemic patients and in patients undergoing regular dialysis treatment. Clin Pharmacokinet 1:373–384
Laskin OL, Longstreth JA, Whelton A, Rocco L, Lietman PS, Krasny HC et al (1982) Acyclovir kinetics in end-stage renal-disease. Clin Pharmacol Ther 31:594–601
Kanfer A, Stamatakis G, Torlotin JC, Fredj G, Kenouch S, Mery JP (1987) Changes in erythromycin pharmacokinetics induced by renal-failure. Clin Nephrol 27:147–150
Grubb NG, Rudy DW, Brater DC, Hall SD (1999) Stereoselective pharmacokinetics of ketoprofen and ketoprofen glucuronide in end-stage renal disease: evidence for a ‘futile cycle’ of elimination. Br J Clin Pharmacol 48:494–500
Dickson TZ, Zagrobelny J, Lin CC, Ritter MA, Snavely D, Ramjit D et al (2003) Pharmacokinetics, safety, and antihypertensive efficacy of losartan in combination with hydrochlorothiazide in hypertensive patients with renal impairment. J Clin Pharmacol 43:591–603
Dreisbach AW, Lertora JJL (2003) The effect of chronic renal failure on hepatic drug metabolism and drug disposition. Semin Dial 16:45–50
Mutsaers HAM, Wilmer MJG, Reijnders D, Jansen J, van den Broek PHH, Forkink M et al (2013) Uremic toxins inhibit renal metabolic capacity through interference with glucuronidation and mitochondrial respiration. Biochim Biophys Acta 1832:142–150
Volpe D, Tobin G, Tavakkoli F, Dowling T, Light P, Parker R (2014) Effect of uremic serum and uremic toxins on drug metabolism in human microsomes. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 68:297–303
Huang ZH, Murakami T, Okochi A, Yumoto R, Nagai J, Takano M (2000) Expression and function of P-glycoprotein in rats with glycerol-induced acute renal failure. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 406:453–460
Laouari D, Yang RC, Veau C, Blanke I, Friedlander G (2001) Two apical multidrug transporters, P-gp and MRP2, are differently altered in chronic renal failure. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 280:F636–F645
Ji L, Masuda S, Saito H, Inui K (2002) Down-regulation of rat organic cation transporter rOCT2 by 5/6 nephrectomy. Kidney Int 62:514–524
Deguchi T, Kusuhara H, Takadate A, Endou H, Otagiri M, Sugiyama Y (2004) Characterization of uremic toxin transport by organic anion transporters in the kidney. Kidney Int 65:162–174
Holzer B, Stieger B, Folkers G, Meier PJ, Fattinger K (2005) Differential regulation of basolateral and canalicular transporter expression in rat liver in chronic renal failure. Clin Pharmacol Ther 77:P34
Sun H, Huang Y, Okochi H, Frassetto L, Benet LZ (2005) Uremic toxins inhibit hepatic uptake of eprosartan. Clin Pharmacol Ther 77:P2
Vanholder R, Argiles A, Baurmeister U, Brunet P, Clark W, Cohen G et al (2001) Uremic toxicity: present state of the art. Int J Artif Organs 24:695–725
Vanholder R, De Smet R, Glorieux G, Argiles A, Baurmeister U, Brunet P et al (2003) Review on uremic toxins: classification, concentration, and interindividual variability. Kidney Int 63:1934–1943
Farrell PC, Gotch FA, Peters JH, Berridge BJ Jr, Lam M (1978) Binding of hippurate in normal plasma and in uremic plasma pre- and postdialysis. Nephron 20:40–46
Niwa T, Ise M (1994) Indoxyl sulfate, a circulating uremic toxin, stimulates the progression of glomerular sclerosis. J Lab Clin Med 124:96–104
Hida M, Aiba Y, Sawamura S, Suzuki N, Satoh T, Koga Y (1996) Inhibition of the accumulation of uremic toxins in the blood and their precursors in the feces after oral administration of Lebinin(R), a lactic acid bacteria preparation, to uremic patients undergoing hemodialysis. Nephron 74:349–355
Dedeyn P, Marescau B, Lornoy W, Becaus I, Lowenthal A (1986) Guanidino compounds in uremic dialyzed patients. Clin Chim Acta 157:143–150
Masereeuw R, Terlouw SA, van Aubel R, Russel FGM, Miller DS (2000) Endothelin B receptor-mediated regulation of ATP-driven drug secretion in renal proximal tubule. Mol Pharmacol 57:59–67
Tsujimoto M, Higuchi K, Shima D, Yokota H, Furukubo T, Izumi S et al (2010) Inhibitory effects of uraemic toxins 3-indoxyl sulfate and p-cresol on losartan metabolism in vitro. J Pharm Pharmacol 62:133–138
Knights KM, Rowland A, Miners JO (2013) Renal drug metabolism in humans: the potential for drug-endobiotic interactions involving cytochrome P450 (CYP) and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT). Br J Clin Pharmacol 76:587–602
Rowland A, Miners JO, Mackenzie PI (2013) The UDP-glucuronosyltransferases: their role in drug metabolism and detoxification. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 45:1121–1132
