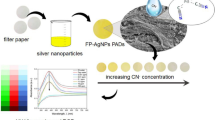
Abstract
Colorimetric, fluorescence, and paper-based method were developed to measure the Hg2+ level in water using iturin A, a lipopeptide produced by Bacillus subtilis. Firstly, iturin was used to synthesize highly stable and uniformly sized silver nanoparticles (AgNPs). Secondly, the iturin-AgNPs were found to be highly selective and sensitive to Hg2+. The absorbance of the reaction system showed a good linear correlation with the Hg2+ concentration from 0.5 to 5 mg/L at 450 nm in the UV-Vis spectroscopy detection with the limit of detection (LOD) of 0.5 mg/L. When the reaction system was detected by fluorescence measurement, a good linear relationship was found between the fluorescence intensity and Hg2+ concentration from 0.05 to 0.5 mg/ at 415 nm with the LOD of 0.05 mg/L. Lastly, a paper-based detection method was developed. The developed method was successfully used to detect Hg2+ in contaminated polluted waters and showed acceptable results in terms of sensitivity, selectivity and stability. The paper-based method could distinguish Hg2+ at levels higher than 0.05 mg/L, thereby meeting the guidelines of the effluent quality standard for industries (0.05 mg/L). In summary, this method can be used daily by various industries to monitor the Hg2+ level in effluent water.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annadhasan M, SankarBabu VR, Naresh R, Umamaheswari K, Rajendiran N (2012) A sunlight-induced rapid synthesis of silver nanoparticles using sodium salt of N-cholyl amino acids and its antimicrobial applications. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 96:14–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.03.009
Buduru P, Reddy BCSR, Naidu NVS (2017) Functionalization of silver nanoparticles with glutamine and histidine for simple and selective detection of Hg2+ ion in water samples. Sensors Actuators B Chem 244:972–982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.01.041
Chandra A, Singh M (2018) Biosynthesis of amino acid functionalized silver nanoparticles for potential catalytic and oxygen sensing applications. Inorg Chem Front 5(1):233–257. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7qi00569e
Chen HY, Teng YG, Lu SJ, Wang YY, Wang JS (2015) Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China. Sci Total Environ 512:143–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.01.025
Cordeiro RA, Weslley Caracas Cedro E, Raquel Colares Andrade A, Serpa R, Jose de Jesus Evangelista A, Sales de Oliveira J, Santos Pereira V, Pereira Alencar L, Bruna Leite Mendes P, Cibelle Soares Farias B, Maria Maciel Melo V, Pires de Camargo Z, de Souza Collares Maia Castelo Branco D, Samia Nogueira Brilhante R, Julio Costa Sidrim J, Fabio Gadelha Rocha M (2018) Inhibitory effect of a lipopeptide biosurfactant produced by Bacillus subtilis on planktonic and sessile cells of Trichosporon spp. Biofouling 34(3):309–319. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927014.2018.1437617
Coutte F, Niehren J, Dhali D, John M, Versari C, Jacques P (2015) Modeling leucine's metabolic pathway and knockout prediction improving the production of surfactin, a biosurfactant from Bacillus subtilis. Biotechnol J 10(8):1216–1234. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.201400541
Farhadi K, Forough M, Molaei R, Hajizadeh S, Rafipour A (2012) Highly selective Hg2+ colorimetric sensor using green synthesized and unmodified silver nanoparticles. Sensors Actuators B Chem 161(1):880–885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2011.11.052
Jiang CM, Shi JL, Liu YL, Zhu CY (2014) Inhibition of Aspergillus carbonarius and fungal contamination in table grapes using Bacillus subtilis. Food Control 35(1):41–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2013.06.054
Kailasa SK, Chandel M, Mehta VN, Park TJ (2018a) Influence of ligand chemistry on silver nanoparticles for colorimetric detection of Cr3+ and Hg2+ ions. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 195:120–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2018.01.038
Kailasa SK, Chandel M, Mehta VN, Park TJ (2018b) Influence of ligand chemistry on silver nanoparticles for colorimetric detection of Cr(3+) and Hg(2+) ions. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 195:120–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2018.01.038
Kim H, Lee W, Yoon Y (2019) Heavy metal (loid) biosensor based on split-enhanced green fluorescent protein: development and characterization. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103:6345–6352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-09908-7
Li C, Wei C (2017) DNA-templated silver nanocluster as a label-free fluorescent probe for the highly sensitive and selective detection of mercury ions. Sensors Actuators B Chem 242:563–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.11.091
Li Q, Zhang Z, Wang Z (2014) Determination of Hg2+ by on-line separation and pre-concentration with atmospheric-pressure solution-cathode glow discharge atomic emission spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 845:7–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2014.08.008
Mussini T, Longhi P, Rondinini S (1985) Standard potentials of amalgam electrodes in aqueous-solutions, temperature coefficients and activity-coefficients of metals in mercury. Pure Appl Chem 57(1):169–179. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac198557010169
