Abstract
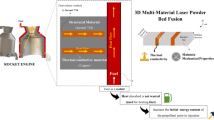
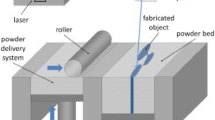
The substantial growth of laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) technology has partly been driven by its opportunity to provide high-performance complex design solutions with outstanding benefits for the aerospace industry. The key opportunities for metal additive manufacturing in aerospace applications include significant cost and lead-time reductions in addition to the possibility of highly efficient complex and lightweight designs. Inconel 718 (IN718) alloy is one of the most common materials usually employed in rocket engines, turbine blades, and turbocharges. The high geometrical complexity of the type of components demanded a detailed exploration of the LPBF of IN718 parts in the last years. As-built and post-processed IN718 LPBFed parts are covered both in terms of the processing parameters as for the metallurgical and physical properties and the mechanical properties (tensile, hardness, and fatigue properties). These complex inter-relations are presented in such a manner (graphs and tables) that can act as engineering tools for helping engineers and designers to obtain near-net-shape parts made of IN718 with the desired properties. This comprehensive overview of the influence of LPBF processing parameters on the final properties of IN718 alloy allows understanding that there is no straightforward relation between energy density and final properties of LPBFed IN718 parts. Thus, the combination of different parameters must be considered and studied individually based on the requirements of each final application. Based on these observations, challenges and future opportunities are also highlighted for the LPBF production of multi-functional IN718 aerospace parts.













Similar content being viewed by others
Availability or data and material
All data used in this work have been properly cited within the article.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Chakraborty S, Pradhan BB (2017) Laser beam machining of Inconel alloys: a review 11:9–14
Davis JR (2000) ASM specialty handbook : nickel, cobalt, and their alloys. ASM Intern, USA
Hunt R (2020) Inconel 718: a workhorse material for additive manufacturing. Protolabs Manuf Accel. https://www.protolabs.com/resources/blog/inconel-718-a-workhorse-material-for-additive-manufacturing/. Accessed 20 Nov 2021
Qi H, Azer M, Ritter A (2009) Studies of standard heat treatment effects on microstructure and mechanical properties of laser net shape manufactured. Metall Mater Trans A 2:2410–2422. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-009-9949-3
Yap CY, Chua CK, Dong ZL, Liu ZH, Zhang DQ, Loh LE, Sing SL (2015) Review of selective laser melting: materials and applications. Appl Phys Rev 2. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4935926
Bartolomeu F, Buciumeanu M, Costa MM, Alves N, Gasik M, Silva FS, Miranda G (2019) Multi-material Ti6Al4V & PEEK cellular structures produced by selective laser melting and hot pressing: a tribocorrosion study targeting orthopedic applications. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 89:54–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2018.09.009
Costa MM, Lima R, Melo-Fonseca F, Bartolomeu F, Alves N, Miranda A, Gasik M, Silva FS, Silva NA, Miranda G (2019) Development of β-TCP-Ti6Al4V structures: driving cellular response by modulating physical and chemical properties. Mater Sci Eng C 98:705–716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.01.016
Bartolomeu F, Fonseca J, Peixinho N, Alves N, Gasik M, Silva FS, Miranda G (2019) Predicting the output dimensions, porosity and elastic modulus of additive manufactured biomaterial structures targeting orthopedic implants. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 99:104–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2019.07.023
Bartolomeu F, Abreu CS, Moura CG, Costa MM, Alves N, Silva FS, Miranda G (2019) Ti6Al4V-PEEK multi-material structures – design, fabrication and tribological characterization focused on orthopedic implants. Tribol Int 131:672–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2018.11.017
Gorji NE, O’Connor R, Brabazon D (2021) XPS, SEM, AFM, and nano-indentation characterization for powder recycling within additive manufacturing process. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 1182:012025. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/1182/1/012025
Parimi LL, Ravi GA, Clark D, Attallah MM (2014) Microstructural and texture development in direct laser fabricated IN718. Mater Charact 102–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2013.12.012
Tucho WM, Cuvillier P, Sjolyst-Kverneland A, Hansen V (2017) Microstructure and hardness studies of Inconel 718 manufactured by selective laser melting before and after solution heat treatment. Mater Sci Eng A 689:220–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.02.062
