Abstract
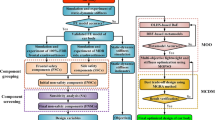
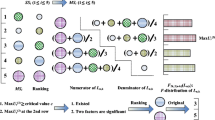
This paper demonstrates a conjoint method integrating the proposed Hybrid Contribution Analysis (HCA) method, the Artificial Neutral Network (ANN) meta-model, the modified Non-dominated Soring Genetic Algorithm II (MNSGAII) and the Ideal Point Method (IPM), used for multi-objective lightweight and crashworthiness optimization of the side structure of an automobile body. First of all, the static-dynamic stiffness models of the automobile body and the vehicle side crashworthiness model are separately established and validated against corresponding actual experiments. Next, the initially selected parts for optimization are screened using the proposed HCA method to determine the final parts for optimization, thicknesses of which are taken as design variables. After that, design of experiment (DoE) coupled with ANN-based meta-models are utilized to approximate the output performance indicators of the automobile body, based on which the modified NSGA-II (MNSGAII) with ε-elimination technique is then employed to solve the multi-objective optimization process, considering the total mass and the torsional stiffness of the automobile body, the maximum intrusion deformation of the measuring point P1 on the inner panel of B-pillar and the measuring point D1 on the inner panel of front door as four optimization objectives. Finally, the IPM method identifies the optimal trade-off solution from the obtained Pareto set, and a comprehensive comparison between the optimized design and the baseline design further confirms the validity of the proposed conjoint method. Specially, the four-objective Pareto set approximately embodies that of each pair of separately run two-objective optimization, thus providing more optimization schemes for designers.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- P(x 1, x 2, ⋯x k):
-
Any performance indicator of automobile body;
- Q i(x i):
-
Main effect of thickness variables xi;
- R ij(x i, x j):
-
Cross effect of any two variables xi and xj;
- μ :
-
The constant term;
- ε :
-
The error;
- \( {\widehat{\varphi}}_i \) :
-
The coefficient of main effect of design variable xi;
- DCV(x i):
-
Direct contribution value of design variable xi;
- RCV(x i):
-
Relative contribution value of design variable xi
- HCV(x i):
-
Hybrid contribution value of design variable xi.
- p :
-
Number of static-dynamic stiffness indicators;
- q :
-
Number of crashworthiness indicators;
- θ i :
-
DCV of variable xi to total mass of automobile body;
- λ i :
-
DCVs of variable xi to static-dynamic stiffness indicators;
- η i :
-
DCVs of variable xi to crashworthiness indicators
- ω 1, ω 2, …, ω p :
-
Weight coefficients of RCV of static-dynamic stiffness indicators;
- ξ 1, ξ 2, ⋯, ξ q :
-
Weight coefficients of RCV of crashworthiness indicators;
- α, β and γ :
-
Weight coefficients;
- R 2 :
-
R square;
- e max :
-
Maximum relative error;
- e avg :
-
Average relative error;
- eRMS :
-
Root mean square value of relative error;
- H :
-
Number of checking points;
- \( {f}_i^Z(e) \) :
-
Normalized data of fi(e);
- \( {\overline{f}}_i \) :
-
Mean value of fi;
- σ(f i):
-
Standard deviation of fi;
- ψ :
-
The non-dominated set;
- N f :
-
Number of objective functions;
- d(e):
-
Euclidean distance of solution e;
- M :
-
Total mass of automobile body;
- f T :
-
First-order torsional frequency;
- f B :
-
First-order bending frequency;
- S T :
-
Torsional stiffness;
- S B :
-
Bending stiffness;
- ϕ :
-
Twist angle;
- Torque :
-
The loaded torque;
- T :
-
Vector of thickness variables
- M(T):
-
Total mass of the automobile body
- P(T):
-
Vector of performance indicators
- P i(T):
-
ith performance indicator of automobile body
- \( {T}_i^L \) :
-
Lower bound of thickness variables Ti;
- \( {T}_i^U \) :
-
Upper bound of thickness variables Ti;
- A i :
-
Area of the ith component;
- n :
-
Number of independent components;
- m :
-
Number of employed materials;
- B i :
-
Materials properties of the ith material;
- ρ i :
-
Density of material;
- E i :
-
Elastic modulus;
- σ i :
-
Yield strength;
- \( {f}_M\left(\mathbf{x}\right) \) :
-
Function of total mass of automobile body;
- \( {f}_T\left(\mathbf{x}\right) \) :
-
Function of torsional stiffness of automobile body;
- P 1(x):
-
Function of maximum intrusion deformation of P1;
- \( {D}_1\left(\mathbf{x}\right) \) :
-
