Abstract
A new rhodamine B derivative (RDB) was synthesized and utilized for the colorimetric detection of copper ions (Cu2+). This chemosensor utilized a paper strip as a support and a smartphone as a detector for on-site quantitative detection of Cu2+ in water samples. Silica nanoparticles (SiNPs) were investigated as the modifier nanoparticles to achieve uniform color on the paper strip and showed a color response 1.9-fold higher than the one without SiNPs. The RDB chemosensor-based paper strip provided high selectivity toward Cu2+ with a detection limit of 0.7 mg/L, and the working concentrations for Cu2+ ranged from 1 to 17 mg/L. Parallel analyses of eight drinking water samples were conducted by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy. The results were in good agreement, indicating the practical reliability of the established method with a short assay time and high selectivity. These indicate its great potential for on-site detection of Cu2+.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Linder MC, Hazegh-Azam M. Copper biochemistry and molecular biology. Am Soc Clin Nutr. 1996;63(5):797S-811S.
Uauy R, Olivares M, Gonzalez M. Essentiality of copper in humans. Am Soc Clin Nutr. 2009;45(8):176–80.
Stern BR, Solioz M, Krewski D, Aggett P, Aw TC, Baker S, et al. Copper and human health: biochemistry, genetics, and strategies for modeling dose-response relationships. J Toxicol Environ Health. 2007;10(3):157–222.
Darrel JW, Thomas BB, Jonathan DG. The role of copper in neurodegenerative disease. Neurobiol Dis. 1999;6:221–30.
Cotton PA, Subar AF, Friday JE, Cook A. Dietary sources of nutrients among US adults, 1994 to 1996. J Am Diet Assoc. 2004;104(6):921–30.
Olivares M, Uauy R. Copper as an essential nutrient. Am Soc Clin Nutr. 1996;63(5):791S-S796.
Satheeswaran T, Yuvaraj P, Damotharan P, Karthikeyan V, Jha DK, Dharani G, et al. Assessment of trace metal contamination in the marine sediment, seawater, and bivalves of Parangipettai, southeast coast of India. Mar Pollut Bull. 2019;149: 110499.
Harvey PJ, Handley HK, Taylor MP. Widespread copper and lead contamination of household drinking water, New South Wales Australia. Environ Res. 2016;151:275–85.
Ahmed S, Akhtar N, Rahman A, Mondal NC, Khurshid S, Sarah S, et al. Evaluating groundwater pollution with emphasizing heavy metal hotspots in an urbanized alluvium watershed of Yamuna River, northern India. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag. 2022;18: 100744.
World Health Organization. Guidelines for drinking-water quality [electronic resource] : incorporating 1st and 2nd addenda. Vol. 1, recommendations, 3rd ed. World Health Organization. 2008;1:335–7.
Fei JJ, Wu XH, Sun YL, Zhao LY, Min H, Cui XB, et al. Preparation of a novel amino functionalized ion-imprinted hybrid monolithic column for the selective extraction of trace copper followed by ICP-MS detection. Anal Chim Acta. 2021;1162: 338477.
Neri TS, Rocha DP, Muñoz RAA, Coelho NMM, Batista AD. Highly sensitive procedure for determination of Cu(II) by GF AAS using single-drop microextraction. Microchem J. 2019;147:894–8.
Escudero LA, Cerutti S, Olsina RA, Salonia JA, Gasquez JA. Factorial design optimization of experimental variables in the on-line separation/preconcentration of copper in water samples using solid phase extraction and ICP-OES determination. J Hazard Mater. 2010;183(1–3):218–23.
Zhang W, Zhang Y, Liu X, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Wang W, et al. Ratiometric fluorescence and colorimetric dual-mode sensing platform based on carbon dots for detecting copper(II) ions and D-penicillamine. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2022;414(4):1651–62.
