Abstract
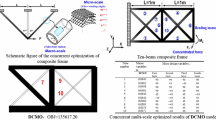
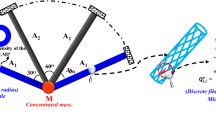
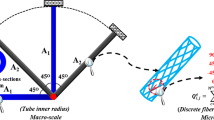
This paper presents a gradient based concurrent multi-scale design optimization method for composite frames considering specific manufacturing constraints raised from the aerospace industrial requirements. Geometrical parameters of the frame components at the macro-structural scale and the discrete fiber winding angles at the micro-material scale are introduced as the independent design variables at the two geometrical scales. The DMO (Discrete Material Optimization) approach is utilized to couple the two geometrical scales and realize the simultaneous optimization of macroscopic topology and microscopic material selection. Six kinds of manufacturing constraints are explicitly included in the optimization model as series of linear inequalities or equalities. The capabilities of the proposed optimization model are demonstrated with the example of compliance minimization, subject to constraint on the composite volume. The linear constraints and optimization problems are solved by Sequential Linear Programming (SLP) optimization algorithm with move limit strategy. Numerical results show the potential of weight saving and structural robustness design with the proposed concurrent optimization model. The multi-scale optimization model, considering specific manufacturing constraints, provides new choices for the design of the composite frame structure in aerospace and other industries.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailie JA, Ley RP, Pasricha A (1997) A summary and review of composite laminate design guidelines. Technical report NASA, NAS1–19347. Northrop Grumman-Military Aircraft Systems Division
Baker AA, Dutton SE, Kelly DW (2004) Composite materials for aircraft structures, 2nd edn. American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics
Bakis CE, Bank LC, Brown VL, Cosenza E, Davalos JF, Lesko JJ, Machida A, Rizkalla SH, Triantafillou TC (2002) Fiber-reinforced polymer composites for construction-state-of-the-art review. J Compos Constr 6(2):73–87
Bendsoe MP (1989) Optimal shape design as a material distribution problem. Struct Multidiscip Optim 1(4):193–202
Bendsøe M, Sigmund O (2003) Topology optimization-Theory, Methods and Applications, 2nd edn. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg
Blasques JP (2014) Multi-material topology optimization of laminated composite beams with eigenfrequency constraints. Compos Struct 111:45–55
Blasques J, Lazarov B (2012) User's manual for BECAS: a cross section analysis tool for anisotropic and inhomogeneous beam sections of arbitrary geometry. Risø DTU–National Laboratory for Sustainable Energy
Blasques JP, Stolpe M (2011) Maximum stiffness and minimum weight optimization of laminated composite beams using continuous fiber angles. Struct Multidiscip Optim 43(4):573–588
Blasques JP, Stolpe M (2012) Multi-material topology optimization of laminated composite beam cross sections. Compos Struct 94(11):3278–3289
Bruyneel M (2011) SFP - a new parameterization based on shape functions for optimal material selection: application to conventional composite plies. Struct Multidiscip Optim 43(1):17–27
Bruyneel M, Beghin C, Craveur G, Grihon S, Sosonkina M (2012) Stacking sequence optimization for constant stiffness laminates based on a continuous optimization approach. Struct Multidiscip Optim 46(6):783–794
Costin DP, Wang BP (1993) Optimum design of a composite structure with manufacturing constraints. Thin-Walled Struct 17(3):185–202
Deng JD, Yan J, Cheng GD (2013) Multi-objective concurrent topology optimization of thermoelastic structures composed of homogeneous porous material. Struct Multidiscip Optim 47(4):583–597
Duan ZY, Yan J, Zhao GZ (2014) Integrated optimization of the material and structure of composites based on the Heaviside penalization of discrete material model. Struct Multidiscip Optim 51(3):721–732
Eschenauer HA, Olhoff N (2001) Topology optimization of continuum structures: A review. Appl Mech Rev 54(4):331–390
Ferreira RTL, Rodrigues HC, Guedes J, Hernandes JA (2013) Hierarchical optimization of laminated fiber reinforced composites. Compos Struct 107:246–259
Fletcher R, Leyffer S, Toint PL (1998) On the global convergence of an SLP-filter algorithm. Numerical Analysis Report NA/183, University of Dundee, UK, August
Gao T, Zhang W, Duysinx P (2012) A bi-value coding parameterization scheme for the discrete optimal orientation design of the composite laminate. Int J Numer Methods Eng 91(1):98–114
Gao T, Zhang WH, Duysinx P (2013) Simultaneous design of structural layout and discrete fiber orientation using bi-value coding parameterization and volume constraint. Struct Multidiscip Optim 48(6):1075–1088
Ghiasi H, Pasini D, Lessard L (2009) Optimum stacking sequence design of composite materials Part I: Constant stiffness design. Compos Struct 90(1):1–11