Function of maximum intrusion deformation of D1;
- N S :
-
Total number of the static-dynamic stiffness indicators as constraints
- N C :
-
Total number of the crashworthiness indicators as constraints
- x L :
-
Lower constraint limits of x;
- x U :
-
Upper constraint limits of x;
- \( {H}_j^{\ast } \) :
-
Five-star reference thresholds of the jth indicator;
- ε:
-
Elimination threshold of modified NSGA-II;
References
Abbasi M, Ghafari-Nazari A, Reddy S, Fard M (2014) A new approach for optimizing automotive crashworthiness: concurrent usage of ANFIS and Taguchi method. Struct Multidiscip Optim 49:485–499. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-013-0986-6
Ahmad Z, Thambiratnam DP, Tan ACC (2010) Dynamic energy absorption characteristics of foam-filled conical tubes under oblique impact loading. Int J Impact Eng 37:475–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2009.11.010
Ariffin AH et al. (2014) Development of mobile deformable barrier for side impact crashworthiness evaluation in ASEAN new car assessment programme (ASEAN NCAP) vol 663. doi:https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.663.562
Asanjarani A, Dibajian SH, Mandian A (2017) Multi-objective crashworthiness optimization of tapered thin-walled square tubes with indentations. Thin-Walled Struct 116:26–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2017.03.015
Bhattacharya A, Singla S (2016) Dissimilar GTAW between AISI 304 and AISI 4340 steel: Multi-response optimization by analytic hierarchy process. Proc Ins Mech Eng Part E J Process Mech Eng. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954408916641458
Chen G, Chen C, Lu S, Chen Y, Li Y (2016) Lightweight Design of Vehicle Front Rails Based on the Theory of Thin-walled Beam Crush and Bending. Automot Eng 38:1269–1273
Chen W, Zuo W (2014) Component sensitivity analysis of conceptual vehicle body for lightweight design under static and dynamic stiffness demands. Int J Veh Des 66:107–123. https://doi.org/10.1504/ijvd.2014.064546
Chen Y, Liu G, Zhang Z, Hou S (2017) Integrated design technique for materials and structures of vehicle body under crash safety considerations. Struct Multidiscip Optim 56:455–472. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-017-1674-8
Deb K, Pratap A, Agarwal S, Meyarivan T (2002) A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 6:182–197
Del Pero F, Delogu M, Pierini M (2017) The effect of lightweighting in automotive LCA perspective: Estimation of mass-induced fuel consumption reduction for gasoline turbocharged vehicles. J Clean Prod 154:566–577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.04.013
Ding R, Su X, Wang H (2015) Lightweight sub-frame design for passenger car. J Mach Des 32:37–40
Duan L, Xiao N-C, Hu Z, Li G, Cheng A (2017) An efficient lightweight design strategy for body-in-white based on implicit parameterization technique. Struct Multidiscip Optim 55:1927–1943. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-016-1621-0
Ebrahimi S, Vahdatazad N (2015) Multiobjective optimization and sensitivity analysis of honeycomb sandwich cylindrical columns under axial crushing loads. Thin-Walled Struct 88:90–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2014.12.004
Fan Z, Gui L, Su R (2014) Research and development of automotive lightweight technology. J Autom Saf Energy 5:1–16
Fang J, Gao Y, Sun G, Li Q (2013) Multiobjective reliability-based optimization for design of a vehicledoor. Finite Elem Anal Des 67:13–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.finel.2012.11.007
Fang J, Gao Y, Sun G, Qiu N, Li Q (2015) On design of multi-cell tubes under axial and oblique impact loads. Thin-Walled Struct 95:115–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2015.07.002
Fang J, Gao Y, Sun G, Xu C, Li Q (2015) Multiobjective robust design optimization of fatigue life for a truck cab. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 135:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2014.10.007
Fang JG, Gao YK, Sun GY, Xu CM, Li Q (2016) Multiobjective sequential optimization for a vehicle door using hybrid materials tailor-welded structure. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part C-J Mech Eng Sci 230:3092–3100. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954406215607901
