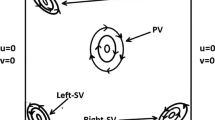
Abstract
This paper reports a numerical investigation of the steady two-dimensional incompressible flow in a three-sided lid-driven cavity of unit aspect ratios (Г = 1). The two opposite horizontal walls move in parallel and antiparallel motions, while the left vertical sidewall moves upwards and downwards. The right vertical sidewall is stationary. A detailed analysis of the fluid flow has been carried out with the finite volume method for a Reynolds number up to 5000 using a fine mesh resolution, whereas the coupled algorithm has been employed to handle the pressure–velocity coupling. The results are displayed in terms of stream-function contours, fluid properties, and velocity profiles and have indicated a good agreement with the set of literature. Among the three driving processes considered, a most complex topological flow pattern has been shown with the antiparallel-downwards case. This is embodied by a significant amount of robustness induced in three opposing directions leading to multiple changes of streamline patterns. This is accompanied by high rotation rates of secondary vortices in the near-wall regions.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Code Availability
Ansys Fluent.
Abbreviations
- H :
-
Physical height of the cavity [m]
- p :
-
Pressure [N m−2]
- Re :
-
Reynolds number
- u, v :
-
Velocity components [m s−1]
- U, V :
-
Dimensionless velocity components
- U 0 :
-
Initial velocity components
- x, y :
-
Cartesian coordinates [m]
- X, Y :
-
Dimensionless coordinates
- α :
-
Under-relaxation factor
- Г :
-
Cavity aspect ratio
- μ :
-
Fluid dynamic viscosity [Pa s]
- ρ :
-
Fluid density [kg/m3]
- ψ :
-
Stream-function [m2/s]
- Ψ :
-
Dimensionless stream-function
- ω :
-
Vorticity [s−1]
- BR:
-
Bottom right secondary vortex
- BL:
-
Bottom left secondary vortex
- CFL:
-
Flow courant number
- PV:
-
Primary vortex
- SV:
-
Secondary vortex
- 1-6:
-
Hierarchy of vortices’ appearance
References
Burggraf, O.R.: Analytical and numerical studies of the structure of steady separated flows. J. Fluid Mech. 24, 113–151 (1966)
Shankar, N., Deshpande, M.D.: Fluid mechanics in the driven cavity. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 32, 93–136 (2000)
Kuhlmann, H.C., Romanò, F.: The lid-driven cavity. In: Gelfgat, A. (ed.) Computational Modelling of Bifurcations and Instabilities in Fluid Dynamics, pp. 233–309. Springer, Cham (2019)
Aidun, C.K., Triantafillopoulos, N.G., Benson, J.D.: Global stability of a lid-driven cavity with throughflow: flow visualization studies. Phys. Fluids A. 3, 2081–2091 (1991)
Malone, B.: An experimental investigation of roll coating phenomena. Ph.D. thesis, University of Leeds (1992)
Leong, C.W., Ottino, J.M.: Experiments on mixing due to chaotic advection in a cavity. J. Fluid Mech. 209, 463–499 (1989)
Alleborn, N., Raszillier, H., Durst, F.: Lid-driven cavity with heat and mass transport. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 42, 833–853 (1999)
Zdanski, P., Ortega, M.A., Nide, G.C.R., Fico, J.R.: Numerical study of the flow over shallow cavities. Comput. Fluids. 32, 953–974 (2003)
Canedo, E.L., Denson, C.D.: Flow in a driven cavity with a free surface. AIChE J. 35, 129–138 (1989)
Ghia, U., Ghia, K.N., Shin, C.: High-Re solutions for incompressible flow using the Navier-Stokes equations and a multigrid method. J. Comput. Phys. 48, 387–411 (1982)
Schreiber, R., Keller, H.: Driven cavity flows by efficient numerical techniques. J. Comput. Phys. 49, 310–333 (1983)
Botella, O., Peyret, R.: Benchmark spectral results on the lid driven cavity flow. Comput. Fluids. 27, 421–433 (1998)
Gupta, M.M., Kalita, J.C.: A new paradigm for solving Navier Stokes equations: streamfunction–velocity formulation. J. Comput. Phys. 207, 52–68 (2005)
Erturk, E.: Discussions on driven cavity flow. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids. 60, 275–294 (2009)
Wahba, E.M.: Steady flow simulations inside a driven cavity up to Reynolds number 35000. Comput. Fluids. 66, 85–97 (2012)
AbelMigid, T.A., Saqr, K.M., Kotb, M.A., Aboelfarag, A.A.: Revisiting the lid-driven cavity flow problem: Review and new steady state benchmarking results using GPU accelerated code. Alex. Eng. J. 56, 123–135 (2016)
Azzouz, E.A., Houat, S., Benhizia, O.: Numerical study of steady flow inside a lid-driven square cavity for Reynolds number up to 50000, 23eme Congès Français de Mécanique, Lille, Aug. 2017, France.
