Abstract
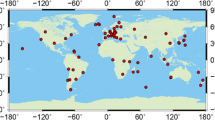
The rapid development of the Chinese BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) brings a promising prospect for the real-time retrieval of zenith tropospheric delays (ZTD) and precipitable water vapor (PWV), which is of great benefit for supporting the time-critical meteorological applications such as nowcasting or severe weather event monitoring. In this study, we develop a real-time ZTD/PWV processing method based on Global Positioning System (GPS) and BDS observations. The performance of ZTD and PWV derived from BDS observations using real-time precise point positioning (PPP) technique is carefully investigated. The contribution of combining BDS and GPS for ZTD/PWV retrieving is evaluated as well. GPS and BDS observations of a half-year period for 40 globally distributed stations from the International GNSS Service Multi-GNSS Experiment and BeiDou Experiment Tracking Network are processed. The results show that the real-time BDS-only ZTD series agree well with the GPS-only ZTD series in general: the RMS values are about 11–16 mm (about 2–3 mm in PWV). Furthermore, the real-time ZTD derived from GPS-only, BDS-only, and GPS/BDS combined solutions are compared with those derived from the Very Long Baseline Interferometry. The comparisons show that the BDS can contribute to real-time meteorological applications, slightly less accurately than GPS. More accurate and reliable water vapor estimates, about 1.3–1.8 mm in PWV, can be obtained if the BDS observations are combined with the GPS observations in the real-time PPP data processing. The PWV comparisons with radiosondes further confirm the performance of BDS-derived real-time PWV and the benefit of adding BDS to standard GPS processing.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Askne J, Nordius H (1987) Estimation of tropospheric delay for microwaves from surface weather data. Radio Sci 22:379–386
Bender M, Dick G, Wickert J, Ramatschi M, Ge M, Gendt G, Rothacher M, Raabe A, Tetzlaff G (2009) Estimates of the information provided by GPS slant data observed in Germany regarding tomographic applications. J Geophys Res 114:D06303. doi:10.1029/2008JD011008
Böhm J, Niell A, Tregoning P, Schuh H (2006) Global Mapping Function (GMF): a new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data. Geophys Res Lett 33:L07304. doi:10.1029/2005GL025546
Böhm J, Böhm S, Nilsson T, Pany A, Plank L, Spicakova H, Teke K, Schuh H (2012) The new Vienna VLBI software VieVS, Geodesy for Planet Earth. In: Proceedings of the 2009 IAG symp, Buenos Aires, International Association of Geodesy Symposia Series, vol 136, pp 1007–1011
Bevis M, Businger S, Herring T, Rocken C, Anthes R, Ware R (1992) GPS meteorology: remote sensing of atmospheric water vapor using GPS. J Geophys Res 97:15787–15801
Caissy M, Agrotis L, Weber G, Hernandez-Pajares M, Hugentobler U (2012) Coming soon: the International GNSS Real-Time Service, GPS World, vol 23(6), pp 52–58
China Satellite Navigation Office (2012) BeiDou navigation satellite system signal in space interface control document. http://gge.unb.ca/test/beidou_icd_english.pdf
Dow J, Neilan R, Rizos C (2009) The International GNSS Service in a changing landscape of Global Navigation Satellite Systems. J Geod 83:191–198. doi:10.1007/s00190-008-0300-3
Davis J, Herring T, Shapiro I, Rogers A, Elgered G (1985) Geodesy by radio interferometry: effects of atmospheric modeling errors on estimates of baseline length. Radio Sci 20(6):1593–1607. doi:10.1029/RS020i006p01593
Dousa J, Vaclavovic P (2014) Real-time zenith tropospheric delays in support of numerical weather prediction applications. Adv Space Res 53(9):1347–1358
Elgered G, Plag H, van der Marel H, Barlag S, Nash J (eds) (2005) COST 716: exploitation of ground-based GPS for climate and numerical weather prediction applications, Final Report, European Community, EUR 21639, ISBN 92-898-0012-7
Fang P, Bevis M, Bock Y, Gutman S, Wolfe D (1998) GPS meteorology: reducing systematic errors in geodetic estimates for zenith delay. Geophys Res Lett 25:3583–3586
Gendt G, Dick G, Reigber C, Tomassini M, Liu Y, Ramatschi M (2004) Near real-time GPS water vapor monitoring for numerical weather prediction in Germany. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 82:361–370
Gutman S, Sahm R, Benjamin G, Schwartz E, Holub L, Stewart Q, Smith L (2004) Rapid retrieval and assimilation of ground based GPS-Met observations at the NOAA forecast systems laboratory: impact on weather forecasts. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 82:351–360
Ge M, Zhang H, Jia X, Song S, Wickert J (2012) What is achievable with the current COMPASS constellation? GPS World November, pp 29–34
Haan S, Barlag S, Baltink H, Debie F (2004) Synergetic use of GPS water vapor and meteosat images for synoptic weather forecasting. J Appl Meterol 43:514–518
Heinkelmann R, Böhm J, Schuh H, Bolotin S, Engelhardt G, MacMillan D, Negusini M, Skurikhina E, Tesmer V, Titov O (2007) Combination of long time-series of troposphere zenith delays observed by VLBI. J Geod 81(6–8):483–501
Kouba J (2009) A guide to using International GNSS Service (IGS) Products. http://igscb.jpl.nasa.gov/igscb/resource/pubs/UsingIGSProductsVer21.pdf
