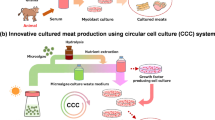
Abstract
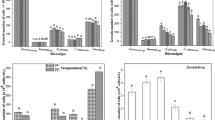
‘Cultured food’ has tremendous potential as a sustainable meat alternative. Increased cultured food production is increasing the amount of waste medium from cell culture. Nitrogen- and phosphorus-containing compounds in waste medium can cause eutrophication of water bodies. Currently, microalgae are used in energy production, environmental protection, agriculture and pharmaceutical and health food industries. Here, we used the microalgae, Chlorococcum littorale and Chlorella vulgaris and the waste medium of C2C12 cells for a case study. We found that 80% and 26% of ammonia and 16% and 15% of phosphorus in the waste medium were consumed by C. littorale and C. vulgaris, respectively. In addition, C. littorale and C. vulgaris proliferated 3.2 folds and 1.6 folds, respectively, after seven days in the waste medium that was enhanced by adjusting medium salt concentration. This report demonstrates the potential of sustainability for solving the issue of waste medium production during the production of cultured food.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajjawi I, Verruto J, Aqui M, Soriaga LB, Coppersmith J, Kwok K, Peach L, Orchard E, Kalb R, Xu W, Carlson TJ, Francis K, Konigsfeld K, Bartalis J, Schultz A, Lambert W, Schwartz AS, Brown R, Moellering ER (2017) Lipid production in Nannochloropsis gaditana is doubled by decreasing expression of a single transcriptional regulator. Nat Biotechnol 35:647–652. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3865
Alori ET, Babalola OO (2018) Microbial inoculants for improving crop quality and human health in Africa. Front Microbiol 9:2213. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.02213
Cheng J, Zhu Y, Zhang Z, Yang W (2019) Modification and improvement of microalgae strains for strengthening CO2 fixation from coal-fired flue gas in power plants. Bioresour Technol 291:121850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121850
Chisti Y (2007) Biodiesel from microalgae. Biotechnol Adv 25:294–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2007.02.001
Chiu SY, Kao CY, Chen TY, Chang YB, Kuo CM, Lin CS (2015) Culture of microalgal chlorella for biomass and lipid production using wastewater as nutrient resource. Bioresour Technol 184:179–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.11.080
Gerhardt C, Suhlmann G, Ziemßen F, Donnan D, Warschun M, Kühnle HJ (2020) How will cultured meat and meat alternatives disrupt the agricultural and food industry? Ind Biotechnol 16:262–270. https://doi.org/10.1089/ind.2020.29227.cge
Gregory JA, Topol AB, Doerner DZ, Mayfield S (2013) Alga-produced cholera toxin-Pfs25 fusion proteins as oral vaccines. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:3917–3925. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00714-13
Gutiérrez-Salmeán G, Fabila-Castillo L, Chamorro-Cevallos G (2015) Nutritional and toxicological aspects of Spirulina (Arthrospira). Nutr Hosp 32:34–40. https://doi.org/10.3305/nh.2015.32.1.9001
Haraguchi Y, Shimizu T (2021) Three-dimensional tissue fabrication system by co-culture of microalgae and animal cells for production of thicker and healthy cultured food. Biotechnol Lett 43:1117–1129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-021-03106-0
Haraguchi Y, Shimizu T, Sasagawa T, Sekine H, Sakaguchi K, Kikuchi T, Sekine W, Sekiya S, Yamato M, Umezu M, Okano T (2012) Fabrication of functional three-dimensional tissues by stacking cell sheets in vitro. Nat Protoc 7:850–858. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2012.027
Haraguchi Y, Kagawa Y, Sakaguchi K, Matsuura K, Shimizu T, Okano T (2017) Thicker three-dimensional tissue from a “symbiotic recycling system” combining mammalian cells and algae. Sci Rep 7:41594. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep41594
Harun R, Yip JWS, Thiruvenkadam S, Ghani WAWAK, Cherrington T, Danquah MK (2014) Algal biomass conversion to bioethanol—a step-by-step assessment. Biotechnol J 9:73–86. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.201200353
Ho SH, Huang SW, Chen CY, Hasunuma T, Kondo A, Chang JS (2013) Bioethanol production using carbohydrate-rich microalgae biomass as feedstock. Bioresour Technol 135:191–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.10.015
Lee DJ, Chang JS, Lai JY (2015) Microalgae-microbial fuel cell: a mini review. Bioresour Technol 198:891–895. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.09.061
Mattick CS, Landis AE, Allenby BR, Genovese NJ (2015) Anticipatory life cycle analysis of in vitro biomass culture for cultured meat production in the United States. Environ Sci Technol 49:11941–11949. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b01614
McCusker S, Buff PR, Yu Z, Fascetti AJ (2014) Amino acid content of selected plant, algae and insect species: a search for alternative protein sources for use in pet foods. J Nutr Sci 3:e39. https://doi.org/10.1017/jns.2014.33
Mulukutla BC, Yongky A, Le T, Mashek DG, Hu WS (2016) Regulation of glucose metabolism—a perspective from cell bioprocessing. Trends Biotechnol 34:638–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2016.04.012
Norsker NH, Barbosa MJ, Vermuë MH, Wijffels RH (2011) Microalgal production—a close look at the economics. Biotechnol Adv 29:24–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2010.08.005
Okamoto Y, Haraguchi Y, Sawamura N, Asahi T, Shimizu T (2020) Mammalian cell cultivation using nutrients extracted from microalgae. Biotechnol Prog 36:e2941. https://doi.org/10.1002/btpr.2941
