Abstract
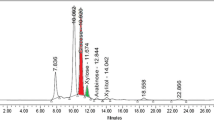
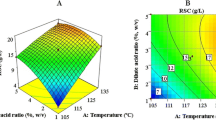
Rice straw is a suitable alternative to a cheaper carbohydrate source for the production of ethanol. For pretreatment efficiency, different sodium hydroxide concentrations (0.5–2.5% w/v) were tested. When compared to other concentrations, rice straw processed with 2% NaOH (w/v) yielded more sugar (8.17 ± 0.01 mg/ml). An alkali treatment induces effective delignification and swelling of biomass. The pretreatment of rice straw with 2% sodium hydroxide (w/v) is able to achieve 55.34% delignification with 53.30% cellulose enrichment. The current study shows the effectiveness of crude cellulolytic preparation from Aspergillus niger resulting in 80.51 ± 0.4% cellulose hydrolysis. Rice straw hydrolysate was fermented using ethanologenic Saccharomyces cerevisiae (yeast) and Zymomonas mobilis (bacteria). Overall, superior efficiency of sugar conversion to ethanol 70.34 ± 0.3% was obtained with the yeast compared to bacterial strain 39.18 ± 0.5%. The current study showed that pretreatment with sodium hydroxide is an effective method for producing ethanol from rice straw and yeast strain S. cerevisiae having greater fermentative potential for bioethanol production than bacterial strain Z. mobilis.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not available.
References
Ahmed I, Zia MA, Iqbal HM (2010) Bioprocessing of proximally analyzed wheat straw for enhanced production of cellulase through parameters optimization with Trichodermaviride under SSF. Int J Biol Sci 6:164–170
Allen SA, REE AG, Ayodeji SA, Deborah SA, (2016) Lignocelluloses: an economical and ecological resource for bio-ethanol production-a review. Management 1(3):128–144. https://doi.org/10.11648/J.IJNREM.20160103.18
Arora A, Priya S, Sharma P, Sharma S, Nain L (2016) Evaluating biological pretreatment as a feasible methodology for ethanol production from paddy straw. BiocatalAgricBiotechnol 8:66–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2016.08.006
Ashoor S, Sukumaran RK (2020) Mild alkaline pretreatment can achieve high hydrolytic and fermentation efficiencies for rice straw conversion to bioethanol. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 50(8):814–819. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826068.2020.1744007
Bay MS, Karimi K, Mirmohamadsadeghi S (2021) Improved environmental and socio-economic impacts of ethanol production from rice straw. Biomass Convers Biorefin 11(5):1909–1920. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-019-00573-4
Bhattacharya P, Bisen J, Bhaduri D, Priyadarsini S, Munda S, Chakraborti M, Adak T, Panneerselva P, Mukherjee AK, Swain SL, Dash PK, Padhy SR, Nayak AK, Pathak H, Kumar S, Nimbrayan P (2021) Turn the wheel from waste to wealth: economic and environmental gain of sustainable rice straw management practices over field burning in reference to India. Sci Total Environ 775:145896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145896
Caputi A, Ueda M, Brown T (1968) Spectrophotometric determination of ethanol in wine. Am J EnolVitic 19(3):160–165
Dehkhoda A, Brandberg T (2009) Comparison of vacuum and high pressure evaporated wood hydrolyzate for ethanol production by repeated fed-batch using flocculating Saccharomyces cerevisiae. BioResources 4(1):309–320
Di Blasi C, Signorelli G, Di Russo C, Rea G (1999) Product distribution from pyrolysis of wood and agricultural residues. Ind Eng Chem Res 38(6):2216–2224
Díaz GV, Coniglio RO, Chungara CI, Zapata PD, Villalba LL, Fonseca MI (2021) Aspergillus niger LBM 134 isolated from rotten wood and its potential cellulolytic ability. Mycology 12(3):160–173. https://doi.org/10.1080/21501203.2020.1823509
Erdei B, Barta Z, Sipos B, Réczey K, Galbe M, Zacchi G (2010) Ethanol production from mixtures of wheat straw and wheat meal. Biotechnol Biofuels 3(1):1–9
Ghose TK (1987) Measurement of cellulase activities. Pure Appl Chem 59(2):257–268. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac198759020257
Goswami SB, Mondal R, Mandi SK (2019) Crop residue management options in rice-rice system: a review. Arch Agron Soil Sci 66(9):1218–1234. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2019.1661994
Gundupalli MP, Chuetor S, Cheenkachorn K, Rattanaporn K, Show PL, Cheng YS, Sriariyanun M (2021) Interferences of Waxes on Enzymatic Saccharification and Ethanol Production from Lignocellulose Biomass. Bioengineering 8(11):171
Hashem M, Ali EH, Abdel-Basset R (2013) Recycling rice straw into biofuel. J Agric Sci Technol 15(4):709–721
Joon Lee K, Tribe DE, Rogers PL (1979) Ethanol production by Zymomonasmobilis in continuous culture at high glucose concentrations. Biotechnol Lett 1(10):421–426