Zhang H, Li Y, Lu H, Gan F. A ratiometric fluorescence and colorimetric dual-mode sensing platform based on sulfur quantum dots and carbon quantum dots for selective detection of Cu(2+). Anal Bioanal Chem. 2022;414(7):2471–80.
Manring N, Ahmed MMN, Smeltz JL, Pathirathna P. Electrodeposition of dopamine onto carbon fiber microelectrodes to enhance the detection of Cu(2+) via fast-scan cyclic voltammetry. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-04488-4.
Holman JB, Zhengdi Shi Z, Fadahunsi AA, Li C, Ding W. Advances on microfluidic paper-based electroanalytical devices. Biotech Adv. 2023;63: 108093.
Wang CM, Chen CY, Liao WS. Enclosed paper-based analytical devices: concept, variety, and outlook. Anal Chim Acta. 2021;1144:158–74.
Özbek O, Berkel C. Recent advances in potentiometric analysis: Paper–based devices. Sens International. 2022;3:100189.
Martinez AW, Phillips ST, Butte MJ, Whitesides GM. Patterned paper as a platform for inexpensive, low-volume, portable bioassays. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2007;46(8):1318–20.
Nery EW, Kubota LT. Sensing approaches on paper-based devices: a review. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2013;405(24):7573–95.
Evans E, Moreira Gabriel EF, Benavidez TE, Tomazelli Coltro WK, Garcia CD. Modification of microfluidic paper-based devices with silica nanoparticles. Analyst. 2014;139(21):5560–7.
Deroco PB, Fatibello-Filho O, Arduini F, Moscone D. Electrochemical determination of capsaicin in pepper samples using sustainable paper-based screen-printed bulk modified with carbon black. Electrochimica Acta. 2020;354:136628.
Fernandes GM, de Sousa J, da Silveira Petruci JF, Batista AD. Paper-based analytical device for colorimetric detection of Cu2+ in Brazilian sugarcane spirits by digital image treatment. Microchem J. 2020;159:105463.
Zhou J, Wu Q, Chen X, Qin X, Zhang G, Wu M, et al. Two-component ratiometric sensor for Cu(2+) detection on paper-based device. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019;411(23):6165–72.
Bendicho C, Lavilla I, Pena-Pereira F, la Calle I, Romero V. Paper-based analytical devices for colorimetric and luminescent detection of mercury in waters: an overview. Sensors (Basel). 2021;21(22):7571.
Sharifi S, Wahid Mesbah A, Iravani E. A new unsymmetrical ferrocene-based double azine as a multichannel chemosensor for the detection of Cu2+ ions. Results in Chem. 2023;5:100747.
Rajasekar M, Agash SGS, Narendran C, Rajasekar K. Recent trends in fluorescent-based copper (II) chemosensors and their biomaterial applications. Inor Chem Comm. 2023;151: 110609.
Trevino KM, Wagner CR, Tamura EK, Garcia J, Louie AY. Small molecule sensors for the colorimetric detection of copper(II): a review of the literature from 2010 to 2022. Dyes Pigm. 2023;214: 110881.
Chandrasekhar V, Das S, Yadav R, Hossain S, Parihar R, Subramaniam G, et al. Novel chemosensor for the visual detection of copper(II) in aqueous solution at the ppm level. Inorganic Chem. 2012;51(16):8664–6.
Kim HN, Lee MH, Kim HJ, Kim JS, Yoon J. A new trend in rhodamine-based chemosensors: application of spirolactam ring-opening to sensing ions. Chem Soc Rev. 2008;37(8):1465–72.
Arumugaperumal R, Srinivasadesikan V, C. Lin M, Shellaiah M, Shuklaa T, Lin HC. Facile rhodaminebased colorimetric sensors for sequential detections of Cu (II) ion and pyrophosphate (P2O74-) anion. RSC Adv. 2016;6(108):106631–40.
Yu C, Zhang J, Wang R, Chen L. Highly sensitive and selective colorimetric and off-on fluorescent probe for Cu2+ based on rhodamine derivative. Org Biomol Chem. 2010;8(23):5277–9.