Ramanan, N., Homsy, G.M.: Linear stability of lid-driven cavity flow. Phys. Fluids. 6, 2690–2701 (1994)
Ding, Y., Kawahara, M.: Linear stability of incompressible fluid flow in a cavity using finite element method. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids. 27, 139–157 (1998)
Albensoeder, S., Kuhlmann, H.C., Rath, H.J.: Three-dimensional centrifugal-flow instabilities in the lid-driven cavity problem. Phys. Fluids 13, 121–135 (2001)
Theofilis, V., Duck, P.W., Owen, J.: Viscous linear stability analysis of rectangular duct and cavity flows. J. Fluid Mech. 505, 249–286 (2004)
Fortin, A., Jardak, M., Gervais, J., Pierre, R.: Localization of Hopf bifurcation in fluid flow problems. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids. 24, 1185–1210 (1997)
Peng, Y.-H., Shiau, Y.-H., Hwang, R.R.: Transition in a 2-D lid-driven cavity flow. Comput. Fluids. 32, 337–352 (2003)
Bruneau, C.-H., Saad, M.: The 2d lid-driven cavity problem revisited. Comput. Fluids. 35, 326–348 (2006)
Murdock, J.R., Ickes, J.C., Yang, S.L.: Transition flow with an incompressible lattice Boltzmann method. AAM M. 9, 1271–1288 (2017)
An, B., Mellibovsky, F., Bergadà, J.M., Sang, W.M.: Towards a better understanding of wall-driven square cavity flows using the Lattice Boltzmann method. Appl. Math. Model. 82, 469–486 (2020)
Koseff, J.R., Street, R.L.: Visualization studies of a shear driven three-dimensional recirculating flow. J. Fluids Eng. 106, 21–27 (1984)
Koseff, J.R., Street, R.L.: On end wall effects in a lid-driven cavity flow. J. Fluids Eng. 106, 385–389 (1984)
Prasad, A.K., Koseff, J.R.: Reynolds number and end-wall effects on a lid-driven cavity flow. Phys. Fluids A. Fluid Dyn. 1, 208–218 (1989)
Kuhlmann, H.C., Wanschura, M., Rath, H.J.: Flow in two-sided lid-driven cavities: non-uniqueness, instabilities, and cellular structures. J. Fluid Mech. 336, 267–299 (1997)
Chen, S., Tolke, J., Krafczyk, M.: A new method for the numerical solution ofvorticity–streamfunction formulations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 198, 367–376 (2008)
Perumal, D.A., Dass, A.K.: Simulation of incompressible flows in two-sided lid–driven square cavities, Part II. LBM. CFD Lett. 2, 25–38 (2010)
Mendu, S.S., Das, P.: Flow of power-law fluids in a cavity driven by the motion of two facing lids—a simulation by lattice Boltzmann method. J. Non-Newton. Fluid mech. 175–176, 10–24 (2012)
Perumal, D.A.: Simulation of flow in two-sided lid-driven deep cavities by finite difference method. JASTFM. 6, 1–6 (2012)
Arun, S., Satheesh, A.: Analysis of flow behaviour in a two sided lid driven cavity using lattice Boltzmann technique. Alex. Eng. J. 54, 795–806 (2015)
Azzouz, E.A., Houat, S.: Numerical analysis and explore of asymmetrical fluid flow in a two-sided lid-driven cavity. J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 14(3), 7269–7281 (2020)
Azzouz, E.A., Houat, S.: Asymmetrical flow driving in two-sided lid-driven square cavity with antiparallel wall Motion. Matec web conf., 330 (2020).