Rowland A, Mangoni AA (2014) Cytochrome P450 and ischemic heart disease: current concepts and future directions. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 10:191–213
Bowalgaha K, Elliot DJ, Mackenzie PI, Knights KM, Swedmark S, Miners JO (2005) S-Naproxen and desmethylnaproxen glucuronidation by human liver microsomes and recombinant human UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGT): role of UGT2B7 in the elimination of naproxen. Br J Clin Pharmacol 60:423–433
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Boase S, Miners JO (2002) In vitro-in vivo correlations for drugs eliminated by glucuronidation: investigations with the model substrate zidovudine. Br J Clin Pharmacol 54:493–503
McLure JA, Miners JO, Birkett DJ (2000) Nonspecific binding of drugs to human liver microsomes. Br J Clin Pharmacol 49:453–461
Miners JO, Bowalgaha K, Elliot DJ, Baranczewski P, Knights KM (2011) Characterization of niflumic acid as a selective inhibitor of human liver microsomal UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A9: application to the reaction phenotyping of acetaminophen glucuronidation. Drug Metab Dispos 39:644–652
Rowland A, Knights KM, Mackenzie PI, Miners JO (2008) The “albumin effectˮ and drug glucuronidation: bovine serum albumin and fatty acid-free human serum albumin enhance the glucuronidation of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) 1A9 substrates but not UGT1A1 and UGT1A6 activities. Drug Metab Dispos 36:1056–1062
Reidenberg MM, Drayer DE (1984) Alteration of drug-protein binding in renal-disease. Clin Pharmacokinet 9:18–26
Sun H, Frassetto LA, Huang Y, Benet LZ (2010) Hepatic clearance, but not gut availability, of erythromycin is altered in patients with end-stage renal disease. Clin Pharmacol Ther 87:465–472
Sun H, Huang Y, Frassetto L, Benet LZ (2004) Effects of uremic toxins on hepatic uptake and metabolism of erythromycin. Drug Metab Dispos 32:1239–1246
Dreisbach AW, Japa S, Gebrekal AB, Mowry SE, Lertora JJL, Kamath BL et al (2003) Cytochrome P4502C9 activity in end-stage renal disease. Clin Pharmacol Ther 73:475–477
Lehmann CR, Heironimus JD, Collins CB, Oneil TJ, Pierson WP, Crowe JT et al (1985) Metoclopramide kinetics in patients with impaired renal-function and clearance by hemodialysis. Clin Pharmacol Ther 37:284–289
Terao N, Shen DD (1985) Reduced extraction of I-propranolol by perfused rat liver in the presence of uremic blood. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 233:277–284
Yeung CK, Shen DD, Thummel KE, Himmelfarb J (2014) Effects of chronic kidney disease and uremia on hepatic drug metabolism and transport. Kidney Int 85:522–528
Fujita K, Sunakawa Y, Miwa K, Akiyama Y, Sugiyama M, Kawara K et al (2011) Delayed elimination of SN-38 in cancer patients with severe renal failure. Drug Metab Dispos 39:161–164
Singlas E, Pioger JC, Taburet AM, Colin JN, Fillastre JP (1989) Zidovudine disposition in patients with severe renal impairment - influence of hemodialysis. Clin Pharmacol Ther 46:190–197
Rowland A, Elliot DJ, Knights KM, Mackenzie PI, Miners JO (2008) The “albumin effectˮ and in vitro-in vivo extrapolation: sequestration of long-chain unsaturated fatty acids enhances phenytoin hydroxylation by human liver microsomal and recombinant cytochrome P450 2C9. Drug Metab Dispos 36:870–877
Rowland A, Elliot D, Williams J, Mackenzie P, Dickinson R, Miners J (2006) In vitro characterization of lamotrigine N2-glucuronidation and the lamotrigine - valproic acid interaction. Drug Metab Dispos 34:1055–1062
Miners JO, Mackenzie PI, Knights KM (2010) The prediction of drug-glucuronidation parameters in humans: UDP-glucuronosyltransferase enzyme-selective substrate and inhibitor probes for reaction phenotyping and in vitro-in vivo extrapolation of drug clearance and drug-drug interaction potential. Drug Metab Rev 42:196–208
Vanholder R, Bammens B, de Loor H, Glorieux G, Meijers B, Schepers E et al (2011) Warning: the unfortunate end of p-cresol as a uraemic toxin. Nephrol Dial Transplant 26:1464–1467
Wardle EN, Wilkinson K (1976) Free phenols in chronic renal failure. Clin Nephrol 6:361–364
Niwa T, Maeda K, Ohki T, Saito A, Kobayashi K (1981) A gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric analysis for phenols in uremic serum. Clin Chim Acta 110:51–57
De Smet R, David F, Sandra P, Van Kaer J, Lesaffer G, Dhondt A et al (1998) A sensitive HPLC method for the quantification of free and total p-cresol in patients with chronic renal failure. Clin Chim Acta 278:1–21