Sunnapu O, Kotla NG, Maddiboyina B, Singaravadivel S, Sivaraman G. A rhodamine based “turn-on” fluorescent probe for Pb(II) and live cell imaging. RSC Adv. 2016;6(1):656–60.
Maji A, Lohar S, Siddhartha P, Chattopadhyay P. A new rhodamine based ‘turn-on’ Cu2+ ion selective chemosensor in aqueous system applicable in bioimaging. J Chem Sci. 2017;129(9):1423–30.
Huang Q, Chen YT, Ren YW, Wang ZY, Zhu YX, Zhang Y. A rapid and naked-eye visible rhodamine 6G-based chemosensor for sensitive detection of copper(II) ions in aqueous solution. Analyt Method. 2018;6:5731–7.
Ren D, Liua Y, Liub X, Li Z, Li H, Yang XF. Spirohydrazine rhodamine as a fluorescent chemodosimeter for the selective detection of Cu(II) ions and its application in live cell imaging. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2018;255:2321–8.
Sawminathan S, Munusamy S, Manickam S, KulathuIyer S. A simple quinazolinone-isophorone based colorimetric chemosensor for the reversible detection of copper (II) and its application in real samples. J Mol Struct. 2022;1257: 132633.
Mohanasundaram D, Bhaskar R, Sankarganesh M, Nehru K, Gangatharan Vinoth Kumar G, Rajesh J. A simple pyridine based fluorescent chemosensor for selective detection of copper ion. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2022;265:120395.
Nelson M, Muniyasamy H, Ongi P, Balakrishnan S, Sepperumal M, Ayyanar S, et al. Incredible colorimetric sensing behavior of pyrazole-based imine chemosensor towards copper (II) ion detection: synthesis, characterization and theoretical investigations. Results in Chem. 2022;4:100501.
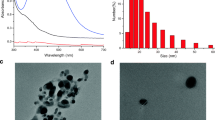
Fernandes RS, Raimundo IM, Pimentel MF. Revising the synthesis of Stöber silica nanoparticles: a multivariate assessment study on the effects of reaction parameters on the particle size. Colloids Surf A. 2019;577:1–7.
Kim HJ, Wang S, Son YA. Synthesis and properties of novel rhodamine 6G fluorescent dye compound. Text Color and Finish. 2012;24(3):153-7.
Huo F-J, Su J, Sun Y-Q, Yin C-X, Tong H-B, Nie Z-X. A rhodamine-based dual chemosensor for the visual detection of copper and the ratiometric fluorescent detection of vanadium. Dyes Pigm. 2010;86(1):50–5.
Lin Q, Chen P, Liu J, Fu Y-P, Zhang Y-M, Wei T-B. Colorimetric chemosensor and test kit for detection copper(II) cations in aqueous solution with specific selectivity and high sensitivity. Dyes Pigm. 2013;98(1):100–5.
Guo Y, Wang L, Zhuo J, Xu B, Li X, Zhang J, et al. A pyrene-based dual chemosensor for colorimetric detection of Cu 2+ and fluorescent detection of Fe 3+. Tetrahedron Lett. 2017;58(42):3951–6.
Geetha M, Sadasivuni KK, Al-Ejji M, Sivadas N, Bhattacharyya B, Musthafa FN, et al. Design and development of inexpensive paper-based chemosensors for detection of divalent copper. J Fluoresc. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-023-03220-4.
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by the Reinventing University Project (RMUTT) 2022, Office of the Ministry of Higher Education, Science, Research and Innovation, Thailand Science Research and Innovation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sannok, T., Wechakorn, K., Jantra, J. et al. Silica nanoparticle–modified paper strip–based new rhodamine B chemosensor for highly selective detection of copper ions in drinking water. Anal Bioanal Chem 415, 4703–4712 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-023-04754-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-023-04754-z