Abstract
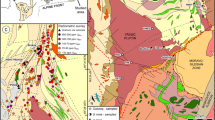
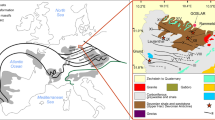
The world-class Jinchuan magmatic Ni-Cu-PGE (platinum-group element) sulfide deposit comprises four large orebodies (No. 1, 2, 3 and 24). Underground fan drilling discovered significant lateral extension of No. 2 orebody, referred as No. 2a in this study. From base to top, the No. 2a orebody comprises disseminated sulfide in olivine pyroxenites, net-textured ore in lherzolite, and massive ore. Despite different host rocks, the contents of Ni, Cu and PGE of the same types of sulfide ores from No. 2 and No. 2a orebodies are comparable. Mass balance calculation indicates that the parental magmas contained 0.01–0.05 ppb Ir and 0.2-0.8 ppb Pd, which are about one order of magnitude less than PGE abundances of undepleted continental flood basalts. PGE tenors (recalculated to 100% sulfides) of the net-textured ores from both orebodies increase upward. We attribute this to variations in magma:sulfide ratios of successive batches of recharged magmas and/or reaction of sulfides with less evolved magma. We propose that the No. 2a and No. 2 orebodies were located in the upstream and downstream parts of an originally sub-horizontal magma conduit, respectively. Sulfide liquids accumulated in the wider parts of the magma conduit to form No. 2a and No. 2 orebodies progressively. Variable locations within the intrusion and sharp contacts with other types of sulfide ore indicate that the massive ores formed by injection of pooled sulfide melt. Significant Pt-depletion of the massive ores and Pt enrichment in the adjacent net-textured ores suggest migration of residual fractionated sulfide liquids.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes S-J, Lightfoot PC (2005) Formation of magmatic nickel-sulfide ore deposits and processes affecting their copper and platinum-group element contents. Econ Geol 100:179–213
Barnes SJ, Liu WH (2012) Pt and Pd mobility in hydrothermal fluids: Evidence from komatiites and from thermodynamic modelling. Ore Geol Rev 44:49–58
Barnes S-J, Maier WD (1999) The fractionation of Ni, Cu and the noble metals in silicate and sulphide liquids. Short Course Notes-Geol Assoc Canada 13:69–106
Barnes SJ, Tang ZL (1999) Chrome spinels from the Jinchuan Ni-Cu sulfide deposit, Gansu province, People’s Republic of China. Econ Geol 94:343–356
Barnes S-J, Makovicky E, Makovicky M, RoseHansen J, KarupMoller S (1997) Partition coefficients for Ni, Cu, Pd, Pt, Rh, and Ir between monosulfide solid solution and sulfide liquid and the formation of compositionally zoned Ni-Cu sulfide bodies by fractional crystallization of sulfide liquid. Can J Earth Sci 34:366–374
Barnes S-J, Prichard HM, Cox RA, Fisher PC, Godel B (2008) The location of the chalcophile and siderophile elements in platinum group element ore deposits (a textural, microbeam and whole rock geochemical study): implications for the formation of the deposits. Chem Geol 248:295–317
Barnes SJ, Fiorentini ML, Fardon MC (2012) Platinum group element and nickel sulphide ore tenors of the Mount Keith nickel deposit, Yilgarn Craton, Australia. Miner Deposita 47:129–150
Barnes SJ, Heggie GJ, Fiorentini ML (2013) Spatial variation in platinum group element concentrations in ore-bearing komatiite at the Long-Victor Deposit, Kambalda Dome, Western Australia: enlarging the footprint of nickel sulfide orebodies. Econ Geol 108:913–933
Barnes SJ, Stanley CR, Taranovic V (2022) Compositions and nicu-platinum group element tenors of Nova-Bollinger Ores with implications for the origin of pt anomalies in platinum group element-poor massive sulfides. Econ Geol 117:1687–1707. https://doi.org/10.5382/econgeo.4894
Bezmen NI, Asif M, Brügmann G, Romanenko I, Naldrett A (1994) Distribution of Pd, Rh, Ru, Jr, Os, and Au between sulfide and silicate metals. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 58:1251–1260
Campbell IH, Naldrett AJ (1979) Influence of silicate-sulfide ratios on the geochemistry of magmatic sulfides. Econ Geol 74:1503–1506
Capobianco CJ, Hervig RL, Drake MJ (1994) Experiments on crystal/liquid partitioning of Ru, Rh and Pd for magnetite and hematite solid solutions crystallized from silicate melt. Chem Geol 113:23–43
Chai G, Naldrett AJ (1992) Characteristics of Ni-Cu-Pge Mineralization and Genesis of the Jinchuan Deposit, Northwest China. Econ Geol Bull Soc Econ Geol 87:1475–1495
Chen LM, Song XY, Keays RR, Tian YL, Wang YS, Deng YF, Xiao JF (2013) Segregation and fractionation of magmatic Ni-Cu-PGE sulfides in the western Jinchuan intrusion, northwestern China: insights from platinum group element geochemistry. Econ Geol 108:1793–1811
Chen LM, Song XY, Danyushevsky LV, Wang YS, Tian YL, Xiao JF (2015) A laser ablation ICP-MS study of platinum-group and chalcophile elements in base metal sulfide minerals of the Jinchuan Ni-Cu sulfide deposit, NW China. Ore Geol Rev 65:955–967