Ni M, Liu S, Chen C, Li R, Zhang X, Zhou K (2019) Effect of heat treatment on the microstructural evolution of a precipitation-hardened superalloy produced by selective laser melting. Mater Sci Eng A 748:275–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2019.01.109
Jiang R, Mostafaei A, Wu Z, Choi A, Guan PW, Chmielus M, Rollett AD (2020) Effect of heat treatment on microstructural evolution and hardness homogeneity in laser powder bed fusion of alloy 718. Addit Manuf 35:101282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2020.101282
Liu C, Chen D, Hill MR, Tran MN, Zou J (2017) Effects of ultrasonic impact treatment on weld microstructure, hardness, and residual stress. Mater Sci Technol (United Kingdom) 33:1601–1609. https://doi.org/10.1080/02670836.2017.1299277
Lesyk DA, Martinez S, Mordyuk BN, Dzhemelinskyi VV, Lamikiz А, Prokopenko GI (2020) Prokopenko, Post-processing of the Inconel 718 alloy parts fabricated by selective laser melting: effects of mechanical surface treatments on surface topography, porosity, hardness and residual stress. Surf Coatings Technol 381:125136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2019.125136
Boschetto A, Bottini L (2015) Surface improvement of fused deposition modeling parts by barrel finishing. Rapid Prototyp J 21:686–696. https://doi.org/10.1108/RPJ-10-2013-0105
Maleki E, Unal O, Guagliano M, Bagherifard S (2021) The effects of shot peening, laser shock peening and ultrasonic nanocrystal surface modification on the fatigue strength of Inconel 718. Mater Sci Eng A 810:141029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2021.141029
Hosseini E, Popovich VA (2019) A review of mechanical properties of additively manufactured Inconel 718. Addit Manuf 30:100877. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2019.100877
Martínez S, Lamikiz A, Ukar E, Calleja A, Arrizubieta JA, Lopez de Lacalle LN (2017) Analysis of the regimes in the scanner-based laser hardening process. Opt Lasers Eng 90:72–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2016.10.005
Li R, Liu J, Shi Y, Wang L, Jiang W (2012) Balling behavior of stainless steel and nickel powder during selective laser melting process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 59:1025–1035. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-011-3566-1
Panwisawas C, Tang YT, Reed RC (2020) Metal 3D printing as a disruptive technology for superalloys. Nat Commun 11:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16188-7
Karayagiz K, Elwany A, Tapia G, Franco B, Johnson L, Ma J, Karaman I, Arróyave R (2019) Numerical and experimental analysis of heat distribution in the laser powder bed fusion of Ti-6Al-4V. IISE Trans 51:136–152. https://doi.org/10.1080/24725854.2018.1461964
Liu SY, Li HQ, Qin CX, Zong R, Fang XY (2020) The effect of energy density on texture and mechanical anisotropy in selective laser melted Inconel 718. Mater Des 191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2020.108642
Jia Q, Gu D (2014) Selective laser melting additive manufacturing of Inconel 718 superalloy parts: densification, microstructure and properties. J Alloys Compd 585:713–721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.09.171
Nguyen QB, Nai MLS, Zhu Z, Sun CN, Wei J, Zhou W (2017) Characteristics of Inconel powders for powder-bed additive manufacturing. Engineering 3:695–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENG.2017.05.012
Caiazzo F, Alfieri V, Casalino G (2020) On the relevance of volumetric energy density in the investigation of Inconel 718 laser powder bed fusion. Materials (Basel) 13:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13030538
Balbaa M, Mekhiel S, Elbestawi M, McIsaac J (2020) On selective laser melting of Inconel 718: densification, surface roughness, and residual stresses. Mater Des 193:108818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2020.108818
Mondragón-Rodríguez GC, Torres-Padilla N, Camacho N, Espinosa-Arbeláez DG, de León-Nope GV, González-Carmona JM, Alvarado-Orozco JM (2020) Surface modification and tribological behavior of plasma nitrided Inconel 718 manufactured via direct melting laser sintering method. Surf Coatings Technol 387:125526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.125526
Anandakrishnan V, Sathish S, Muthukannan D, Dillibabu V, Balamuralikrishnan N (2020) Dry sliding wear behavior of Inconel 718 additively manufactured by DMLS technique. Ind Lubr Tribol 72:491–496. https://doi.org/10.1108/ILT-08-2019-0322
Luo YW, Zhang B, Song ZM, Li CP, Chen GF, Zhang GP (2020) A comparative investigation of long-term oxidation behavior of selective laser melting-fabricated Inconel 718 at 650 °C. J Mater Res 35:2036–2045. https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2020.98
Cao Y, Bai P, Liu F, Hou X, Guo Y (2020) Effect of the solution temperature on the precipitates and grain evolution of IN718 fabricated by laser additive manufacturing. Materials (Basel) 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13020340
Samuel C, Arivarasu M, Prabhu TR (2020) High temperature dry sliding wear behaviour of laser powder bed fused Inconel 718. Addit Manuf 34101279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2020.101279.