Nolan EM, Lippard SJ (2003) A “Turn-On” fluorescent sensor for the selective detection of mercuric ion in aqueous media. J Am Chem Soc 125(47):14270–14271. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja037995g
Pathak KV, Keharia H (2014) Identification of surfactins and iturins produced by potent fungal antagonist, Bacillus subtilis K1 isolated from aerial roots of banyan (Ficus benghalensis) tree using mass spectrometry. 3 Biotech 4(3):283–295. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-013-0151-3
Priyadarshini E, Pradhan N, Pradhan AK, Pradhan P (2016) Label free and high specific detection of mercury ions based on silver nano-liposome. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 163:127–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2016.03.040
Qin L, Zeng G, Lai C, Huang D, Xu P, Zhang C, Cheng M, Liu X, Liu S, Li B, Yi H (2018) “Gold rush” in modern science: fabrication strategies and typical advanced applications of gold nanoparticles in sensing. Coord Chem Rev 359:1–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2018.01.006
Qing WX, Zhao MN, Kou CH, Lu MH, Wang Y (2018) Functionalization of silver nanoparticles with mPEGylated luteolin for selective visual detection of Hg2+ in water sample. RSC Adv 8(51):28843–28846. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra05243c
Sebastian M, Aravind A, Mathew B (2018) Green silver-nanoparticle-based dual sensor for toxic Hg (II) ions. Nanotechnology 29(35):355502. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/aacb9a
Sengan M, Veeramuthu D, Veerappan A (2018) Photosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Durio zibethinus aqueous extract and its application in catalytic reduction of nitroaromatics, degradation of hazardous dyes and selective colorimetric sensing of mercury ions. Mater Res Bull 100:386–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2017.12.038
Sharma V, Kaushik S, Pandit P, Dhull D, Yadav JP, Kaushik S (2019) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from medicinal plants and evaluation of their antiviral potential against chikungunya virus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103(2):881–891. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9488-1
Smith BR, Gambhir SS (2017) Nanomaterials for in vivo imaging. Chem Rev 117(3):901–986. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00073
Srivastava AK, Dev A, Karmakar S (2017) Nanosensors and nanobiosensors in food and agriculture. Environ Chem Lett 16(1):161–182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-017-0674-7
Wang SL, Xu XR, Sun YX, Liu JL, Li HB (2013) Heavy metal pollution in coastal areas of South China: a review. Mar Pollut Bull 76(1-2):7–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.08.025
Zhao H, Shao D, Jiang C, Shi J, Li Q, Huang Q, Rajoka MSR, Yang H, Jin M (2017a) Biological activity of lipopeptides from Bacillus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101(15):5951–5960. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8396-0
Zhao X, Zhou L, Riaz Rajoka MS, Yan L, Jiang C, Shao D, Zhu J, Shi J, Huang Q, Yang H, Jin M (2017b) Fungal silver nanoparticles: synthesis, application and challenges. Crit Rev Biotechnol 38(6):817–835. https://doi.org/10.1080/07388551.2017.1414141
Zhao H, Li J, Zhang Y, Lei S, Zhao X, Shao D, Jiang C, Shi J, Sun H (2018a) Potential of iturins as functional agents: safe, probiotic, and cytotoxic to cancer cells. Food Funct 9(11):5580–5587. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8fo01523f
Zhao H, Xu X, Lei S, Shao D, Jiang C, Shi J, Zhang Y, Liu L, Lei S, Sun H, Huang Q (2018b) Iturin A-like lipopeptides from Bacillus subtilis trigger apoptosis, paraptosis, and autophagy in Caco-2 cells. J Cell Physiol 234(5):6414–6427. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27377
Zhao H, Yan L, Xu X, Jiang C, Shi J, Zhang Y, Liu L, Lei S, Shao D, Huang Q (2018c) Potential of Bacillus subtilis lipopeptides in anti-cancer I: induction of apoptosis and paraptosis and inhibition of autophagy in K562 cells. AMB Express 8(1):78. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-018-0606-3
Zhao X, Yan L, Xu X, Zhao H, Lu Y, Wang Y, Jiang C, Shao D, Zhu J, Shi J (2019) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its contribution to the capability of Bacillus subtilis to deal with polluted waters. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103(15):6319–6332. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-09880-2
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge funding by the Innovation Foundation for Doctor Dissertation of Northwestern Polytechnical University (CX201929), the Modern Agricultural Industry Technology System (CARS-30), the Key research and development plan of Shaanxi Province (2017ZDXL-NY-0304, 2019ZDLNY01-02-02), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2017 M613211), the Shaanxi Postdoctoral Science Foundation(2017BSHEDZZ119), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (3102018jgc010). We also thank Key Laboratory for Space Bioscience and Biotechnology, School of Life Sciences, Analytical &Testing Center, Northwestern Polytechnical University for providing all instruments used in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, X., Ai, C., Li, Z. et al. Development of a paper-based method to detect Hg2+ in waste water using iturin from Bacillus subtilis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103, 8609–8618 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10109-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10109-5