de Loor H, Bammens B, Evenepoel P, De Preter V, Verbeke K (2005) Gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric analysis for measurement of p-cresol and its conjugated metabolites in uremic and normal serum. Clin Chem 51:1535–1538
Meert N, Schepers E, Glorieux G, Van Landschoot M, Goeman JL, Waterloos MA et al (2012) Novel method for simultaneous determination of p-cresylsulphate and p-cresylglucuronide: clinical data and pathophysiological implications. Nephrol Dial Transplant 27:2388–2396
Pletinck A, Glorieux G, Schepers E, Van Landschoot M, Van de Voorde J, Van Biesen W et al (2012) In vivo effects of the protein-bound uremic toxins p-cresylsulfate, p-cresylglucuronide and indoxylsulfate on the cross-talk between leukocytes and the vessel wall. Nephrol Dial Transplant 27:16
Lesaffer G, De Smet R, Belpaire FM, Van Vlem B, Van Hulle M, Cornelis R et al (2003) Urinary excretion of the uraemic toxin p-cresol in the rat: contribution of glucuronidation to its metabolization. Nephrol Dial Transplant 18:1299–1306
Coughtrie MWH, Sharp S, Maxwell K, Innes NP (1998) Biology and function of the reversible sulfation pathway catalysed by human sulfotransferases and sulfatases. Chem Biol Interact 109:3–27
Butler JM, Begg EJ (2008) Free drug metabolic clearance in elderly people. Clin Pharmacokinet 47:297–321
Tassaneeyakul W, Birkett DJ, Veronese ME, McManus ME, Tukey RH, Miners JO (1994) Direct characterization of the selectivity of furafylline as an inhibitor of human cytochromes P450 1A1 and 1A2. Pharmacogenetics 4:281–284
Tassaneeyakul W, Birkett DJ, Veronese ME, McManus ME, Tukey RH, Quattrochi LC et al (1993) Specificity of substrate and inhibitor probes for human cytochromes-P450 1A1 and 1A2. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 265:401–407
Miners JO, Smith KJ, Robson RA, McManus ME, Veronese ME, Birkett DJ (1988) Tolbutamide hydroxylation by human-liver microsomes - kinetic characterization and relationship to other cytochrome-P-450 dependent xenobiotic oxidations. Biochem Pharmacol 37:1137–1144
Polasek TM, Elliot DJ, Somogyi AA, Gillam EMJ, Lewis BC, Miners JO (2006) An evaluation of potential mechanism-based inactivation of human drug metabolizing cytochromes P450 by monoamine oxidase inhibitors, including isoniazid. Br J Clin Pharmacol 61:570–584
Tassaneeyakul W, Veronese ME, Birkett DJ, Gonzalez FJ, Miners JO (1993) Validation of 4-nitrophenol as an in-vitro substrate probe for human liver CYP2E1 using cDNA expression and microsomal kinetic techniques. Biochem Pharmacol 46:1975–1981
Polasek TM, Miners JO (2006) Quantitative prediction of macrolide drug-drug interaction potential from in vitro studies using testosterone as the human cytochrome P4503A substrate. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 62:203–208
Raungrut P, Uchaipichat V, Elliot DJ, Janchawee B, Somogyi AA, Miners JO (2010) In vitro-in vivo extrapolation predicts drug-drug interactions arising from inhibition of codeine glucuronidation by dextropropoxyphene, fluconazole, ketoconazole, and methadone in humans. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 334:609–618
Udomuksorn W, Elliot DJ, Lewis BC, Mackenzie P, Yoovathaworn K, Miners JO (2007) Influence of mutations associated with Gilbert and Crigler-Najjar type II syndromes on the glucuronidation kinetics of bilirubin and other UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A substrates. Pharmacogenet Genomics 17:1017–1029
Uchaipichat V, Mackenzie PI, Elliot DJ, Miners JO (2006) Selectivity of substrate (trifluoperazine) and inhibitor (amitriptyline, androsterone, canrenoic acid, hecogenin, phenylbutazone, quinidine, quinine, and sulfinpyrazone) “probesˮ for human UDP- glucuronosyltransferases. Drug Metab Dispos 34:449–456
Uchaipichat V, Winner LK, Mackenzie PI, Elliot DJ, Williams JA, Miners JO (2006) Quantitative prediction of in vivo inhibitory interactions involving glucuronidated drugs from in vitro data: the effect of fluconazole on zidovudine glucuronidation. Br J Clin Pharmacol 61:427–439
Acknowledgments
We thank Professors Kathleen Knights and Peter Mackenzie for useful feedback on the study design and data analysis.
Conflict of interests
None declared
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barnes, K.J., Rowland, A., Polasek, T.M. et al. Inhibition of human drug-metabolising cytochrome P450 and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase enzyme activities in vitro by uremic toxins. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 70, 1097–1106 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-014-1709-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-014-1709-7