Gao Y, Zhang D, Cao M, Chen R, Feng Z, Poprawe R, Schleifenbaum JH, Ziegler S (2019) Effect of δ phase on high temperature mechanical performances of Inconel 718 fabricated with SLM process. Mater Sci Eng A 767:138327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2019.138327
Li X, Shi JJ, Cao GH, Russell AM, Zhou ZJ, Li CP, Chen GF (2019) Improved plasticity of Inconel 718 superalloy fabricated by selective laser melting through a novel heat treatment process. Mater Des 180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2019.107915
Li X, Shi JJ, Wang CH, Cao GH, Russell AM, Zhou ZJ, Li CP, Chen GF (2018) Effect of heat treatment on microstructure evolution of Inconel 718 alloy fabricated by selective laser melting. J Alloys Compd 764:639–649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.06.112
Pei C, Shi D, Yuan H, Li H (2019) Assessment of mechanical properties and fatigue performance of a selective laser melted nickel-base superalloy Inconel 718. Mater Sci Eng A 759:278–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2019.05.007
Calandri M, Yin S, Aldwell B, Calignano F, Lupoi R, Ugues D (2019) Texture and microstructural features at different length scales in Inconel 718 produced by selective laser melting. Materials (Basel) 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12081293
Wan HY, Zhou ZJ, Li CP, Chen GF, Zhang GP (2019) Effect of scanning strategy on mechanical properties of selective laser melted Inconel 718. Mater Sci Eng A 753:42–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2019.03.007
Song H, McGaughy T, Sadek A, Zhang W (2019) Effect of structural support on microstructure of nickel base superalloy fabricated by laser-powder bed fusion additive manufacturing. Addit Manuf 26:30–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2018.12.017
Gribbin S, Ghorbanpour S, Ferreri NC, Bicknell J, Tsukrov I, Knezevic M (2019) Role of grain structure, grain boundaries, crystallographic texture, precipitates, and porosity on fatigue behavior of Inconel 718 at room and elevated temperatures. Mater Charact 149:184–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2019.01.028
Wang LY, Zhou ZJ, Li CP, Chen GF, Zhang GP (2019) Comparative investigation of small punch creep resistance of Inconel 718 fabricated by selective laser melting. Mater Sci Eng A 745:31–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.12.083
Tao P, Li H, Huang B, Hu Q, Gong S, Xu Q (2019) The crystal growth, intercellular spacing and microsegregation of selective laser melted Inconel 718 superalloy. Vacuum 159:382–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2018.10.074
Wan HY, Zhou ZJ, Li CP, Chen GF, Zhang GP (2018) Enhancing fatigue strength of selective laser melting-fabricated Inconel 718 by tailoring heat treatment route. Adv Eng Mater 20:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.201800307
Wan HY, Zhou ZJ, Li CP, Chen GF, Zhang GP (2018) Effect of scanning strategy on grain structure and crystallographic texture of Inconel 718 processed by selective laser melting. J Mater Sci Technol 34:1799–1804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2018.02.002
Gu D, Shi Q, Lin K, Xi L (2018) Microstructure and performance evolution and underlying thermal mechanisms of Ni-based parts fabricated by selective laser melting. Addit Manuf 22:265–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2018.05.019
Gribbin S, Bicknell J, Jorgensen L, Tsukrov I, Knezevic M (2016) Low cycle fatigue behavior of direct metal laser sintered Inconel alloy 718. Int J Fatigue 93:156–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2016.08.019
Vieille B, Keller C, Mokhtari M, Briatta H, Breteau T, Nguejio J, Barbe F, Azzouna MB, Baustert E (2020) Investigations on the fracture behavior of Inconel 718 superalloys obtained from cast and additive manufacturing processes. Mater Sci Eng A 790:139666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2020.139666
Ardi DT, Guowei L, Maharjan N, Mutiargo B, Leng SH, Srinivasan R (2020) Effects of post-processing route on fatigue performance of laser powder bed fusion Inconel 718. Addit Manuf 36:101442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2020.101442
Fayed EM, Shahriari D, Saadati M, Brailovski V, Jahazi M, Medraj M (2020) Influence of homogenization and solution treatments time on the microstructure and hardness of Inconel 718 fabricated by laser powder bed fusion process. Materials (Basel) 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13112574
Li Y, Zhang Z, Guan Y (2020) Thermodynamics analysis and rapid solidification of laser polished Inconel 718 by selective laser melting. Appl Surf Sci 511:145423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.145423
Kuo YL, Nagahari T, Kakehi K (2018) The effect of post-processes on the microstructure and creep properties of Alloy718 built up by selective laser melting. Materials (Basel) 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11060996
Zhao Y, Li K, Gargani M, Xiong W (2020) A comparative analysis of Inconel 718 made by additive manufacturing and suction casting: microstructure evolution in homogenization. Addit Manuf 36:101404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2020.101404
Kim S, Choi H, Lee J, Kim S (2020) Room and elevated temperature fatigue crack propagation behavior of Inconel 718 alloy fabricated by laser powder bed fusion. Int J Fatigue 140:105802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2020.105802
Hazeli K, Babamiri BB, Indeck J, Minor A, Askari H (2019) Microstructure-topology relationship effects on the quasi-static and dynamic behavior of additively manufactured lattice structures. Mater Des 176:107826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2019.107826