Jung YH, Park HM, Kim DH, Park YC, Seo JH, Kim KH (2015) Combination of high solids loading pretreatment and ethanol fermentation of whole slurry of pretreated rice straw to obtain high ethanol titers and yields. Bioresour Technol 198:861–866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.09.102
Kataria R, Ghosh S (2014) NaOH pretreatment and enzymatic hydrolysis of Saccharumspontaneum for reducing sugars production. Energy Sources a: Recovery Util Environ Eff 36(9):1028–1035
Kaur P, Kocher GS, Monica ST (2018) Comparison of ethanol production from rice straw by Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Zymomonas mobilis. Jbiofuels 9(2):92. https://doi.org/10.5958/0976-4763.2018.00010.7
Kaur M, Malik DP, Malhi GS, Sardana V, Bolan NS, Lal R, Siddique KH (2022) Rice residue management in the Indo-Gangetic Plains for climate and food security. A Review. Agron Sustain Dev 42(5):1–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-022-00817-0
Khan MA, Bonifacio S, Clowes J, Foulds A, Holland R, Matthews JC, Percival CJ, Shallcross DE (2021) Investigation of biofuel as a potential renewable energy source. Atmosphere 12(10):1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12101289
Kim DH, Jo IS, Kang BJ, Lee BD, Kumar S, Kim SH, Yoon JJ (2022) Evaluation of bio-hydrogen production using rice straw hydrolysate extracted by acid and alkali hydrolysis. Int J Hydrog Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.12.177
Kumar V, Patel SK, Gupta RK, Otari SV, Gao H, Lee JK, Zhang L (2019) Enhanced saccharification and fermentation of rice straw by reducing the concentration of phenolic compounds using an immobilized enzyme cocktail. Biotechnol J 14(6):1800468. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.201800468
Kumar A, Jain KK, Singh B (2020) Process optimization for chemical pretreatment of rice straw for bioethanol production. Renew Energy 156:1233–1243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.04.052
Kumar V, Singh D, Singh B (2021) A greener, mild, and efficient bioprocess for the pretreatment and saccharification of rice straw. Biomass Convers Biorefin 30:1–3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-01450-9
Kumar N, Mittal M, Yadav A, Saini DK, Aggarwal NK (2022) Statistical optimization of enzymatic saccharification of sodium hydroxide pretreated partheniumhysterophorus biomass using response surface methodology. J Wood Chem Technol 7:1–2
Kumar N, Sharma R, Aggarwal N, Yadav A (2023) Parthenium hysterophorus weed as a novel substrate for β-Glucosidase production by Penicillium citrinum NAF5: Application of the crude extract to biomass saccharification. Lett Appl Nano BioScience 12:1. https://doi.org/10.33263/LIANBS121.013
Kumari D, Jain Y, Singh R (2021) A study on green pretreatment of rice straw using Petha wastewater and Mausami waste assisted with microwave for production of ethanol and methane. Energy Convers ManagX 10:100067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecmx.2020.100067
Łukajtis R, Kucharska K, Hołowacz I, Rybarczyk P, Wychodnik K, Słupek E, Nowak P, Kamiński M (2018) Comparison and optimization of saccharification conditions of alkaline pre-treated triticale straw for acid and enzymatic hydrolysis followed by ethanol fermentation. Energies 11(3):639. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11030639
Madadi M, Tu Y, Abbas A (2017) Pretreatment of lignocelollusic biomass based on improving enzymatic hydrolysis. Int J Appl Sci Biotechnol 5(1):1–1. https://doi.org/10.3126/ijasbt.v5i1.17018
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31(3):426–428. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60147a030
Ouyang J, Li Z, Li X, Ying H, Yong Q (2009) Enhanced enzymatic conversion and glucose production via two-step enzymatic hydrolysis of corncob residue from xylo-oligosaccharides producer’s waste. BioResources 4(4):1586–1599
Prajapati BP, Kango N (2021) Rice straw saccharification using cellulolytic cocktail from Aspergillustubingensis and structure alterations studies of the wall polymer. Biomass Convers Biorefin 2:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-020-01237-4
Rogers PL, Lee KJ, Tribe DE (1980) High productivity ethanol fermentations with Zymomonasmobilis. Process Biochem 1;15(6):7–11
Samar W, Arora A, Sharma A, Sharma S, Nandal P (2021) Material flow of cellulose in rice straw to ethanol and lignin recovery by NaOH pretreatment coupled with acid washing. Biomass Convers Biorefin 7:1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-01278-3
Saritha M, Arora A, Nain L (2012) Pretreatment of paddy straw with Trametes hirsuta for improved enzymatic saccharification. Bioresour Technol 104:459–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.10.043
Sharma S, Nandal P, Arora A (2019) Ethanol production from NaOH pretreated rice straw: a cost effective option to manage rice crop residue. Waste Biomass Valorization 10(11):3427–3434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0360-4