Albensoeder, S., Kuhlmann, H., Rath, H.: Multiplicity of steady two-dimensional flows in two-sided lid-driven cavities. Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 14, 223–241 (2001)
Lemée, T., Kasperski, G., Labrosse, G., Narayanan, R.: Multiple stable solutions in the 2d symmetrical two-sided square lid-driven cavity. Comput. Fluids. 119, 204–212 (2015)
Prasad, C., Dass, A.K.: Use of an HOC scheme to determine the existence of multiple steady states in the antiparallel lid-driven flow in a two-sided square cavity. Comput. Fluids. 140, 297–307 (2016)
Perumal, D.A.: Lattice Boltzmann computation of multiple solutions in a double sided square and rectangular cavity flows. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 6, 48–56 (2018)
Kuhlmann, H.C., Wanschura, M., Rath, H.J.: Elliptic instability in two-sided lid-driven cavity flow. Eur. J. Mech. B Fluids. 17, 561–569 (1998)
Chen, K.T., Tsai, C.C., Luo, W.J., Chen, C.N.: Multiplicity of steady solutions in a two-sided lid-driven cavity with different aspect ratios. Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 27, 767–776 (2013)
Chen, K.T., Tsai, C.C., Lu, C.W., Luo, W.J., Chen, C.H.: Aspect ratio effect on multiple flows solution in a two-sided parallel motion lid-driven cavity. J. Mech. 31, 153–160 (2015)
An, B., Bergadà, J.M., Mellibovsky, F., Sang, W.M.: New applications of numerical simulation based on lattice Boltzmann method at high Reynolds numbers. Comput. Math. Appl. 79, 1718–1741 (2019)
Azzouz, E.A., Houat, S., Dellil, A.Z.: Numerical assessment of turbulent flow driving in a two-sided lid-driven cavity with antiparallel wall motion. DDF. 406, 133–148 (2021)
Wahba, E.M.: Multiplicity of states for two-sided and four-sided lid driven cavity flows. Comput. Fluids. 38, 247–253 (2009)
Perumal, D.A., Dass, A.K.: Multiplicity of steady solutions in two-dimensional lid-driven cavity flows by the Lattice Boltzmann method. Comput. Math Appl. 61, 3711–3721 (2001)
Chen, K.T., Tsai, C.C., Luo, W.J.: Multiplicity flow solutions in a four-sided lid-driven cavity. Appl. Mech. Mater. 368, 838–843 (2013)
Kamel, A.G., Haraz, E.H., Hanna, S.N.: Numerical simulation of three-sided lid-driven square cavity. Eng. Rep. 2:e12151 (2020)
Ferziger, J.H., Peric, M.: Computational Methods for Fluid Dynamics, 3rd edn. Springer, Berlin (2002)
Ghobadian, A., Vasquez, S.A.: A general purpose implicit coupled algorithm for the solution of eulerian multiphase transport equation. In: International Conference on Multiphase Flow, Leipzig, Germany (2007)
Caretto, L.S., Curr, R.M., Spalding, D.B.: Two numerical methods for three-dimensional boundary layers. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1, 39–57 (1972)
Darwish, M., Sraj, I., Moukalled, F.: A coupled incompressible flow solver on structured grids. Numer Heat Transf. B: Fundam. 52, 353–371 (2007)
Darwish, M., Sraj, I., Moukalled, F.: A coupled incompressible flow solver for the solution of incompressible flows on unstructured grids. J. Comput. Phys. 228, 180–201 (2009)
Acknowledgements
Our sincere thanks to the reviewers for the time and consecrated efforts. The authors wish also to acknowledge the helpful technical support of Professor Dellil Ahmed Zineddine from University of Mohamed Ben Ahmed Oran2 (IMSI).
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors conducted the numerical investigation which also concern the writing and editing of the paper. Professor Houat Samir gave the final approval for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
See Tables 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azzouz, E.A., Houat, S. Numerical Solutions of Steady Flow in a Three-Sided Lid-Driven Square Cavity. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math 8, 118 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-022-01314-4
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-022-01314-4