Jiang R, Mostafaei A, Pauza J, Kantzos C, Rollett AD (2019) Varied heat treatments and properties of laser powder bed printed Inconel 718. Mater Sci Eng A 755:170–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2019.03.103
Zhao JR, Hung FY, Lui TS (2020) Microstructure and tensile fracture behavior of three-stage heat treated inconel 718 alloy produced via laser powder bed fusion process. J Mater Res Technol 9:3357–3367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.01.030
Wang LY, Wang YC, Zhou ZJ, Wan HY, Li CP, Chen GF, Zhang GP (2020) Small punch creep performance of heterogeneous microstructure dominated Inconel 718 fabricated by selective laser melting. Mater Des 195:109042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2020.109042
Delcuse L, Bahi S, Gunputh U, Rusinek A, Wood P, Miguelez MH (2020) Effect of powder bed fusion laser melting process parameters, build orientation and strut thickness on porosity, accuracy and tensile properties of an auxetic structure in IN718 alloy. Addit Manuf 36:101339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2020.101339
Georgilas K, Khan RHU, Kartal ME (2020) The influence of pulsed laser powder bed fusion process parameters on Inconel 718 material properties. Mater Sci Eng A 769:138527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2019.138527
Yang H, Meng L, Luo S, Wang Z (2020) Microstructural evolution and mechanical performances of selective laser melting Inconel 718 from low to high laser power. J Alloys Compd 828:154473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154473
Wang Z, Guan K, Gao M, Li X, Chen X, Zeng X (2012) The microstructure and mechanical properties of deposited-IN718 by selective laser melting. J Alloys Compd 513:518–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.10.107
Luo S, Huang W, Yang H, Yang J, Wang Z, Zeng X (2019) Microstructural evolution and corrosion behaviors of Inconel 718 alloy produced by selective laser melting following different heat treatments. Addit Manuf 30:100875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2019.100875
Yang H, Yang J, Huang W, Jing G, Wang Z, Zeng X (2019) Controllable in-situ aging during selective laser melting: stepwise precipitation of multiple strengthening phases in Inconel 718 alloy. J Mater Sci Technol 35:1925–1930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2019.05.024
Popovich VA, Borisov EV, Popovich AA, Sufiiarov VS, Masaylo DV, Alzina L (2017) Impact of heat treatment on mechanical behaviour of inconel 718 processed with tailored microstructure by selective laser melting. Mater Des 131:12–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.05.065
Popovich VA, Borisov EV, Popovich AA, Sufiiarov VS, Masaylo DV, Alzina L (2017) Functionally graded Inconel 718 processed by additive manufacturing: crystallographic texture, anisotropy of microstructure and mechanical properties. Mater Des 114:441–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.10.075
Zhang D, Niu W, Cao X, Liu Z (2015) Effect of standard heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of selective laser melting manufactured inconel 718 superalloy. Mater Sci Eng A 644:32–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2015.06.021
Popovich AA, Sufiiarov VS, Polozov IA, Borisov EV (2015) Microstructure and mechanical properties of Inconel 718 produced by SLM and subsequent heat treatment. Key Eng Mater 651–653:665–670. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.651-653.665
Tillmann W, Schaak C, Nellesen J, Schaper M, Aydinöz ME, Hoyer KP (2017) Hot isostatic pressing of IN718 components manufactured by selective laser melting. Addit Manuf 13:93–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2016.11.006
Pröbstle M, Neumeier S, Hopfenmüller J, Freund LP, Niendorf T, Schwarze D, Göken M (2016) Superior creep strength of a nickel-based superalloy produced by selective laser melting. Mater Sci Eng A 674:299–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.07.061
Yao X, Moon SK, Lee BY, Bi G (2017) Effects of heat treatment on microstructures and tensile properties of IN718/TiC nanocomposite fabricated by selective laser melting. Int J Precis Eng Manuf 18:1693–1701. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-017-0197-y
Watring DS, Benzing JT, Hrabe N, Spear AD (2020) Effects of laser-energy density and build orientation on the structure–property relationships in as-built inconel 718 manufactured by laser powder bed fusion. Addit Manuf 36:101425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2020.101425
Wang X, Kang J, Wang T, Wu P, Feng T, Zheng L (2019) Effect of layer-wise varying parameters on the microstructure and soundness of selective laser melted Inconel 718 alloy. Materials (Basel) 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12132165
Rezaei A, Rezaeian A, Kermanpur A, Badrossamay M, Foroozmehr E, Marashi M, Foroozmehr A, Han J (2020) Microstructural and mechanical anisotropy of selective laser melted IN718 superalloy at room and high temperatures using small punch test. Mater Charact 162:110200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2020.110200
Amirjan M, Sakiani H (2019) Effect of scanning strategy and speed on the microstructure and mechanical properties of selective laser melted IN718 nickel-based superalloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 103:1769–1780. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03545-0