Fang JG, Sun GY, Qiu N, Kim NH, Li Q (2017) On design optimization for structural crashworthiness and its state of the art. Struct Multidiscip Optim 55:1091–1119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-016-1579-y
Fang Y, Zhan Z, Yang J, Liu X (2017) A Mixed-Kernel-Based Support Vector Regression Model for Automotive Body Design Optimization Under Uncertainty. ASCE-ASME J Risk Uncertain Eng Syst Part B: Mech Eng 3:041008
Gao X, Xu Y, Wang Q (2014) A Study on the Crashworthiness and Lightweighting of B-pillar in a Car Based on Bench Test and Simulation. Automot Eng 36(957–962):973
Gu X, Dai J, Huang X, Li G (2017) Reliable optimisation design of vehicle structure crashworthiness under multiple impact cases. Int J Crashworthiness 22:26–37. https://doi.org/10.1080/13588265.2016.1215585
Gu X, Sun G, Li G, Mao L, Li Q (2013) A Comparative study on multiobjective reliable and robust optimization for crashworthiness design of vehicle structure. Struct Multidiscip Optim 48:669–684. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-013-0921-x
Hou SJ, Dong D, Ren LL, Han X (2012) Multivariable crashworthiness optimization of vehicle body by unreplicated saturated factorial design. Struct Multidiscip Optim 46:891–905. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-012-0799-z
Hou SJ, Liu TY, Dong D, Han X (2014) Factor screening and multivariable crashworthiness optimization for vehicle side impact by factorial design. Struct Multidiscip Optim 49:147–167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-013-0957-y
Hu Y, Liu X, Neal-Sturgess CE, Jiang CY (2011) Lower leg injury simulation for EuroNCAP compliance. Int J Crashworthiness 16:275–284. https://doi.org/10.1080/13588265.2011.559797
Jafarian F, Taghipour M, Amirabadi H (2013) Application of artificial neural network and optimization algorithms for optimizing surface roughness, tool life and cutting forces in turning operation. J Mech Sci Technol 27:1469–1477
Khalkhali A, Mostafapour M, Tabatabaie SM, Ansari B (2016) Multi-objective crashworthiness optimization of perforated square tubes using modified NSGAII and MOPSO. Struct Multidiscip Optim 54:45–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-015-1385-y
Kohar CP, Zhumagulov A, Brahme A, Worswick MJ, Mishra RK, Inal K (2016) Development of high crush efficient, extrudable aluminium front rails for vehicle lightweighting. Int J Impact Eng 95:17–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2016.04.004
Lei F, Chen X, Xie XP, Zhu J (2015) Research on three main lightweight approaches for automotive body engineering considering materials. Structural performances and costs SAE technical papers 2015-April. doi:https://doi.org/10.4271/2015-01-0580
Li A-D, He Z, Zhang Y (2016) Bi-objective variable selection for key quality characteristics selection based on a modified NSGA-II and the ideal point method. Comput Ind 82:95–103
Li GY, Xu FX, Huang XD, Sun GY (2015) Topology optimization of an automotive tailor-welded blank door. J Mech Des 137. doi:https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4028704
Li GY, Xu FX, Sun GY, Li Q (2015) Crashworthiness study on functionally graded thin-walled structures. Int J Crashworthiness 20:280–300. https://doi.org/10.1080/13588265.2015.1010396
Li MH, Li ZR, Jiang L (2016) Preliminary study of automobile lightweight technology. In: Zhu SH (ed) Proceedings of the 2016 4th international conference on mechanical materials and manufacturing engineering, vol 79. AER-advances in engineering research. pp 798–802
Li Z, Yu Q, Zhao X, Chen J, Fan Q (2016) Crashworthiness and Lightweight Optimization for Frontal Structure of Automobile Under Low-speed Impact. China J Highway and Transp 29:149–158
Liang C, Mahadevan S (2017) Pareto surface construction for multi-objective optimization under uncertainty. Struct Multidiscip Optim 55:1865–1882. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-016-1619-7
Liao X, Li Q, Yang X, Zhang W, Li W (2008) Multiobjective optimization for crash safety design of vehicles using stepwise regression model. Struct Multidiscip Optim 35:561–569. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-007-0163-x
Liu W, Gao Y, Guo Q, Zhou D, Zhao F (2015) Lightweight design for car-body based on crashworthiness. J Mach Des 32:62–66
Liu ZF, Huang ZC, Qin QH (2017) Experimental and theoretical investigations on lateral crushing of aluminum foam-filled circular tubes. Compos Struct 175:19–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.05.004
