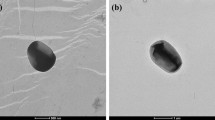
Abstract
Two Gram-staining-negative, aerobic and rod-shaped strains, designated c23x22T and sex2T, were isolated from forest soil collected from Chebaling National Nature Reserve in Guangdong Province and Limu Mountain National Forest Park in Hainan Province, P. R. China, respectively. Phylogenetic analyses based on 16S rRNA gene sequences revealed that they belonged to the genus Microvirga, and strain c23 x22T was most closely related to ‘Microvirga alba’ KCTC 72385, while strain sex2T showed close relationship with Microvirga guangxiensis CGMCC 1.7666T. The average nucleotide identity and digital DNA–DNA hybridization values between strains c23 x22T and sex2T and their close relatives, ‘M. alba’ KCTC 72385 and M. guangxiensis CGMCC 1.7666T, were all below the threshold values for species delimitation. The predominant quinones of the two novel strains were ubiquinone 10, and the major fatty acids contained C19:0 cyclo ω8c and summed feature 8 (C18:1 ω7c and/or C18:1 ω6c). Their predominant polar lipids were phosphatidylglycerol, diphosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine. The phenotypic, genotypic and chemotaxonomic analyses clearly supported that strains c23 x 22T and sex2T represent two novel species of the genus Microvirga, for which the name Microvirga terricola sp. nov. (type strain c23 x 22T = GDMCC 1.1700T = KCTC 62432T) and Microvirga solisilvae sp. nov. (type strain sex2T = GDMCC 1.1651T = KACC 21311T) are proposed, respectively.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The 16S rRNA gene sequence accession numbers of strains c23x22T and sex2T are MT078707 and OM758350, and genome sequence accession numbers of the two strains are JAATJS000000000 and JAKUCN000000000, respectively.
Abbreviations
- NA:
-
Nutrient agar
- TSA:
-
Tryptone soya agar
- R2A:
-
Reasoner’s 2A
- CMC:
-
CM-cellulose
- ANI:
-
Average nucleotide identity
- dDDH:
-
Digital DNA–DNA hybridization
- PHB:
-
Poly-β-hydroxybutyric acid
- Q-10:
-
Ubiquinone 10
- RAST:
-
Rapid annotation using subsystem technology
- DPG:
-
Diphosphatidylglycerol
- PG:
-
Phosphatidylglycerol
- PC:
-
Phosphatidylcholine
- PE:
-
Phosphatidylethanolamine
- APL:
-
Unidentified aminophospholipid
References
Amin A, Ahmed I, Habib N, Abbas S, Hasan F, Xiao M, Hozzein WN, Li WJ (2016) Microvirga pakistanensis sp. nov., a novel bacterium isolated from desert soil of Cholistan. Pakistan. Arch Microbiol 198:933–939. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-016-1251-3
Ardley JK, Parker MA, De Meyer SE, Trengove RD, O’Hara GW, Reeve WG, Yates RJ, Dilworth MJ, Willems A, Howieson JG (2012) Microvirga lupini sp. nov., Microvirga lotononidis sp. nov. and Microvirga zambiensis sp. nov. are alphaproteobacterial root-nodule bacteria that specifically nodulate and fix nitrogen with geographically and taxonomically separate legume hosts. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:2579–2588. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.035097-0
Aziz RK, Bartels D, Best AA, DeJongh M, Disz T, Edwards RA, Formsma K, Gerdes S, Glass EM, Kubal M, Meyer F, Olsen GJ, Olson R, Osterman AL, Overbeek RA, McNeil LK, Paarmann D, Paczian T, Parrello B, Pusch GD, Reich C, Stevens R, Vassieva O, Vonstein V, Wilke A, Zagnitko O (2008) The RAST server: rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genomics 9:75. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-9-75
Caputo A, Lagier JC, Azza S, Robert C, Mouelhi D, Fournier PE, Raoult D (2016) Microvirga massiliensis sp. nov., the human commensal with the largest genome. Microbiologyopen 5:307–322. https://doi.org/10.1002/mbo3.329
Cerny G (1978) Studies on the aminopeptidase test for the distinction of Gram-negative from Gram-positive bacteria. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 5:113–122. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00498805
Collins MD, Pirouz T, Goodfellow M, Minnikin DE (1977) Distribution of menaquinones in actinomycetes and corynebacteria. J Gen Microbiol 100:221–230. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-100-2-221
Dahal RH, Kim J (2017) Microvirga soli sp. nov., an alphaproteobacterium isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:127–132. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001582
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01734359
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1558-5646.1985.tb00420.x
Fitch WM (1971) Toward defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst Zool 20:406–416. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/20.4.406
Goris J, Konstantinidis KT, Klappenbach JA, Coenye T, Vandamme P, Tiedje JM (2007) DNA-DNA hybridization values and their relationship to whole-genome sequence similarities. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:81–91. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.64483-0
Greenspan P, Mayer EP, Fowler SD (1985) Nile red: a selective fluorescent stain for intracellular lipid droplets. J Cell Biol 100:965–973. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.100.3.965
Hiraishi A, Ueda Y, Ishihara J, Mori T (1996) Comparative lipoquinone analysis of influent sewage and activated sludge by high-performance liquid chromatography and photodiode array detection. J Gen Appl Microbiol 42:457–469. https://doi.org/10.2323/jgam.42.457
Hördt A, Lopez MG, Meier-Kolthoff JP, Schleuning M, Weinhold LM, Tindall BJ, Gronow S, Kyrpides NC, Woyke T, Göker M (2020) Analysis of 1,000+ type-strain genomes substantially improves taxonomic classification of Alphaproteobacteria. Front Microbiol 11:468. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.00468
Kanso S, Patel BK (2003) Microvirga subterranea gen. nov., sp. nov., a moderate thermophile from a deep subsurface Australian thermal aquifer. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:401–406. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.02348-0