Yi JH, Kang JW, Wang TJ, Wang X, Hu YY, Feng T, Feng YL, Wu PY (2019) Effect of laser energy density on the microstructure, mechanical properties, and deformation of Inconel 718 samples fabricated by selective laser melting. J Alloys Compd 786:481–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.01.377
Chlebus E, Gruber K, Kuźnicka B, Kurzac J, Kurzynowski T (2015) Effect of heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Inconel 718 processed by selective laser melting. Mater Sci Eng A 639:647–655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2015.05.035
Pérez-Ruiz JD, de Lacalle LN, Urbikain G, Pereira O, Martínez S, Bris J (2021) On the relationship between cutting forces and anisotropy features in the milling of LPBF Inconel 718 for near net shape parts. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2021.103801
Pérez-Ruiz JD, Marin F, Martínez S, Lamikiz A, Urbikain G, de Lacalle LN (2022) Stiffening near-net-shape functional parts of Inconel 718 LPBF considering material anisotropy and subsequent machining issues. Mech Syst Signal Process 168:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2021.108675
Pauzon C (2019) The process atmosphere as a parameter in the laser-powder bed fusion process. Chalmers University of Technology
Gallmeyer TG, Moorthy S, Kappes BB, Mills MJ, Amin-Ahmadi B, Stebner AP (2020) Knowledge of process-structure-property relationships to engineer better heat treatments for laser powder bed fusion additive manufactured Inconel 718. Addit Manuf 31:100977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2019.100977
Ho IT, Hsu TH, Chang YJ, Li CW, Chang KC, Tin S, Kakehi K, Yeh AC (2020) Effects of CoAl2O4 inoculants on microstructure and mechanical properties of IN718 processed by selective laser melting. Addit Manuf 35:101328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2020.101328
Zhao Y, Guo Q, Ma Z, Yu L (2020) Comparative study on the microstructure evolution of selective laser melted and wrought IN718 superalloy during subsequent heat treatment process and its effect on mechanical properties. Mater Sci Eng A 791:139735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2020.139735
Dunbar AJ, Denlinger ER, Gouge MF, Simpson TW, Michaleris P (2017) Comparisons of laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing builds through experimental in situ distortion and temperature measurements. Addit Manuf 15:57–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2017.03.003
Nezhadfar PD, Soltani-Tehrani A, Shamsaei N (2019) Effect of preheating build platform on microstructure and mechanical properties of additively manufactured 316L stainless steel. In 2019 International Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium pp 415–425
Wang X, Keya T, Chou K (2016) Build height effect on the Inconel 718 parts fabricated by selective laser melting. Procedia Manuf 5:1006–1017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2016.08.089
Cao Y, Bai P, Liu F, Hou X (2019) Investigation on the precipitates of IN718 alloy fabricated by selective laser melting. Metals (Basel) 9:1–10. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9101128
Tucho WM, Hansen V (2019) Characterization of SLM-fabricated Inconel 718 after solid solution and precipitation hardening heat treatments. J Mater Sci 54:823–839. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2851-x
Park E, Kim DM, Park HW, Park YB, Kim N (2020) Evaluation of tool life in the dry machining of Inconel 718 parts from additive manufacturing (AM). Int J Precis Eng Manuf 21:57–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-019-00275-x
Schneider J, Lund B, Fullen M (2018) Effect of heat treatment variations on the mechanical properties of Inconel 718 selective laser melted specimens. Addit Manuf 21:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2018.03.005
Kuo YL, Kakehi K (2017) Influence of powder surface contamination in the Ni-based superalloy alloy718 fabricated by selective laser melting and hot isostatic pressing. Metals (Basel) 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7090367
Kuo YL, Horikawa S, Kakehi K (2017) The effect of interdendritic δ phase on the mechanical properties of alloy 718 built up by additive manufacturing. Mater Des 116:411–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.12.026
Babamiri BB, Indeck J, Demeneghi G, Cuadra J, Hazeli K (2020) Quantification of porosity and microstructure and their effect on quasi-static and dynamic behavior of additively manufactured Inconel 718. Addit Manuf 34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2020.101380
Khairallah SA, Anderson AT, Rubenchik A, King WE (2016) Laser powder-bed fusion additive manufacturing: physics of complex melt flow and formation mechanisms of pores, spatter, and denudation zones. Acta Mater 108:36–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2016.02.014
Bean GE, Witkin DB, McLouth TD, Zaldivar RJ (2020) Process gas influence on microstructure and mechanical behavior of Inconel 718 fabricated via selective laser melting. Prog Addit Manuf 5:405–417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40964-020-00133-7
Varela J, Merino J, Pickett C, Abu-Issa A, Arrieta E, Murr LE, Wicker RB, Ahlfors M, Godfrey D, Medina F (2020) Performance characterization of laser powder bed fusion fabricated Inconel 718 treated with experimental hot isostatic processing cycles. J Manuf Mater Process 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/JMMP4030073
Newell DJ, O’Hara RP, Cobb GR, Palazotto AN, Kirka MM, Burggraf LW, Hess JA (2019) Mitigation of scan strategy effects and material anisotropy through supersolvus annealing in LPBF IN718. Mater Sci Eng A 764:138230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2019.138230
