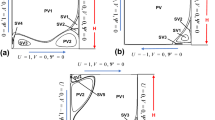
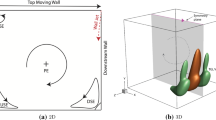
Abstract
Primary instability of the lid-driven flow in a cube is studied by a linear stability approach. Two cases, in which the lid moves parallel to the cube sidewall or parallel to the diagonal plane, are considered. It is shown that Krylov vectors required for application of the Newton and Arnoldi iteration methods can be evaluated by the SIMPLE procedure. The finite volume grid is gradually refined from \(100^{3}\) to \(256^{3}\) nodes. The computations result in grid converging values of the critical Reynolds number and oscillation frequency that allow for Richardson extrapolation to the zero grid size. Three-dimensional flow and most unstable perturbations are visualized by a recently proposed approach that allows for a better insight into the flow patterns and appearance of the instability. New arguments regarding the assumption that the centrifugal mechanism triggers the instability are given for both cases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shankar, P.N., Deshpande, M.D.: Fluid mechanics in the driven cavity. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 32, 93–136 (2000)
Kuhlmann, H.C., Romano F.: The lid-driven cavity. In: Computational Modelling of Bifurcations and Instabilities in Fluid Dynamics. In: A. Gelfgat (ed.) Springer, Berlin (2018)
Deshmuck, R., McNamara, J.J., Liang, Z., Kolter, J.Z., Abhijit, G.: Model order reduction using sparse coding exemplified for the lid-driven cavity. J. Fluid Mech. 808, 189–223 (2016)
Kalita, J.C., Gogoi, B.B.: A biharmonic approach for the global stability analysis of 2D incompressible viscous flows. Appl. Math Model. 40, 6831–6849 (2016)
Nuriev, A.N., Egorov, A.G., Zaitseva, O.N.: Bifurcation analysis of steady-state flows in the lid-driven cavity. Fluid Dyn. Res. 48, 061405 (2016)
Babu, V., Korpela, S.A.: Numerical solution of the incompressible, three-dimensional Navier–Stokes equations. Comput. Fluids 23, 675–691 (1994)
Albensoeder, S., Kuhlmann, H.C.: Accurate three-dimensional lid-driven cavity flow. J. Comput. Phys. 206, 536–558 (2006)
Liberzon, A., Feldman, Y., Gelfgat, A.Y.: Experimental observation of the steady—oscillatory transition in a cubic lid-driven cavity. Phys. Fluids 23, 084106 (2011)
Feldman, Y., Gelfgat, A.Y.: On pressure-velocity coupled time-integration of incompressible Navier–Stokes equations using direct inversion of Stokes operator or accelerated multigrid technique. Comput. Struct. 87, 710–720 (2009)
Feldman, Y., Gelfgat, A.Y.: Oscillatory instability of a 3D lid-driven flow in a cube. Phys. Fluids 22, 093602 (2010)
Hammami, F., Ben-Cheikh, N., Campo, A., Ben-Beya, B., Lili, T.: Prediction of unsteady states in lid-driven cavities filled with an incompressible viscous fluid. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 23, 1250030 (2012)
Mynam, M., Pathak, A.D.: Lattice Boltzmann simulation of steady and oscillatory flows in lid-driven cubic cavity. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 24, 1350005 (2013)
Chang, H.W., Hong, P.Y., Lin, L.S., Lin, C.A.: Simulations of flow instability in three dimensional deep cavities with multi relaxation time lattice Boltzmann method on graphic processing units. Comput. Fluids 88, 866–871 (2013)
Kuhlmann, H.C., Albensoeder, S.: Stability of the steady three-dimensional lid-driven flow in a cube and the supercritical flow dynamics. Phys. Fluids 26, 024104 (2014)
Anupindi, K., Lai, W., Frankel, S.: Characterization of oscillatory instability in lid driven cavity flows using lattice Boltzmann method. Comput. Fluids 92, 7–21 (2014)