Kazumori M, Wataru I (2020) Environmental atlas of prokaryotes enables powerful and intuitive habitat-based analysis of community structures. iScience 23:101624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2020.101624
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01731581
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Liu ZT, Xian WD, Li MM, Liu L, Ming YZ, Jiao JY, Fang BZ, Xiao M, Li WJ (2020) Microvirga arsenatis sp. nov., an arsenate reduction bacterium isolated from Tibet hot spring sediments. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 113:1147–1153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-020-01421-6
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk HP, Göker M (2013) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform 14:60. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-60
Na SI, Kim YO, Yoon SH, Ha SM, Baek I, Chun J (2018) UBCG: up-to-date bacterial core gene set and pipeline for phylogenomic tree reconstruction. J Microbiol 56:280–285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-018-8014-6
Oh H, Kim MK, Srinivasan S (2021) Microvirga pudoricolor sp. nov., and Microvirga alba sp. nov., isolated from soil in South Korea. Arch Microbiol 203:6071–6077. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-021-02569-z
Radl V, Simões-Araújo JL, Leite J, Passos SR, Martins LMV, Xavier GR, Rumjanek NG, Baldani JI, Zilli JE (2014) Microvirga vignae sp. nov., a root nodule symbiotic bacterium isolated from cowpea grown in semi-arid Brazil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:725–730. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.053082-0
Richter M, Rossellò-mòra R (2009) Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:19126–19131. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0906412106
Safronova VI, Kuznetsova IG, Sazanova AL, Belimov AA, Andronov EE, Chirak ER, Osledkin YS, Onishchuk OP, Kurchak ON, Shaposhnikov AI, Willems A, Tikhonovich IA (2017) Microvirga ossetica sp. nov., a species of rhizobia isolated from root nodules of the legume species Vicia alpestris Steven. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:94–100. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001577
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454
Sasser M (1990) Bacterial identification by gas chromatographic analysis of fatty acid methyl esters (GC-FAME). Technical note 101. Microbial ID USA Inc, Newark, p 6
Tapase SR, Mawlankar RB, Sundharam SS, Krishnamurthi S, Dastager SG, Kodam KM (2017) Microvirga indica sp. nov., an arsenite-oxidizing Alphaproteobacterium, isolated from metal industry waste soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:3525–3531. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.002157
Tindall BJ, Sikorski J, Smibert RA, Krieg NR (2007) Phenotypic characterization and the principles of comparative systematics. In: Reddy CA, Beveridge TJ, Breznak JA, Marzluf GA, Schmidt TM et al (eds) Methods for general and molecular microbiology, 3rd edn. ASM Press, Washington, DC, pp 330–393
Veyisoglu A, Tatar D, Saygin H, Inan K, Cetin D, Guven K, Tuncer M, Sahin N (2016) Microvirga makkahensis sp. nov., and Microvirga arabica sp. nov., isolated from sandy arid soil. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 109:287–296. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-015-0631-z
Weon HY, Kwon SW, Son JA, Jo EH, Kim SJ, Kim YS, Kim BY, Ka JO et al (2010) Description of Microvirga aerophila sp. nov. and Microvirga aerilata sp. nov., isolated from air, reclassification of Balneimonas flocculans Takeda et al. 2004 as Microvirga flocculans comb. nov. and emended description of the genus Microvirga. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:2596–2600. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.018770-0
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Kwon S, Lim J, Kim Y, Seo H, Chun J (2017a) Introducing Ezbiocloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1613–1617. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001755
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Lim JM, Kwon SJ, Chun J (2017b) A large-scale evaluation of algorithms to calculate average nucleotide identity. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 110:1281–1286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-017-0844-4
Zhang J, Song F, Xin YH, Zhang J, Fang C (2009) Microvirga guangxiensis sp. nov., a novel alphaproteobacterium from soil, and emended description of the genus Microvirga. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:1997–2001. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.007997-0
Zhang XJ, Zhang J, Yao Q, Feng GD, Zhu HH (2019) Microvirga flavescens sp. nov., a novel bacterium isolated from forest soil and emended description of the genus Microvirga. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 69:667–671. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.003189
Funding
This work was jointly supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (32000007), the Science and Technology Program of Guangdong Province (2021B1212050022) and the GDAS' Project of Science and Technology Development (2021GDASYL-20210103020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: XZ and GF; data curation: XZ; formal analysis: XZ; funding acquisition: XZ and HZ; investigation: ZX, GF, XZ, YZ, XD, QY, and HZ; methodology: ZX, XZ, YZ and XD; project administration: XZ and HZ; software: XZ; supervision and validation: XZ, GF, XZ, YZ and HZ; visualization: XZ; writing-original draft: XZ; writing—review and editing: GF, QY and HZ. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Feng, GD., Zhen, X. et al. Microvirga terricola sp. nov. and Microvirga solisilvae sp. nov, isolated from forest soil. Arch Microbiol 204, 423 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-02963-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-02963-1