Ma M, Yi H (2011) Lightweight car body and application of high strength steels. In, Berlin, Heidelberg. Advanced steels. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, pp 187–198
Nariman-Zadeh N, Salehpour M, Jamali A, Haghgoo E (2010) Pareto optimization of a five-degree of freedom vehicle vibration model using a multi-objective uniform-diversity genetic algorithm (MUGA). Eng Appl Artif Intell 23:543–551
Pang T, Li YF, Kang HH, Sun GY, Fang JG, Li Q (2017) On functionally-graded crashworthy shape of conical structures for multiple load cases. J Mech Sci Technol 31:2861–2873. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-017-0529-y
Qi C, Yang S, Dong F (2012) Crushing analysis and multiobjective crashworthiness optimization of tapered square tubes under oblique impact loading. Thin-Walled Struct 59:103–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2012.05.008
Qiu N, Gao Y, Fang J, Feng Z, Sun G, Li Q (2016) Theoretical prediction and optimization of multi-cell hexagonal tubes under axial crashing. Thin-Walled Struct 102:111–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2016.01.023
Qiu R, Chen Y, Lei F, Yang S, Li Y (2016) Lightweight of the vehicle B pillar based on six sigma robust design under side impact. Jixie Qiangdu J Mech Strength 38:502–508. https://doi.org/10.16579/j.issn.1001.9669.2016.03.014
Ramakrishnan R, Arumugam R (2012) Optimization of operating parameters and performance evaluation of forced draft cooling tower using response surface methodology (RSM) and artificial neural network (ANN). J Mech Sci Technol 26:1643–1650
Song X, Sun G, Li G, Gao W, Li Q (2013) Crashworthiness optimization of foam-filled tapered thin-walled structure using multiple surrogate models. Struct Multidiscip Optim 47:221–231. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-012-0820-6
Song X, Sun G, Li Q (2016) Sensitivity analysis and reliability based design optimization for high-strength steel tailor welded thin-walled structures under crashworthiness. Thin-Walled Struct 109:132–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2016.09.003
Srinivas GR, Deb A, Chou CC (2016) Lightweighting of an automotive front end structure considering frontal NCAP and pedestrian lower leg impact safety requirements. SAE Technical Papers 2016-April. doi:https://doi.org/10.4271/2016-01-1520
Sun G, Li G, Zhou S, Li H, Hou S, Li Q (2011) Crashworthiness design of vehicle by using multiobjective robust optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 44:99–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-010-0601-z
Sun G, Xu F, Li G, Li Q (2014) Crashing analysis and multiobjective optimization for thin-walled structures with functionally graded thickness. Int J Impact Eng 64:62–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2013.10.004
Sun GY, Pang T, Zheng G, Song J, Li Q (2016) On energy absorption of functionally graded tubes under transverse loading. Int J Mech Sci 115:465–480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2016.06.021
Sun GY, Zhang HL, Lu GX, Guo JW, Cui JJ, Li Q (2017) An experimental and numerical study on quasi-static and dynamic crashing behaviors for tailor rolled blank (TRB) structures. Mater Des 118:175–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.12.073
Tastan A, Acar E, Guler MA, Kilinckaya U (2016) Optimum crashworthiness design of tapered thin-walled tubes with lateral circular cutouts. Thin-Walled Struct 107:543–553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2016.07.018
Vinayagar K, Kumar AS (2017) Multi-response optimization of crashworthiness parameters of bi-tubular structures. Steel Compos Struct 23:31–40
Wang D, Cai K (2018) Optimizing the static–dynamic performance of the body-in-white using a modified non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm coupled with grey relational analysis. Eng Optim 50:615–633
Wang D, Jiang R, Wu Y (2016) A hybrid method of modified NSGA-II and TOPSIS for lightweight design of parameterized passenger car sub-frame. J Mech Sci Technol 30:4909–4917
Wang D, Zhang S, Wang C, Zhang C (2017) Structure-material-performance integration lightweight optimisation design for frontal bumper system. Int J Crashworthiness:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/13588265.2017.1317468
Wu S, Zheng G, Sun G, Liu Q, Li G, Li Q (2016) On design of multi-cell thin-wall structures for crashworthiness. Int J Impact Eng 88:102–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2015.09.003