Lagler K, Schindelegger M, Boehm J, Krásná H, Nilsson T (2013) GPT2: Empirical slant delay model for radio space geodetic techniques. Geophys Res Lett 40:1069–1073. doi:10.1002/grl.50288
Li M, Li W, Shi C, Zhao Q, Su X, Qu L, Liu Z (2014a) Assessment of precipitable water vapor derived from ground-based BeiDou observations with Precise Point Positioning approach. Adv Space Res 55(1):150–162
Li X, Zhang X, Ge M (2011) Regional reference network augmented precise point positioning for instantaneous ambiguity resolution. J Geod 85:151–158
Li X, Ge M, Zhang H, Nischan T, Wickert J (2013a) The GFZ real-time GNSS precise positioning service system and its adaption for COMPASS. Adv Space Res 51(6):1008–1018
Li X, Ge M, Zhang H, Wickert J (2013b) A method for improving uncalibrated phase delay estimation and ambiguity-fixing in real-time precise point positioning. J Geod 87(5):405–416
Li X, Ge M, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Guo B, Wang R, Klotz J, Wickert J (2013c) Real-time high-rate co-seismic displacement from ambiguity-fixed precise point positioning: application to earthquake early warning. Geophys Res Lett 40(2):295–300. doi:10.1002/grl.50138
Li X, Dick G, Ge M, Heise S, Wickert J, Bender M (2014b) Real-time GPS sensing of atmospheric water vapor: precise point positioning with orbit, clock and phase delay corrections. Geophys Res Lett 41(10):3615–3621
Li X, Zhang X, Ren X, Fritsche M, Wickert J, Schuh H (2015) Precise positioning with current multi-constellation Global Navigation Satellite Systems: GPS, GLONASS, Galileo and BeiDou. Sci Rep 5:8328
Montenbruck O, Steigenberger P, Khachikyan R, Weber G, Langley RB, Mervart L, Hugentobler U (2014) IGS-MGEX: preparing the ground for multi-constellation GNSS science. Inside GNSS 9(1):42–49
Nilsson T, Elgered G (2008) Long-term trends in the atmospheric water vapor content estimated from ground-based GPS data. J Geophys Res 113:D19101. doi:10.1029/2008JD010110
Nothnagel A (2009) Conventions on thermal expansion modeling of radio telescopes for geodetic and astrometric VLBI. J Geod 83:787–792. doi:10.1007/s00190-008-0284-z
Ning T, Haas R, Elgered G, Willén U (2012) Multi-technique comparisons of 10 years of wet delay estimates on the west coast of Sweden. J Geod 86(7):565–575. doi:10.1007/s00190-011-0527-2
Petit G, Luzum B (eds) (2010) IERS Conventions (2010), IERS Technical Note 36, Verlagdes Bundesamts für Kartographie und Geodäsie, Frankfurt am Main, Germany. http://tai.bipm.org/iers/conv2010/
Ran C (2010) COMPASS Satellite System Development and Plan. In: Proceedings of The First China Satellite Navigation Conference, Beijing, China, 19–21 May 2010
Rocken C, Van Hove T, Ware R (1997) Near real-time sensing of atmospheric water vapor. Geophys Res Lett 24:3221–3224
Schuh H, Behrend D (2012) VLBI: a fascinating technique for geodesy and astrometry. J Geodyn 61:68–80. doi:10.1016/j.jog.2012.07.007
Shi C, Zhao Q, Li M, Tang W, Hu Z, Lou Y, Zhang H, Niu X, Liu J (2012) Precise orbit determination of BeiDou Satellites with precise positioning. Sci China Earth Sci 55:1079–1086
Saastamoinen J (1973) Contributions to the theory of atmospheric refraction—part II. Refraction corrections in satellite geodesy. Bull Géod 47(1):13–34. doi:10.1007/BF02522083
Teke K, Boehm J, Nilsson T, Schuh H, Steigenberger P, Dach R, Heinkelmann R, Willis P, Haas R, Garcia-Espada S, Hobiger T, Ichikawa R, Shimizu S (2011) Multi-technique comparison of troposphere zenith delays and gradients during CONT08. J Geod 85:395–413. doi:10.1007/s00190-010-0434-y
Wang J, Zhang L, Dai A (2005) Global estimates of water-vapor-weighted mean temperature of the atmosphere for GPS applications. J Geophys Res 110:D21101. doi:10.1029/2005JD006215
Wang X, Wang X, Dai Z, Ke F, Cao Y, Wang F, Song L (2014) Tropospheric wet refractivity tomography based on the BeiDou Satellite System. Adv Atmos Sci. doi:10.1007/s00376-013-2311-0
Xu A, Xu Z, Ge M, Xu X, Zhu H, Sui X (2013) Estimating zenith tropospheric delays from BeiDou navigation satellite system observations. Sensors 13:4514–4526
Yang Y, Li J, Xu J, Tang J, Guo H, He H (2011) Contribution of the compass satellite nagivation system to global PNT users. Chin. Sci. Bull. 56(26):2813–2819. doi:10.1007/s11434-001-4627-4
Yuan Y, Zhang K, Rohm W, Choy S, Norman R, Wang C (2014) Real-time retrieval of precipitable water vapor from GPS precise point positioning. J Geophys Res Atmos 119:10044–10057
Zumberge J, Heflin M, Jefferson D, Watkins M, Webb F (1997) Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J Geophys Res 102(B3):5005–5017
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge IGS, MGEX, and BETN for providing the GPS and BDS data and IVS for providing the VLBI data. We also thank NOAA for the online provision of radiosonde data. One of the authors (C. Lu) is supported by the China Scholarship Council, which is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, C., Li, X., Nilsson, T. et al. Real-time retrieval of precipitable water vapor from GPS and BeiDou observations. J Geod 89, 843–856 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-015-0818-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-015-0818-0