Zhou L, Mehta A, McWilliams B, Cho K, Sohn Y (2019) Microstructure, precipitates and mechanical properties of powder bed fused Inconel 718 before and after heat treatment. J Mater Sci Technol 35:1153–1164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2018.12.006
Sabelkin VP, Cobb GR, Doane BM, Kemnitz RA, O’Hara RP (2020) Torsional behavior of additively manufactured nickel alloy 718 under monotonic loading and low cycle fatigue. Mater Today Commun 24:101256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.101256
McLouth TD, Witkin DB, Bean GE, Sitzman SD, Adams PM, Lohser JR, Yang JM, Zaldivar RJ (2020) Variations in ambient and elevated temperature mechanical behavior of IN718 manufactured by selective laser melting via process parameter control. Mater Sci Eng A 780:139184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2020.139184
Lu Y, Wu S, Gan Y, Huang T, Yang C, Junjie L, Lin J (2015) Study on the microstructure, mechanical property and residual stress of SLM Inconel-718 alloy manufactured by differing island scanning strategy. Opt Laser Technol 75:197–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2015.07.009
Jia H, Sun H, Wang H, Wu Y, Wang H (2021) Scanning strategy in selective laser melting (SLM): a review. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 113:2413–2435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-06810-3
Carter LN, Martin C, Withers PJ, Attallah MM (2014) The influence of the laser scan strategy on grain structure and cracking behaviour in SLM powder-bed fabricated nickel superalloy. J Alloys Compd 615:338–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.06.172
Sutton B, Herderick E, Thodla R, Ahlfors M, Ramirez A (2019) Heat treatment of alloy 718 made by additive manufacturing for oil and gas applications. Jom 71:1134–1143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-018-03321-7
Sabelkin VP, Cobb GR, Shelton TE, Hartsfield MN, Newell DJ, O’Hara RP, Kemnitz RA (2019) Mitigation of anisotropic fatigue in nickel alloy 718 manufactured via selective laser melting. Mater Des 182:108095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2019.108095
Bremen S, Meiners W, Diatlov A (2012) Selective laser melting: a manufacturing technology for the future? Laser Tech J 9:33–38. https://doi.org/10.1002/latj.201290018
Yang K, Huang Q, Wang Q, Chen Q (2020) Competing crack initiation behaviors of a laser additively manufactured nickel-based superalloy in high and very high cycle fatigue regimes. Int J Fatigue 136:105580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2020.105580
Materials A (2020) Nickel alloy inconel 718 - properties and applications by United Performance Metals. https://www.azom.com/article.aspx?ArticleID=4459. Accessed 20 Apr 2021
Bean GE, Witkin DB, McLouth TD, Patel DN, Zaldivar RJ (2018) Effect of laser focus shift on surface quality and density of Inconel 718 parts produced via selective laser melting. Addit Manuf 22:207–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2018.04.024
Schaak C, Tillmann W, Schaper M, Aydinöz ME (2016) Process gas infiltration in Inconel 718 samples during SLM processing. RTe Journal Fachforum Für Rapid Technol 1–8
Gibson LJ, Ashby MF, Schajer GS, Robertson CI (1982) The mechanics of two-dimensional cellular material 348(19AD):101–127
Calleja-Ochoa A, Gonzalez-barrio H, de Lacalle NL, Martínez S, Albizuri J, Lamikiz A (2021) A new approach in the design of microstructured ultralight components to achieve maximum functional performance. Materials (Basel) 14:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14071588
Zhou X, Liu X, Zhang D, Shen Z, Liu W (2015) Balling phenomena in selective laser melted tungsten. J Mater Process Technol 222:33–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2015.02.032
Huang W, Yang J, Yang H, Jing G, Wang Z, Zeng X (2019) Heat treatment of Inconel 718 produced by selective laser melting: microstructure and mechanical properties. Mater Sci Eng A 750:98–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2019.02.046
Cao Y, Farouk N, Taheri M, Yumashev AV, Bozorg SFK, Ojo OO (2021) Evolution of solidification and microstructure in laser-clad IN625 superalloy powder on GTD-111 superalloy. Surf Coatings Technol 412:127010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.127010
Lee J, Lee M, Jung ID, Choe J, Yu J-H, Kim S, Sung H (2020) Correlation between microstructure and tensile properties of STS 316L and Inconel 718 fabricated by selective laser melting (SLM). J Nanosci Nanotechnol 20:6807–6814. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2020.18792
Nguyen QB, Luu DN, Nai SML, Zhu Z, Chen Z, Wei J (2018) The role of powder layer thickness on the quality of SLM printed parts. Arch Civ Mech Eng 18:948–955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acme.2018.01.015
Chen Z, Yan X, Yin S, Liu L, Liu X, Zhao G, Ma W, Qi W, Ren Z, Liao H, Liu M, Cai D, Fang H (2020) Influence of the pore size and porosity of selective laser melted Ti6Al4V ELI porous scaffold on cell proliferation, osteogenesis and bone ingrowth. Mater Sci Eng C 106:110289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.110289
Nguyen QB, Zhu Z, Chua BW, Zhou W, Wei J, Nai SML (2018) Development of WC-Inconel composites using selective laser melting. Arch Civ Mech Eng 18:1410–1420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acme.2018.05.001
Wan HY, Luo YW, Zhang B, Song ZM, Wang LY, Zhou ZJ, Li CP, Chen GF, Zhang GP (2020) Effects of surface roughness and build thickness on fatigue properties of selective laser melted Inconel 718 at 650 °C. Int J Fatigue 137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2020.105654.
