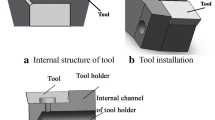
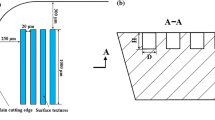
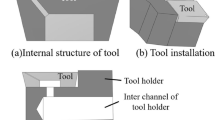
Abstract
In recent years, there has been a challenge: how to meet the requirements of cutting lubrication and use the least cutting fluid for environmental protection simultaneously. To resolve this problem, novel cutting tools with micro textures on the rake face for lubrication were proposed, which can directly transport the cutting fluid to the tool-chip contact interface by using a micro-pipe. Cutting tests were performed on AISI 1045 steel. Then, the cutting force, friction coefficient, tool-chip contact length as well as wear of tools were investigated. The results show that the novel tools with micro textures have better cutting performance than other tools, by using much less cutting fluid than traditional flood lubricating cutting. Especially for the TVT tool, it has the best comprehensive performance. The main lubricating mechanism is that the cutting fluids can be more widely distributed on the tool rake face by the micro textures. This leads to better lubrication and less adhesion of the rake face.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klocke F, Eisenblätter G (1997) Dry cutting. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 46(2):519–526
Weinert K, Inasaki I, Sutherland JW, Wakabayashi T (2004) Dry machining and minimum quantity lubrication. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 53(2):511–537
Halim N, Haron C, Ghani JA, Azhar MF (2019) Tool wear and chip morphology in high-speed milling of hardened Inconel 718 under dry and cryogenic CO2 conditions. Wear 426:1683–1690
Pereira WH, Delijaicov S (2019) Surface integrity of INCONEL 718 turned under cryogenic conditions at high cutting speeds. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 104:2163–2177
Deng JX, Cao TK, Liu LL, Zhao JL (2006) Self-lubrication of sintered ceramic tools with CaF2 addition in dry cutting. Int J Mach Tool Manu 46(9):957–963
Tang SW, Wang R, Liu PF, Niu QL, Yang GQ (2020) Preparation of WC-TiC-Ni3Al-CaF2 functionally graded self-lubricating tool material by microwave sintering and its cutting performance. High Temp Mater Processes 39:45–53
Wang T, Zhang J, Li Y, Li Y, Gao F, Zhang GJ (2019) Self-lubricating TiN/MoN and TiAlN/MoN nano-multilayer coatings for drilling of austenitic stainless steel. Ceram Int 45(18):24248–24253
Lian YS, Deng JX, Li SP, Yan GY, Lei ST (2014) Friction and wear behavior of WS2/Zr self-lubricating soft coatings in dry sliding against 40Cr-hardened steel balls. Tribol Lett 53(1):237–246
Lian YS, Long YY, Zhao GL, Mu CL, Li XM, Deng JX, Xie CP (2020) Performance of CrCN-WS2 hard/soft composite coated tools in dry cutting of titanium alloys. J Manuf Process 54:201–209
Brzezinka TL, Rao J, Paiva JM, Kohlscheen J, Fox-Rabinovich GS, Veldhuis SC, Endrino JL (2019) DLC and DLC-WS2 coatings for machining of aluminium alloys. Coatings 9(3):192
Song WL, Deng JX, Zhang H, Yan P (2010) Study on cutting forces and experiment of MoS2/Zr-coated cemented carbide tool. Int J Adv Manuf 49(9):903–909
Songmene V, Kouam J, Balhoul A (2018) Effect of minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) on fine and ultrafine particle emission and distribution during polishing of granite. Measurement 114:398–408
Shah P, Gadkari A, Sharma A, Shokrani A, Khanna N (2021) Comparison of machining performance under MQL and ultra-high voltage EMQL conditions based on tribological properties. Tribol Int 153:106595
Sharma AK, Tiwari AK, Dixit AR (2016) Effects of minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) in machining processes using conventional and nanofluid based cutting fluids: a comprehensive review. J Clean Prod 127:1–18
Chiffre L, Andreasen JL, Lagerberg S (2007) Performance testing of cryogenic CO2 as cutting fluid in parting/grooving and threading austenitic stainless steel. Ann ICRP 56(1):101–104
Wang YG, Li CH, Zhang YB, Li BK, Yang M, Zhang XP, Guo SM, Liu GT (2016) Experimental evaluation of the lubrication properties of the wheel/workpiece interface in MQL grinding with different nanofluids. Tribol Int 99:198–210
Li M, Yu T, Yang L, Li H, Wang W (2019) Parameter optimization during minimum quantity lubrication milling of TC4 alloy with graphene-dispersed vegetable-oil-based cutting fluid. J Clean Prod 209:1508–1522
Li CH, Wang S, Zhang Q, Jia DZ (2013) Valuation of minimum quantity lubrication grinding with nano-particles and recent related patents. Recent Pat Nanotech 2:167–181
Cai CY, Liang X, An QL, Tao ZR, Ming WW, Chen M (2021) Cooling/lubrication performance of dry and supercritical CO2-based minimum quantity lubrication in peripheral milling Ti-6Al-4V. Int J Pr Eng Man-G T 8:405–421
Ranjan P, Hiremath SS (2019) Role of textured tool in mproving machining performance: A review. J Manuf Process 43:47–73
Liu YY, Deng JX, Wang W, Duan R, Meng R, Ge DL, Li XM (2018) Effect of texture parameters on cutting performance of flank-faced textured carbide tools in dry cutting of green Al2O3 ceramics. Ceram Int 44:13205–13217
Rathod P, Aravindan S, Paruchuri VR (2015) Evaluating the effectiveness of the novel surface textured tools in enhancing the machinability of titanium alloy (Ti6Al4V). J Adv Mech Des Syst 9:1–19
Cao TK, Liu YJ, Xu YT (2020) Cutting performance of tool with continuous lubrication at tool-chip interface. Int J Pr Eng Man-G T 7:347–359
Xing YQ, Deng JX, Wu Z, Liu L, Huang P, Jiao AQ (2018) Analysis of tool-chip interface characteristics of self-lubricating tools with nanotextures and WS2/Zr coatings in dry cutting. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 97:1637–1647
Lee EH, Shaffer BW (1951) The theory of plasticity applied to a problem of machining. Trans ASME: J Appl Mech 73:405–413
Lü M, Guo JY (2010) Simulation for effects of tool-chip friction on chip flow characteristics in oblique cutting. Acta Armamentarii 31:1491–1497 (in Chinese)
Shaw MC (2005) Metal cutting principles. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the “Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation, China (ZR2016EEM41).”
Funding
This work was supported by Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation, China” (Grant numbers ZR2016EEM41).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Tongkun Cao and Weifeng Zhang contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, cutting tests, and data collection were performed by Zonggao Li and Siguo Zhang. The analysis was accomplished by all authors. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Tongkun Cao and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing intersts.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, T., Li, Z., Zhang, S. et al. Cutting performance and lubrication mechanism of microtexture tool with continuous lubrication on tool-chip interface. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 125, 1815–1826 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-10821-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-10821-7