Osanai T, Kuwahara A, Iijima H, Toyooka K, Sato M, Tanaka K, Ikeuchi M, Saito K, Hirai MY (2013) Pleiotropic effect of sigE over-expression on cell morphology, photosynthesis and hydrogen production in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Plant J 76:456–465. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12310
Post MJ (2014) An alternative animal protein source: cultured beef. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1328:29–33. https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.12569
Rasala BA, Muto M, Lee PA, Jager M, Cardoso RMF, Behnke CA, Kirk P, Hokanson CA, Crea R, Mendez M, Mayfield SP (2010) Production of therapeutic proteins in algae, analysis of expression of seven human proteins in the chloroplast of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Biotechnol J 8:719–733. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-7652.2010.00503.x
Rossi F, Olguín EJ, Diels L, De Philippis R (2015) Microbial fixation of CO2 in water bodies and in drylands to combat climate change, soil loss and desertification. N Biotechnol 32:109–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2013.12.002
Satoh A, Kurano N, Harayama S, Miyachi S (2004) Effects of chloramphenicol on photosynthesis, protein profiles and transketolase activity under extremely high CO2 concentration in an extremely-high-CO2-tolerant green microalga, Chlorococcum littorale. Plant Cell Physiol 45:1857–1862. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pch196
Schneider M, Marison IW, von Stockar U (1996) The importance of ammonia in mammalian cell culture. J Biotechnol 46:161–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-1656(95)00196-4
Singh AK, Singh MP (2014) Importance of algae as a potential source of biofuel. Cell Mol Biol 60:106–109
Song Y, Johnson D, Peng R, Hensley DK, Bonnesen PV, Liang L, Huang J, Yang F, Zhang F, Qiao R, Baddorf AP, Tschaplinski TJ, Engle NL, Hatzell MC, Wu Z, Cullen DA, Meyer HM 3rd, Sumpter BG, Rondinone AJ (2018) A physical catalyst for the electrolysis of nitrogen to ammonia. Sci Adv 4:e1700336. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1700336
Specht EA, Mayfield SP (2014) Algae-based oral recombinant vaccines. Front Microbiol 5:60. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00060
Spolaore P, Joannis-Cassan C, Duran E, Isambert A (2006) Commercial applications of microalgae. J Biosci Bioeng 101:87–96. https://doi.org/10.1263/jbb.101.87
Széliová D, Ruckerbauer DE, Galleguillos SN, Petersen LB, Natter K, Hanscho M, Troyer C, Causon T, Schoeny H, Christensen HB, Lee DY, Lewis NE, Koellensperger G, Hann S, Nielsen LK, Borth N, Zanghellini J (2020) What CHO is made of: variations in the biomass composition of Chinese hamster ovary cell lines. Metab Eng 61:288–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2020.06.002
Tanabe Y, Hodoki Y, Sano T, Tada K, Watanabe MM (2018) Adaptation of the freshwater bloom-forming cyanobacterium Microcystis aerguinosa to brackish water is driven by recent horizontal transfer of sucrose genes. Front Microb 9:1150. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01150
Tarayre C, Clercq LD, Charlier R, Michels E, Meers E, Camargo-Valero M, Delvigne F (2016) New perspectives for the design of sustainable bioprocesses for phosphorus recovery from waste. Bioresour Technol 206:264–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.01.091
Tsujimoto R, Kotani H, Yokomizo K, Yamakawa H, Nonaka A, Fujita Y (2018) Functional expression of an oxygen-labile nitrogenase in an oxygenic photosynthetic organism. Sci Rep 8:7380. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-25396-7
Tuomisto HL, Teixeira de Mattos MJ (2011) Environmental impacts of cultured meat production. Environ Sci Technol 45:6117–6123. https://doi.org/10.1021/es200130u
Wang L, Min M, Li Y, Chen P, Chen Y, Liu Y, Wang Y, Ruan R (2010) Culture of green algae Chlorella sp. in different wastewaters from municipal wastewater treatment plant. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 162:1174–1186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-009-8866-7
Wang JH, Wang JH, Zhang TY, Dao GH, Xu XQ, Wang XX, Hu HY (2017) Microalgae-based advanced municipal wastewater treatment for reuse in water bodies. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:2659–2675. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8184-x
Ye Y, Ngo HH, Guo W, Liu Y, Chang SW, Nguyen DD, Liang H, Wang J (2018) A critical review on ammonium recovery from wastewater for sustainable wastewater management. Bioresour Technol 268:749–758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.07.111
Zhang J, Pavlova NN, Thompson CB (2017) Cancer cell metabolism: the essential role of the nonessential amino acid, glutamine. EMBO J 36:1302–1315. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201696151
Funding
This work was supported by the Cabinet Office, Government of Japan, Cross-ministerial Moonshot Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries Research and Development Program, ‘Technologies for Smart Bio-industry and Agriculture’ (funding agency: Bio-oriented Technology Research Advancement Institution).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Tokyo Women’s Medical University was receiving research funds from IntegriCulture Inc.
Ethical approval
This study does not include any experimental procedure performed on humans or animals.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haraguchi, Y., Shimizu, T. Microalgal culture in animal cell waste medium for sustainable ‘cultured food’ production. Arch Microbiol 203, 5525–5532 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-021-02509-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-021-02509-x