Soffel F, Eisenbarth D, Hosseini E, Wegener K (2021) Interface strength and mechanical properties of Inconel 718 processed sequentially by casting, milling, and direct metal deposition. J Mater Process Technol 291:117021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2020.117021
Brenne F, Taube A, Pröbstle M, Neumeier S, Schwarze D, Schaper M, Niendorf T (2016) Microstructural design of Ni-base alloys for high-temperature applications : impact of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties after selective laser melting 141–151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40964-016-0013-8
Pereira JC, Aranzabe J, Taboada MC, Ruiz N, Rodriguez PP (2021) Analysis of microstructure and mechanical properties in as-built/as-cast and heat-treated conditions for in718 alloy obtained by selective laser melting and investment casting processes. Crystals 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11101196
Liu F, Lin X, Song M, Zhao W, Chen J, Huang W (2011) Effect of intermediate heat treatment temperature on microstructure and notch sensitivity of laser solid formed Inconel 718 superalloy. J Wuhan Univ Technol Mater Sci Ed 26:908–913. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-011-0335-9
Kouraytem N, Chanut RA, Watring DS, Loveless T, Varga J, Spear AD, Kingstedt OT (2020) Dynamic-loading behavior and anisotropic deformation of pre- and post-heat-treated IN718 fabricated by laser powder bed fusion. Addit Manuf 33:101083. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2020.101083
Ni M, Chen C, Wang X, Wang P, Li R, Zhang X, Zhou K (2017) Anisotropic tensile behavior of in situ precipitation strengthened Inconel 718 fabricated by additive manufacturing. Mater Sci Eng A 701:344–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.06.098
Stevens EL, Toman J, To AC, Chmielus M (2017) Variation of hardness, microstructure, and Laves phase distribution in direct laser deposited alloy 718 cuboids. Mater Des 119:188–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.01.031
Tian Y, McAllister D, Colijn H, Mills M, Farson D, Nordin M, Babu S (2014) Rationalization of microstructure heterogeneity in INCONEL 718 builds made by the direct laser additive manufacturing process. Metall Mater Trans A Phys Metall Mater Sci 45:4470–4483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2370-6
Kreitcberg A, Brailovski V, Turenne S (2017) Effect of heat treatment and hot isostatic pressing on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Inconel 625 alloy processed by laser powder bed fusion. Mater Sci Eng A 689:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.02.038
Bin MH (2012) Homogenization heat treatment to reduce the failure of heat resistant steel castings. Metall - Adv Mater Process. https://doi.org/10.5772/50312
Fayed EM, Saadati M, Shahriari D, Brailovski V, Jahazi M, Medraj M (2021) Effect of homogenization and solution treatments time on the elevated-temperature mechanical behavior of Inconel 718 fabricated by laser powder bed fusion. Sci Rep 11:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-81618-5
Laquai R, Müller BR, Schneider JA, Kupsch A, Bruno G (2020) Using SXRR to probe the nature of discontinuities in SLM additive manufactured Inconel 718 specimens. Metall Mater Trans A Phys Metall Mater Sci 51:4146–4157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-020-05847-5
Ma M, Wang Z, Zeng X (2015) Effect of energy input on microstructural evolution of direct laser fabricated IN718 alloy. Mater Charact 106:420–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2015.06.027
Xia M, Gu D, Yu G, Dai D, Chen H, Shi Q (2016) Selective laser melting 3D printing of Ni-based superalloy: understanding thermodynamic mechanisms. Sci Bull 61:1013–1022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-016-1098-7
Xu Z, Hyde CJ, Tuck C, Clare AT (2018) Creep behaviour of inconel 718 processed by laser powder bed fusion. J Mater Process Technol 256:13–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.01.040
Shi JJ, Li X, Zhang ZX, Cao GH, Russell AM, Zhou ZJ, Li CP, Chen GF (2019) Study on the microstructure and creep behavior of Inconel 718 superalloy fabricated by selective laser melting. Mater Sci Eng A 765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2019.138282
Witkin DB, Patel D, Albright TV, Bean GE, McLouth T (2020) Influence of surface conditions and specimen orientation on high cycle fatigue properties of Inconel 718 prepared by laser powder bed fusion. Int J Fatigue 132:105392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2019.105392
Lamikiz A, Sanchez JA, Lopez de Lacalle LN, del Pozo D, Etayo JM, López JM (2007) Laser polishing techniques for roughness improvement on metallic surfaces. Int J Nanomanuf 1:490–498. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJNM.2007.014568
Rodríguez A, López de Lacalle LN, Celaya A, Lamikiz A, Albizuri J (2012) Surface improvement of shafts by the deep ball-burnishing technique. Surf Coatings Technol 206:2817–2824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2011.11.045
Mordyuk BN, Milman YV, Iefimov MO, Prokopenko GI, Silberschmidt VV, Danylenko MI, Kotko AV (2008) Characterization of ultrasonically peened and laser-shock peened surface layers of AISI 321 stainless steel. Surf Coatings Technol 202:4875–4883. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2008.04.080
Lesyk D, Martinez S, Mordyuk B, Dzhemelinskyi V, Danyleiko O (2019) Combined laser-ultrasonic surface hardening process for improving the properties of metallic products. Lect Notes Mech Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-93587-4_11
Lesyk DA, Martinez S, Mordyuk BN, Dzhemelinskyi VV, Lamikiz A, Prokopenko GI, Grinkevych KE, Tkachenko IV (2018) Laser-hardened and ultrasonically peened surface layers on tool steel AISI D2: correlation of the bearing curves’ parameters, hardness and wear. J Mater Eng Perform 27:764–776. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-017-3107-7
Lesyk DA, Martinez S, Mordyuk BN, Dzhemelinskyi VV (2017) Microstructure related enhancement in wear resistance of tool steel AISI D2 by applying laser heat treatment followed by ultrasonic impact treatment. Surf Coatings Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2017.08.045
Nasab MH, Gastaldi D, Lecis NF, Vedani M (2018) On morphological surface features of the parts printed by selective laser melting (SLM). Addit Manuf 24:373–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2018.10.011