Loiseau, J.C., Robinet, J.C., Leriche, E.: Intermittency and transition to chaos in the cubical lid-driven cavity flow. Fluid Dyn. Res. 48, 061421 (2016)
Gómez, F., Gómez, R., Theofilis, V.: On three-dimensional global linear instability analysis of flows with standard aerodynamics codes. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 32, 223–234 (2014)
Lopez, J.M., Welfert, B.D., Wu, K., Yalim, J.: Transitions to complex dynamics in the cubic lid-driven cavity. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2, 074401 (2017)
Povitsky, A.: High-incidence 3-D lid-driven cavity flow. AIAA Paper, 2847 (2001)
Povitsky, A.: Three-dimensional flow in cavity at yaw. Nonlinear Anal. Theory Methods Appl. 63, e1573–e1584 (2005)
Feldman, Y., Gelfgat, A.Y.: From multi- to single-grid CFD on massively parallel computers: numerical experiments on lid-driven flow in a cube using pressure-velocity coupled formulation. Comput. Fluids 46, 218–223 (2011)
Feldman, Y.: Theoretical analysis of three-dimensional bifurcated flow inside a diagonally lid-driven cavity. Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 29, 245–261 (2015)
Gulberg, Y., Feldman, Y.: On laminar natural convection inside multi-layered spherical shells. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 91, 908–921 (2015)
Gelfgat, A.Y.: Visualization of three-dimensional incompressible flows by quasi-two-dimensional divergence-free projections. Comput. Fluids 97, 143–155 (2014)
Gelfgat, A.Y.: Visualization of three-dimensional incompressible flows by quasi-two-dimensional divergence-free projections in arbitrary flow regions. Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 30, 339–348 (2016)
Patankar, S.V.: Numerical Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow. Taylor & Francis, London (1980)
van der Vorst, H.: Iterative Krylov Methods for Large Linear Systems. Cambridge Univ Press, Cambridge (2003)
Bayly, B.J.: Three-dimensional centrifugal-type instabilities in inviscid two-dimensional flows. Phys. Fluids 31, 56–64 (1988)
Lanzerstorfer, D., Kuhlmann, H.C.: Global stability of the two-dimensional flow over a backward-facing step. J. Fluid Mech. 693, 1–27 (2012)
Albensoeder, S., Kuhlmann, H.C., Rath, H.J.: Three-dimensional centrifugal-flow instabilities in the lid-driven-cavity problem. Phys. Fluids 13, 121–135 (2001)
Feldman, Y.: Direct numerical simulation of transitions and supercritical regimes in confined three-dimensional recirculating flows, Ph.D. Thesis, Tel-Aviv University (2010)
Roache, P.J.: Perspective: a method for uniform reporting of grid refinement studies. J. Fluids Eng. 116, 405–413 (1994)
Sorensen, D.C.: Implicit application of polynomial filters in a k-step Arnoldi method. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 13, 357–385 (1992)
Scott, J.A.: An Arnoldi code for computing selected eigenvalues of sparse real unsymmetric matrices. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 21, 432–475 (1995)
Edwards, W.S., Tuckerman, L.S., Friesner, R.A., Sorensen, D.C.: Krylov methods for the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. J. Comput. Phys. 110, 82–102 (1994)
Tuckerman, L.S., Barkley, D.: Bifurcation analysis for time-steppers. In: Doedel, K., Tuckerman, L. (eds.) Numerical Methods for Bifurcation Problems and Large-Scale Dynamical Systems. IMA Volumes in Mathematics and Its Applications, vol. 119, pp. 453–466. Springer, New York (2000)
Tuckerman, L.S., Bertagnolio, F., Daube, O., Le Quéré, P., Barkley, D.: Stokes preconditioning for the inverse Arnoldi method. In D. Henry, A. Bergeon, Vieweg Göttingen (eds.) Continuation Methods for Fluid Dynamics (Notes on Numerical Fluid Dynamics, 74), pp. 241–255 (2000)
