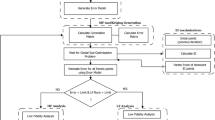
Abstract
Surrogate-based optimization has become a popular approach for solving problems with computationally expensive disciplinary solvers. Recently, the Efficient Global Multidisciplinary Design Optimization (EGMDO) algorithm was introduced as a surrogate-based algorithm for multidisciplinary optimization, where the disciplinary solvers are replaced by Gaussian process (GP) surrogate models. A dedicated model of the resulting random objective function is then used to perform Bayesian optimization and focus the computational effort in promising areas of the design space. While its results are promising, the original EGMDO formulation does not provide a strategy for constraint handling. In this work we reformulate the original EGMDO algorithm to be able to handle both equality and inequality constraints. To do so, surrogate models of the constraint functions are first obtained. Then, the original uncertainty reduction strategy is adapted to account for the uncertainty introduced by the disciplinary GPs in both objective and constraint functions. The performance of the resulting algorithm, called Constrained-EGMDO (C-EGMDO), is then illustrated on a benchmark analytical MDO problem and on an engineering test case.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnst M, Ghanem R, Phipps E, Red-Horse J (2012) Dimension reduction in stochastic modeling of coupled problems. Int J Numer Methods Eng 92(11):940–968. https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.4364
Bartoli N, Lefebvre T, Dubreuil S, Olivanti R, Priem R, Bons N, Martins JR, Morlier J (2019) Adaptive modeling strategy for constrained global optimization with application to aerodynamic wing design. Aerosp Sci Technol 90:85–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2019.03.041
Baudin M, Dutfoy A, Iooss B, Popelin AL (2017) OpenTURNS: an industrial software for uncertainty quantification in simulation. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 2001–2038. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-12385-1_64
Berthelin G, Dubreuil S, Salaün M, Bartoli N, Gogu C (2022) Disciplinary proper orthogonal decomposition and interpolation for the resolution of parameterized multidisciplinary analysis. Int J Numer Methods Eng 123(15):3594–3626. https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.6981
Bons NP, Martins JRRA (2020) Aerostructural design exploration of a wing in transonic flow. Aerospace. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace7080118
Bouhlel M, Bartoli N, Morlier J, Otsmane A (2016) Improving kriging surrogates of high-dimensional design models by partial least squares dimension reduction. Struct Multidisc Optim 53(5):935–952. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-015-1395-9
Bouhlel MA, Hwang JT, Bartoli N, Lafage R, Morlier J, Martins JRRA (2019) A python surrogate modeling framework with derivatives. Adv Eng Softw. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2019.03.005
Cramer EJ, Dennis JE Jr., Frank PD, Lewis RM, Shubin GR (1994) Problem formulation for multidisciplinary optimization. SIAM J Optim 4(4):754–776. https://doi.org/10.1137/0804044
Dubreuil S, Bartoli N, Gogu C, Lefebvre T, Mas Colomer J (2018) Extreme value oriented random field discretization based on an hybrid polynomial chaos expansion—kriging approach. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 332:540–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2018.01.009
Dubreuil S, Bartoli N, Lefebvre T, Gogu C (2020) Towards an efficient global multidisciplinary design optimization algorithm. Struct Multidisc Optim. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-020-02514-6
EDF (1989–2017) Finite element \(code_aster\), analysis of structures and thermomechanics for studies and research. Open source on http://www.code-aster.org
Forrester A, Sobester A, Keane A (2008) Engineering design via surrogate modelling: a practical guide. Wiley, Hoboken. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470770801
Ghanem R, Spanos P (2003) Stochastic finite elements: a spectral approach. Civil, mechanical and other engineering series. Dover Publications, New York
Gray JS, Hwang JT, Martins JRRA, Moore KT, Naylor BA (2019) OpenMDAO: an open-source framework for multidisciplinary design, analysis, and optimization. Struct Multidisc Optim 59:1075–1104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-019-02211-z
Jansen P, Perez RE, Martins JRRA (2010) Aerostructural optimization of nonplanar lifting surfaces. J Aircr 47(5):1491–1503. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.44727
Jasa JP, Hwang JT, Martins JRRA (2018) Open-source coupled aerostructural optimization using Python. Struct Multidisc Optim 57(4):1815–1827. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-018-1912-8
Jones D, Schonlau M, Welch W (1998) Efficient global optimization of expensive black-box functions. J Glob Optim 13:455–492. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008306431147
Katz J, Plotkin A (2001) Low-speed aerodynamics. Cambridge aerospace series, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511810329
Kraft D (1988) A software package for sequential quadratic programming. Forschungsbericht- Deutsche Forschungs- und Versuchsanstalt fur Luft- und Raumfahrt
Krige DG (1951) A statistical approach to some basic mine valuation problems on the Witwatersrand. J S Afr Inst Min Metall 52:201–203