Xiong F, Wang D, Ma Z, Chen S, Lv T, Lu F (2018) Structure-material integrated multi-objective lightweight design of the front end structure of automobile body. Struct Multidiscip Optim 57:829–847
Xiong F, Wang D, Zhang S, Cai K, Wang S, Lu F (2017) Lightweight optimization of the side structure of automobile body using combined grey relational and principal component analysis. Struct Multidiscip Optim 1–21. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-017-1749-6
Xu F, Sun G, Li G, Li Q (2013) Crashworthiness design of multi-component tailor-welded blank (TWB) structures. Struct Multidiscip Optim 48:653–667. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-013-0916-7
Xu F, Tian X, Li G (2015) Experimental Study on Crashworthiness of Functionally Graded Thickness Thin-Walled Tubular Structures. Exp Mech 55:1339–1352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11340-015-9994-3
Xu FX, Wang C (2016) Dynamic axial crashing of tailor-welded blanks (TWBs) thin-walled structures with top-hat shaped section. Adv Eng Softw 96:70–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2016.02.003
Yin HF, Wen GL, Liu ZB, Qing QX (2014) Crashworthiness optimization design for foam-filled multi-cell thin-walled structures. Thin-Walled Struct 75:8–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2013.10.022
Zeng F, Xie H, Liu Q, Li F, Tan W (2016) Design and optimization of a new composite bumper beam in high-speed frontal crashes. Struct Multidiscip Optim 53:115–122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-015-1312-2
Zhang H, Zhang X (2016) Crashworthiness performance of conical tubes with nonlinear thickness distribution. Thin-Walled Struct 99:35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2015.11.007
Zhang S, Zhu P, Chen W, Arendt P (2013) Concurrent treatment of parametric uncertainty and metamodeling uncertainty in robust design. Struct Multidiscip Optim 47:63–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-012-0805-5
Zhang X, Zhang H (2013) Optimal design of functionally graded foam material under impact loading. Int J Mech Sci 68:199–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2013.01.016
Zhang Y, Lu M, Sun G, Li G, Li Q (2015) On functionally graded composite structures for crashworthiness. Compos Struct 132:393–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2015.05.034
Zhang Y, Xu X, Sun G, Lai X, Li Q (2018) Nondeterministic optimization of tapered sandwich column for crashworthiness. Thin-Walled Struct 122:193–207
Zhang ZH, Liu ST, Tang ZL (2009) Design optimization of cross-sectional configuration of rib-reinforced thin-walled beam. Thin-Walled Struct 47:868–878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2009.02.009
Zheng G, Wu S, Sun G, Li G, Li Q (2014) Crushing analysis of foam-filled single and bitubal polygonal thin-walled tubes. Int J Mech Sci 87:226–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2014.06.002
Zhou G, Ma ZD, Li GY, Cheng AG, Duan LB, Zhao WZ (2016) Design optimization of a novel NPR crash box based on multi-objective genetic algorithm. Struct Multidiscip Optim 54:673–684. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-016-1452-z
Zou X, Gao GJ, Dong HP, Xie SC, Chen G, Tan T (2017) Crashworthiness analysis and structural optimisation of multi-cell square tubes under axial and oblique loads. Int J Crashworthiness 22:129–147. https://doi.org/10.1080/13588265.2016.1235109
Zuo W, Yu J, Saitou K (2016) Stress sensitivity analysis and optimization of automobile body frame consisting of rectangular tubes. Int J Automot Technol 17:843–851. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-016-0082-1
Acknowledgements
This research work is supported by the national key research and development project (2016YFB0101601) and State Scholarship Fund of China Scholarship Council ([2016]3100). The authors would like to express their appreciation for the above fund supports.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Qing Li
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiong, F., Wang, D., Chen, S. et al. Multi-objective lightweight and crashworthiness optimization for the side structure of an automobile body. Struct Multidisc Optim 58, 1823–1843 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-018-1986-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-018-1986-3