Sharma S, Swain MR, Mishra A, Mathur AS, Gupta RP, Puri SK, Ramakumar SS, Sharma AK (2021) High solid loading and multiple-fed simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation (mf-SSCF) of rice straw for high titer ethanol production at low cost. Renew Energy 179:1915–1924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2021.07.146
Sindhu R, Kuttiraja M, Prabisha TP, Binod P, Sukumaran RK, Pandey A (2016) Development of a combined pretreatment and hydrolysis strategy of rice straw for the production of bioethanol and biopolymer. Bioresour Technol 215:110–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.02.080
Singh A, Bishnoi NR (2012) Optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis of pretreated rice straw and ethanol production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93(4):1785–1793. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-3870-1
Singh S, Kaur D, Yadav SK, Krishania M (2021) Process scale-up of an efficient acid-catalyzed steam pretreatment of rice straw for xylitol production by C. Tropicalis MTCC 6192. BioresourTechnol 320:124422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124422
Singh B, Bala A, Anu A, Kumar V, Singh D (2022) Biochemical properties of cellulolytic and xylanolytic enzymes from Sporotrichum thermophile and their utility in bioethanol production using rice straw. Prep BiochemBiotechnol 52(2):197–209. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826068.2021.1925911
Sluiter A, Hames B, Ruiz R, Scarlata C, Sluiter J, Templeton D, Crocker DL (2008) Determination of structural carbohydrates and lignin in biomass. Lab Anal Procedure 1617(1):1–6
TejasNamboodiri MM, Manikandan A, Paul T, Pakshirajan K, Pugazhenthi G (2022) Chitosan production by Penicilliumcitrinum using paper mill wastewater and rice straw hydrolysate as low-cost substrates in a continuous stirred tank reactor. EnvironTechnol 3:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2022.2026486
Valles A, Capilla M, Álvarez-Hornos FJ, García-Puchol M, San-Valero P, Gabaldón C (2021) Optimization of alkali pretreatment to enhance rice straw conversion to butanol. Biomass Bioenergy 150:106131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2021.106131
Wang Z, Keshwani DR, Redding AP, Cheng JJ (2010) Sodium hydroxide pretreatment and enzymatic hydrolysis of coastal Bermuda grass. Bioresour Technol 101(10):3583–3585
Wang R, Unrean P, Franzén CJ (2016) Model-based optimization and scale-up of multi-feed simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation of steam pre-treated lignocellulose enables high gravity ethanol production. Biotechnol Biofuels 9(1):1–3. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-016-0500-7
Wang W, Tan X, Imtiaz M, Wang Q, Miao C, Yuan Z, Zhuang X (2021) Rice straw pretreatment with KOH/urea for enhancing sugar yield and ethanol production at low temperature. Ind Crops Prod 170:113776. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.113776
Wati L, Kumari S, Kundu BS (2007) Paddy straw as substrate for ethanol production. Indian J Microbiol 47(1):26–29
Yao S, Wu G, Xing M, Zhou S, Pu J (2010) Determination of lignin content in Acacia spp using near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy. BioResources s5(2):556–562
Ying W, Shi Z, Yang H, Xu G, Zheng Z, Yang J (2018) Effect of alkaline lignin modification on cellulase–lignin interactions and enzymatic saccharification yield. Biotechnol Biofuels 11(1):1–3. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-018-1217-6
Zhang Q, Cai W (2008) Enzymatic hydrolysis of alkali-pretreated rice straw by Trichoderma reesei ZM4-F3. Biomass Bioenergy 32(12):1130–1135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2008.02.006
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Department of Microbiology, Kurukshetra University, Kurukshetra, Haryana, India, for providing the lab facility for performing the experimentation.
Funding
This work was supported by Haryana State Council for Science, Innovation and Technology (HSCSIT), Panchkula: (grant number HSCSIT/R&D/2012/2376-77/ 20–12-12).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NKA, designed the study; NK performed the experiment; AY, GS and AS analysed the data; NKA, NK, AS and PK wrote and finalized the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not available.
Consent to participate
Not available.
Consent for publication
All authors have read and agree to the publish.
Additional information
Communicated by Yusuf Akhter.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, N., Yadav, A., Singh, G. et al. Comparative study of ethanol production from sodium hydroxide pretreated rice straw residue using Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Zymomonas mobilis. Arch Microbiol 205, 146 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03468-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03468-1