Gelfgat, A.Y.: Krylov-subspace-based steady state and stability solvers for incompressible flows: replacing time steppers and generation of initial guess. In: A. Gelfgat (ed.) Computational Modelling of Bifurcations and Instabilities in Fluid Dynamics. Springer, 2018 (to appear)
Chorin, A.J.: Numerical solution of the Navier–Stokes equations. Math. Comput. 22, 745–762 (1968)
Vitoshkin, H., Gelfgat, A.Y.: On direct inverse of Stokes, Helmholtz and Laplacian operators in view of time-stepper-based Newton and Arnoldi solvers in incompressible CFD. Commun. Comput. Phys. 14, 1103–1119 (2013)
Lynch, R.E., Rice, J.R., Thomas, D.H.: Direct solution of partial differential equations by tensor product methods. Numer. Math. 6, 185–199 (1964)
Gelfgat, A.Y.: Stability of convective flows in cavities: solution of benchmark problems by a low-order finite volume method. Intl. J. Num. Methods Fluids 53, 485–506 (2007)
Gelfgat, A.Y.: Implementation of arbitrary inner product in global Galerkin method for incompressible Navier–Stokes equation. J. Comput. Phys. 211, 513–530 (2006)
Poliashenko, M., Aidun, C,K.: A direct method for computation of simple bifurcations. J. Comput. Phys 121, 246–260 (1995)
Gervais, J.J., Lemelin, D., Pierre, R.: Some experiments with stability analysis of discrete incompressible flows in the lid-driven cavity. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids 24, 477–492 (1997)
Fortin, A., Jardak, M., Gervais, J.J., Pierre, R.: Localization of Hopf bifurcations in fluid flow problems. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids 24, 1185–1210 (1997)
Auteri, F., Parolini, N., Quartapelle, L.: Numerical investigations on the stability of singular driven cavity flow. J. Comput. Phys. 183, 1–25 (2002)
Peng, Y.F., Shiau, Y.H., Hwang, R.R.: Transition in a 2-D lid-driven cavity flow. Comput. Fluids 32, 337–352 (2003)
Abouhamza, A., Pierre, R.: A neutral stability curve for incompressible flows in a rectangular driven cavity. Math. Comput. Model. 38, 141–157 (2003)
Cadou, J.M., Potier-Ferry, M., Cochelin, B.: A numerical method for the computation of bifurcation points in fluid mechanics. Eur. J. Mech. B/Fluids 25, 234–254 (2006)
Sahin, M., Owens, R.G.: A novel fully-implicit finite volume method applied to the lid-driven cavity problem. Part II. Linear stability analysis. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids 42, 79–88 (2003)
Boppana, V.B.L., Gajjar, J.S.B.: Global flow instability in a lid-driven cavity. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids 62, 827–853 (2010)
Tiesinga, G., Wubs, F.W., Veldman, A.E.P.: Bifurcation analysis of incompressible flow in a driven cavity by the Newton–Picard method. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 140, 751–772 (2002)
Kalita, J.C., Gogoi, B.B.: A biharmonic approach for the global stability analysis of 2D incompressible viscous flows. Appl. Math. Model. 40, 6831–6849 (2016)
Gelfgat, A.Y., Molokov, S.: Quasi-two-dimensional convection in a 3D laterally heated box in a strong magnetic field normal to main circulation. Phys. Fluids 23, 034101 (2011)
Brès, C.A., Colonius, T.: Three-dimensional instabilities in compressible flow over open cavities. J. Fluid Mech. 599, 309–339 (2008)
Barkley, D., Gomes, G., Gabriela, M., Henderson, D.: Three-dimensional instability in flow over a backward-facing step. J. Fluid Mech 473, 167–190 (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Vassilis Theofilis.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gelfgat, A.Y. Linear instability of the lid-driven flow in a cubic cavity. Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 33, 59–82 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00162-019-00483-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00162-019-00483-1