Maawad E, Brokmeier HG, Wagner L, Sano Y, Genzel C (2011) Investigation on the surface and near-surface characteristics of Ti-2.5Cu after various mechanical surface treatments. Surf Coatings Technol 205:3644–3650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2011.01.001
Li K, Ma R, Zhang M, Chen W, Li X, Zhang DZ, Tang Q, Murr LE, Li J, Cao H (2022) Hybrid post-processing effects of magnetic abrasive finishing and heat treatment on surface integrity and mechanical properties of additively manufactured Inconel 718 superalloys. J Mater Sci Technol 128:10–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2022.03.026
Baicheng Z, Xiaohua L, Jiaming B, Junfeng G, Pan W, Chen-nan S, Muiling N, Guojun Q, Jun W (2017) Study of selective laser melting (SLM) Inconel 718 part surface improvement by electrochemical polishing. Mater Des 116:531–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.11.103
Kaynak Y, Tascioglu E (2018) Finish machining-induced surface roughness, microhardness and XRD analysis of selective laser melted Inconel 718 alloy. Procedia CIRP 71:500–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2018.05.013
Chen Y, Lu F, Zhang K, Nie P, Hosseini SR, Feng K, Li Z (2016) Dendritic microstructure and hot cracking of laser additive manufactured Inconel 718 under improved base cooling. J Alloys Compd 670:312–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.01.250
Xin B, Ren J, Wang X, Zhu L, Gong Y (2020) Effect of laser remelting on cladding layer of Inconel 718 superalloy formed by laser metal deposition. Materials (Basel) 13:1–13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13214927
Hakeem AS, Patel F, Minhas N, Malkawi A, Aleid Z, Ehsan MA, Sharrofna H, Al Ghanim A (2021) Comparative evaluation of thermal and mechanical properties of nickel alloy 718 prepared using selective laser melting, spark plasma sintering, and casting methods. J Mater Res Technol 12:870–881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.03.043
Sutton GP, Ross DM, Biblarz O (2001) Rocket propulsion elements. 7th ed., John Wiley & Sons
Pizzarelli M (n. d.) Regenerative cooling of liquid rocket engine thrust chambers. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/321314974_Regenerative_cooling_of_liquid_rocket_engine_thrust_chambers. Accessed 12 Feb 2022
Choi JP, Shin GH, Yang S, Yang DY, Lee JS, Brochu M, Yu JH (2017) Densification and microstructural investigation of Inconel 718 parts fabricated by selective laser melting. Powder Technol 310:60–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2017.01.030
Kakehi K, Banoth S, Kuo YL, Hayashi S (2020) Effect of yttrium addition on creep properties of a Ni-base superalloy built up by selective laser melting. Scr Mater 183:71–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.03.014
Majchrowicz K, Pakieła Z, Kamiński J, Płocińska M, Kurzynowski T, Chlebus E (2018) The effect of rhenium addition on microstructure and corrosion resistance of Inconel 718 processed by selective laser melting. Metall Mater Trans A Phys Metall Mater Sci 49:6479–6489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-018-4926-3
Tabaie S, Rézaï-Aria F, Jahazi M (2020) Microstructure evolution of selective laser melted Inconel 718: influence of high heating rates. Metals (Basel) 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10050587
Barros R, Silva FJ, Gouveia RM, Saboori A, Marchese G, Biamino S, Salmi A, Atzeni E (2019) Laser powder bed fusion of Inconel 718: residual stress analysis before and after heat treatment. Metals (Basel) 9:1290–1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9121290
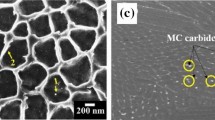
Ferreri NC, Vogel SC, Knezevic M (2020) Determining volume fractions of γ, γ′, γ″, δ, and MC-carbide phases in Inconel 718 as a function of its processing history using an advanced neutron diffraction procedure. Mater Sci Eng A 781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2020.139228
Kaynak Y, Tascioglu E (2020) Post-processing effects on the surface characteristics of Inconel 718 alloy fabricated by selective laser melting additive manufacturing. Prog Addit Manuf 5:221–234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40964-019-00099-1
Wang X, Chou K (2019) The effects of stress relieving heat treatment on the microstructure and residual stress of Inconel 718 fabricated by laser metal powder bed fusion additive manufacturing process. J Manuf Process 48:154–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2019.10.027
Watring DS, Carter KC, Crouse D, Raeymaekers B, Spear AD (2019) Mechanisms driving high-cycle fatigue life of as-built Inconel 718 processed by laser powder bed fusion. Mater Sci Eng A 761:137993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2019.06.003
Funding
This work was supported by FCT national funds, under the national support to R&D unit grant, through the reference projects UIDB/04436/2020 and UIDP/04436/2020, and by the grant number SFRH/BD/148031/2019 and the project Add: additive - add additive manufacturing to Portuguese industry (grant number POCI-01–0247-FEDER-024533).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A. Marques: methodology, investigation, writing – original draft, visualization. A. Cunha: methodology, writing – review and editing, investigation. M. Silva: methodology, writing – review and editing. M. Osendi: visualization, supervision. F.S. Silva: conceptualization, supervision. O. Carvalho: conceptualization, writing – review and editing, supervision. F. Bartolomeu: methodology, writing – review and editing, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
The authors declare that all authors have read and approved to submit this manuscript to IJAMT.
Consent for publication
The authors declare that all authors agree to sign the transfer of copyright for the publisher to publish this article upon on acceptance.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marques, A., Cunha, Â., Silva, M.R. et al. Inconel 718 produced by laser powder bed fusion: an overview of the influence of processing parameters on microstructural and mechanical properties. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 121, 5651–5675 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-09693-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-09693-0