Abstract
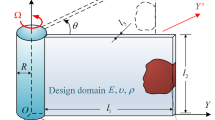
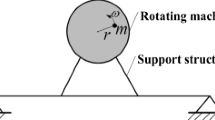
Gyroscopic effects are essential features for vibration analysis and design of rotating structures due to the variation of coordinate system and the presence of inertia force. The purpose of this study is to present a new topology optimization method for designing rotating beam cross-section with gyroscopic effects. Based on the Giavotto beam theory and Hamilton’s principle, the governing motion equations of a rotating beam with an arbitrary geometry section are derived first, and then the dynamic finite element models are formulated. The eigensolution of the rotating beam has complex eigenvalues due to the gyroscopic terms in the governing equations, and this work mainly concerns with the steady rotating state, in which the real parts of all complex eigenvalues equal to zero. Topology optimization models of the beam cross-section are formulated in the variable density frame and the objective is to maximize the fundamental eigenfrequency and the gap between two consecutive eigenfrequencies. In order to alleviate the non-differentiability of min-max problems, the Kreisselmeier-Steinhauser function is used to approximate the objective function. The sensitivities of eigenfrequencies with respect to design variables are derived in the complex space. Numerical examples show that the angular velocity has a significant influence on the optimal topology of the rotating beam cross-section, and also validate the effectiveness and necessity of the proposed method.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bendsøe MP, Sigmund O (1999) Material interpolation schemes in topology optimization. Arch Appl Mech 69:635–654
Blasques JP (2014) Multi-material topology optimization of laminated composite beams with eigenfrequency constraints. Compos Struct 111:45–55
Blasques JP, Stolpe M (2012) Multi-material topology optimization of laminated composite beam cross sections. Compos Struct 94:3278–3289
Bourdin B (2001) Filters in topology optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 50:2143–2158
Chen W, Keer L (1993) Transverse vibrations of a rotating twisted Timoshenko beam under axial loading. ASME Journal of Vibration and Acoustics 115:285–294
Chen TY, Wang BP (1993) Optimum design of rotor-bearing systems with eigenvalue constraints. ASME. J Eng Gas Turbines Power 115:256–260
Díaaz AR, Kikuchi N (1992) Solutions to shape and topology eigenvalue optimization problems using a homogenization method. Int J Numer Methods Eng 35:1487–1502
Donoso A, Sigmund O (2004) Topology optimization of multiple physics problems modelled by Poissons equation. Latin American Journal of Solids and Structures 1:169–184
Du J, Olhoff N (2007) Topological design of freely vibrating continuum structures for maximum values of simple and multiple eigenfrequencies and frequency gaps. Struct Multidiscip Optim 34:91–110
Gans HD, Anderson WJ (1991) Structural optimization incorporating centrifugal and Coriolis effects. AIAA J 29:1743–1750
Giavotto V, Borri M, Mantegazza P, Ghiringhelli G, Carmaschi V, Maffioli G et al (1983) Anisotropic beam theory and applications. Comput Struct 16:403–413
Gunjal S, Dixit U (2007) Vibration analysis of shape-optimized rotating cantilever beams. Eng Optim 39:105–123
Gupta SD, Rajamohan V (2014) Segment optimization of a rotating multilayer sandwich beam. Journal of Sandwich Structures & Materials 16:148–172
Hoa S (1979) Vibration of a rotating beam with tip mass. J Sound Vib 67:369–381
Huang CL, Lin WY, Hsiao KM (2010) Free vibration analysis of rotating Euler beams at high angular velocity. Comput Struct 88:991–1001
Jensen JS, Pedersen NL (2006) On maximal eigenfrequency separation in two-material structures: the 1D and 2D scalar cases. J Sound Vib 289:967–986
Kim YY, Kim TS (2000) Topology optimization of beam cross sections. Int J Solids Struct 37:477–493
Kim TS, Kim YY (2002) Multiobjective topology optimization of a beam under torsion and distortion. AIAA J 40:376–381
Kosaka I, Swan CC (1999) A symmetry reduction method for continuum structural topology optimization. Comput Struct 70:47–61
Kreisselmeier G, Steinhauser R (1979) Systematic control design by optimizing a vector performance index, IFAC Symp. Computer Aided Design of Control Systems, Zurich, Switzerland
Le C, Norato J, Bruns T, Ha C, Tortorelli D (2010) Stress-based topology optimization for continua. Struct Multidiscip Optim 41:605–620
Li L (2008) Structural design of composite rotor blades with consideration of manufacturability, durability, and manufacturing uncertainties: Georgia Institute of. Technology
Li L, Hu Y, Wang X (2012) A parallel way for computing eigenvector sensitivity of asymmetric damped systems with distinct and repeated eigenvalues. Mech Syst Signal Process 30:61–77
Li Q, Chen W, Liu S, Tong L (2016) Structural topology optimization considering connectivity constraint. Struct Multidiscip Optim 54:971–984
Li Y, Zhu JH, Zhang WH, Wang L (2018) Structural topology optimization for directional deformation behavior design with the orthotropic artificial weak element method. Struct Multidiscip Optim 57:1251–1266
Liu S, An X, Jia H (2008) Topology optimization of beam cross-section considering warping deformation. Struct Multidiscip Optim 35:403–411
Ma Z-D, Kikuchi N, Cheng H-C (1995) Topological design for vibrating structures. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 121:259–280
Olhoff N (1989) Multicriterion structural optimization via bound formulation and mathematical programming. Struct Multidiscip Optim 1:11–17
Pedersen NL (2000) Maximization of eigenvalues using topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 20:2–11
Raspanti C, Bandoni J, Biegler L (2000) New strategies for flexibility analysis and design under uncertainty. Comput Chem Eng 24:2193–2209
Seyranian AP, Lund E, Olhoff N (1994) Multiple eigenvalues in structural optimization problems. Structural optimization 8:207–227
Sigmund O (2007) Morphology-based black and white filters for topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 33:401–424
Svanberg K (1987) The method of moving asymptotes—a new method for structural optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 24:359–373
Tcherniak D (2002) Topology optimization of resonating structures using SIMP method. Int J Numer Methods Eng 54:1605–1622
Wang MY, Wang X, Guo D (2003) A level set method for structural topology optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 192:227–246
Yi S, Cheng G, Xu L (2016) Stiffness design of heterogeneous periodic beam by topology optimization with integration of commercial software. Comput Struct 172:71–80
Yokoyama T (1988) Free vibration characteristics of rotating Timoshenko beams. Int J Mech Sci 30:743–755
Yoo H, Shin S (1998) Vibration analysis of rotating cantilever beams. J Sound Vib 212:807–828
Yoo HH, Cho JE, Chung J (2006) Modal analysis and shape optimization of rotating cantilever beams. J Sound Vib 290:223–241
Zhou M, Rozvany G (1991) The COC algorithm, part II: topological, geometrical and generalized shape optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 89:309–336
Zhu J-H, Li Y, Zhang W-H, Hou J (2016) Shape preserving design with structural topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 53:893–906
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support to this work by the National Natural Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11332004, 11372073 and 11402046), the 111 Project (B14013) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (DUT15ZD101).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Li, Q., Liu, S. et al. Dynamic topology optimization design of rotating beam cross-section with gyroscopic effects. Struct Multidisc Optim 58, 1467–1487 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-018-1974-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-018-1974-7