Ghiasi H, Fayazbakhsh K, Pasini D, Lessard L (2010) Optimum stacking sequence design of composite materials Part II: Variable stiffness design. Compos Struct 93(1):1–13
Gomes FA, Senne TA (2011) An SLP algorithm and its application to topology optimization. Comput Appl Math 30(1):53–89
Hvejsel CF, Lund E (2011) Material interpolation schemes for unified topology and multi-material optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 43(6):811–825
Hvejsel CF, Lund E, Stolpe M (2011) Optimization strategies for discrete multi-material stiffness optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 44(2):149–163
Ibrahim S, Polyzois D, Hassan S (2000) Development of glass fiber reinforced plastic poles for transmission and distribution lines. Can J Civ Eng 27(5):850–858
Irisarri FX, Lasseigne A, Leroy FH, Riche RL (2014) Optimal design of laminated composite structures with ply drops using stacking sequence tables. Compos Struct 107:559–569
Kassapoglou C (2013) Design and analysis of composite structures: with applications to aerospace structures, 2nd edn. Sons, John Wiley &
Liu L, Yan J, Cheng GD (2008) Optimum structure with homogeneous optimum truss-like material. Comput Struct 86(13):1417–1425
Liu DZ, Toroporov VV, Querin OM, David CB (2011) Bilevel optimization of blended composite wing panels. J Aircr 48(1):107–118
Lund E (1994) Finite element based design sensitivity analysis and optimization. Institute of Mechanical Engineering, Aalborg University, Denmark
Lund E (2009) Buckling topology optimization of laminated multi-material composite shell structures. Compos Struct 91(2):158–167
Lund E, Stegmann J (2005) On structural optimization of composite shell structures using a discrete constitutive parametrization. Wind Energy 8(1):109–124
Mallick PK (2007) Fiber-reinforced composites: materials, manufacturing, and design. CRC press
Manne PM, Tsai SW (1998) Design optimization of composite plates: Part II—structural optimization by plydrop tapering. J Compos Mater 32(6):572–598
Mehrotra S (1992) On the implementation of a primal-dual interior point method. SIAM J Optim 2(4):575–601
Niu B, Yan J, Cheng GD (2009) Optimum structure with homogeneous optimum cellular material for maximum fundamental frequency. Struct Multidiscip Optim 39(2):115–132
Niu B, Olhoff N, Lund E, Cheng GD (2010) Discrete material optimization of vibrating laminated composite plates for minimum sound radiation. Int J Solids Struct 47(16):2097–2114
Rodrigues H, Guedes JM, Bendsoe M (2002) Hierarchical optimization of material and structure. Struct Multidiscip Optim 24(1):1–10
Schutze R (1997) Lightweight carbon fibre rods and truss structures. Mater Des 18(4–6):231–238
Seresta O, Gurdal Z, Adams DB, Watson LT (2007) Optimal design of composite wing structures with blended laminates. Compos Part B 38(4):469–480
Sigmund O, Torquato S (1997) Design of materials with extreme thermal expansion using a three-phase topology optimization method. J Mech Phys Solids 45(6):1037–1067
Sørensen SN, Lund E (2013) Topology and thickness optimization of laminated composites including manufacturing constraints. Struct Multidiscip Optim 48(2):249–265
Sørensen SN, Sørensen R, Lund E (2014) DMTO–a method for discrete material and thickness optimization of laminated composite structures. Struct Multidiscip Optim 50(1):25–47
Stegmann J, Lund E (2005) Discrete material optimization of general composite shell structures. Int J Numer Methods Eng 62(14):2009–2027
Stolpe M, Svanberg K (2001) An alternative interpolation scheme for minimum compliance topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 22(2):116–124
Wang BP, Costin DP (1992) Optimum design of a composite structure with three types of manufacturing constraints. AIAA J 30(6):1667–1669
Yan J, Hu WB, Wang ZH, Duan ZY (2014) Size effect of lattice material and minimum weight design. Acta Mech Sinica 30(2):191–197
Yan J, Yang SX, Duan ZY, Yang CQ (2015a) Minimum compliance optimization of a thermoelastic lattice structure with size-coupled effects. J Therm Stresses 38(3):338–357
Yan J, Hu WB, Duan ZY (2015b) Structure/material concurrent optimization of lattice materials based on extended multiscale finite element method. Int J Multiscale Comput Eng 13(1):73–90
Zhang Y (1998) Solving large-scale linear programs by interior-point methods under the Matlab environment. Optim Methods Softw 10(1):1–31
Acknowledgments
Financial supports for this research were provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11372060 and 11672057), Program (LJQ2015026) for Excellent Talents at Colleges and Universities in Liaoning Province, the 111 project (B14013), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (DUT16ZD215), and the Program of BK21 Plus. These supports are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, J., Duan, Z., Lund, E. et al. Concurrent multi-scale design optimization of composite frames with manufacturing constraints. Struct Multidisc Optim 56, 519–533 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-017-1750-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-017-1750-0