Lambe AB, Martins JRRA (2011) A unified description of MDO architectures. In: Proceedings of the 9th world congress on structural and multidisciplinary optimization
Lambe AB, Martins JRRA (2012) Extensions to the design structure matrix for the description of multidisciplinary design, analysis, and optimization processes. Struct Multidisc Optim 46(2):273–284. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-012-0763-y
Lorenz R, Monti RP, Violante IR, Faisal AA, Anagnostopoulos C, Leech R, Montana G (2015) Stopping criteria for boosting automatic experimental design using real-time fMRI with Bayesian optimization. arXiv: neurons and cognition
Martins JRRA, Lambe AB (2013) Multidisciplinary design optimization: a survey of architectures. AIAA J 51(9):2049–2075. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.J051895
Martins JRRA, Sturdza P, Alonso JJ (2003) The complex-step derivative approximation. ACM Trans Math Softw 29(3):245–262. https://doi.org/10.1145/838250.838251
Martins J, Alonso J, Reuther J (2004) High-fidelity aerostructural design optimization of a supersonic business jet. J Aircr 41:523–530. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.11478
Martins J, Alonso J, Reuther J (2005) A coupled-adjoint sensitivity analysis method for high-fidelity aero-structural design: special issue on multidisciplinary design optimization. Optim Eng. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:OPTE.0000048536.47956.62
Matheron G (1963) Principles of geostatistics. Econ Geol 58(8):1246–1266. https://doi.org/10.2113/gsecongeo.58.8.1246
Močkus J (1975) On Bayesian methods for seeking the extremum. In: Optimization techniques IFIP technical conference. pp 400–404
Nguyen V, Gupta S, Rana S, Li C, Venkatesh S (2017) Regret for expected improvement over the best-observed value and stopping condition. In: Zhang ML, Noh YK (eds) Proceedings of the ninth Asian conference on machine learning, proceedings of machine learning research, vol 77. PMLR, Yonsei University, Seoul, Republic of Korea, pp 279–294
Picheny V, Gramacy R, Wild S, Le Digabel S (2016) Bayesian optimization under mixed constraints with a slack-variable augmented Lagrangian. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 29:1435–1443. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1605.09466
Powell MJD (1994) A direct search optimization method that models the objective and constraint functions by linear interpolation. Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht, pp 51–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-015-8330-5_4
Priem R, Bartoli N, Diouane Y, Sgueglia A (2020) Upper trust bound feasibility criterion for mixed constrained Bayesian optimization with application to aircraft design. Aerosp Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2020.105980
Sasena MJ, Papalambros P, Goovaerts P (2002) Exploration of metamodeling sampling criteria for constrained global optimization. Eng Optim 34(3):263–278. https://doi.org/10.1080/03052150211751
Scholten W, Hartl D (2021) Uncoupled method for static aeroelastic analysis. J Fluids Struct 101(103):221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2021.103221
Sellar R, Batill S, Renaud J (1996) Response surface based, concurrent subspace optimization for multidisciplinary system design. In: 34th aerospace sciences meeting and exhibit. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.1996-714
Sobol’ I (2001) Global sensitivity indices for nonlinear mathematical models and their Monte Carlo estimates. Math Comput Simul 55(1):271–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4754(00)00270-6
Sudret B (2008) Global sensitivity analysis using polynomial chaos expansions. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 93(7):964–979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2007.04.002
Wang X, Li M, Liu Y, Sun W, Song X (2017) Surrogate based multidisciplinary design optimization of lithium-ion battery thermal management system in electric vehicles. Struct Multidisc Optim 56:1555–1570. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-017-1733-1
Watson AGD, Barnes RJ (1995) Infill sampling criteria to locate extremes. Math Geol 27(5):589–608
Zhang M, Gou W, Li L, Yang F, Yue Z (2017) Multidisciplinary design and multi-objective optimization on guide fins of twin-web disk using kriging surrogate model. Struct Multidisc Optim 55:361–373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-016-1488-0
Acknowledgements
This work is a part of the activities of the ONERA-ISAE-ENAC joint research group.
Funding
This study was supported by ISAE-SUPAERO and ONERA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Replication of results
This section details the numerical tools used to obtain the results presented in this work. All numerical results were obtained using Python 3.8.8 and packages OpenMDAO 3.16.0 (Gray et al. 2019), openTURNS 1.19 (Baudin et al. 2017), numpy 1.20.1, SciPy 1.6.2 and SMT: Surrogate Modelling Toolbox 1.1.0 (Bouhlel et al. 2019).
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Graeme James Kennedy
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cardoso, I., Dubreuil, S., Bartoli, N. et al. Constrained efficient global multidisciplinary design optimization using adaptive disciplinary surrogate enrichment. Struct Multidisc Optim 67, 23 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-023-03736-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-023-03736-0