Dare SAS, Barnes SJ, Prichard HM (2010) The distribution of platinum group elements (PGE) and other chalcophile elements among sulfides from the Creighton Ni-Cu-PGE sulfide deposit, Sudbury, Canada, and the origin of palladium in pentlandite. Miner Deposita 45:765–793. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-010-0295-6
Ding X, Ripley EM, Li CS (2012) PGE geochemistry of the Eagle Ni-Cu-(PGE) deposit, Upper Michigan: constraints on ore genesis in a dynamic magma conduit. Miner Deposita 47:89–104
Dong Y, Wei B and Wang CY. 2021. Major types and occurrences of platinum-group minerals in the Jinchuan Ni-Cu-(PGE) sulfide deposit: Insights for PGE enrichment during hydrothermal alteration. Acta Petrol Sin (in chinese) 10: 2875–2888
Duan J, Li CS, Qian ZZ, Jiao JG, Ripley EM, Feng YQ (2016) Multiple S isotopes, zircon Hf isotopes, whole-rock Sr-Nd isotopes, and spatial variations of PGE tenors in the Jinchuan Ni-Cu-PGE deposit, NW China. Miner Deposita 51:557–574. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-015-0626-8
Ely JC, Neal CR (2002) Method of data reduction and uncertainty estimation for platinum-group element data using inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Geostand Newsl 26:31–39
Fleet ME, Chryssoulis SL, Stone WE, Weisener CG (1993) Partitioning of platinum-group elements and Au in the Fe-Ni-Cu-S system: experiments on the fractional crystallization of sulfide melt. Contrib Miner Petrol 115:36–44
Hanley JJ, Pettke T, Mungall JE, Spooner ETC (2005) The solubility of platinum and gold in NaCl brines at 1.5 kbar, 600 to 800°C: A laser ablation ICP-MS pilot study of synthetic fluid inclusions. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 69:2593–2611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2004.11.005
Holwell DA, Adeyemi Z, Ward LA, Smith DJ, Graham SD, McDonald L, Smith JW (2017) Low temperature alteration of magmatic Ni-Cu-PGE sulfides as a source for hydrothermal Ni and PGE ores: a quantitative approach using automated mineralogy. Ore Geol Rev 91:718–740
Kang J, Song X-Y, Long T-M, Liang Q-L, Barnes SJ, Chen L-M, Li D-X, Ai Q-X, Gao Y-L (2022) Lithologic and geochemical constraints on the genesis of a newly discovered orebody in the Jinchuan intrusion, NW China. Econ Geol 117:1809–1825. https://doi.org/10.5382/econgeo.4911
Keays RR, Lightfoot PC (2010) Crustal sulfur is required to form magmatic Ni–Cu sulfide deposits: evidence from chalcophile element signatures of Siberian and Deccan Trap basalts. Miner Deposita 45:241–257
Kiseeva ES, Wood BJ (2013) A simple model for chalcophile element partitioning between sulphide and silicate liquids with geochemical applications. Earth Planet Sci Lett 383:68–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2013.09.034
Kitakaze A, Machida T, Komatsu R (2016) Phase Relations in the Fe–ni–s System from 875 To 650 °c. Can Mineral 54:1175–1186. https://doi.org/10.3749/canmin.1500087
Kosyakov V, Sinyakova E (2012) Physicochemical prerequisites for the formation of primary orebody zoning at copper-nickel sulfide deposits (by the example of the systems Fe–Ni–S and Cu–Fe–S). Russ Geol Geophys 53:861–882
Latypov R (2015) Basal reversals in mafic sills and layered intrusions In: Charlier B, Namur O, Latypov R, Tegner C (eds) Layered Intrusions. Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht, pp 259–293
Le Vaillant M, Barnes SJ, Fiorentini ML, Miller J, McCuaig TC, Muccilli P (2015) A hydrothermal Ni-As-PGE geochemical halo around the Miitel Komatiite-Hosted nickel sulfide deposit, Yilgarn Craton, western Australia. Econ Geol 110:505–530
Lehmann J, Arndt N, Windley B, Zhou MF, Wang CY, Harris C (2007) Field relationships and geochemical constraints on the emplacement of the Jinchuan intrusion and its Ni-Cu-PGE sulfide deposit, Gansu, China. Econ Geol 102:75–94. https://doi.org/10.2113/gsecongeo.102.1.75
Lesher CM, Stone WE (1996) Exploration geochemistry of komatiites. In: Wyman DA (ed) Igneous trace elements geochemistry, application for massive sulphide exploration, geological association of Canada (Vol 12, pp 153–204). Short Course Notes, St. John’s
Lesher CM, Burnham OM (2001) Multicomponent elemental and isotopic mixing in Ni-Cu-(PGE) ores at kambalda, Western Australia. Can Mineral 39:421–446. https://doi.org/10.2113/gscanmin.39.2.421
Lesher CM (2017) Roles of xenomelts, xenoliths, xenocrysts, xenovolatiles, residues, and skarns in the genesis, transport, and localization of magmatic Fe-Ni-Cu-PGE sulfides and chromite. Ore Geol Rev 90:465–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.08.008
Lesher CM (2019) Up, down, or sideways: emplacement of magmatic Fe–Ni–Cu–PGE sulfide melts in large igneous provinces1. Can J Earth Sci 56:756–773. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjes-2018-0177
Li Y, Audétat A (2012) Partitioning of V, Mn Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Mo, Ag, Sn, Sb, W, Au, Pb, and Bi between sulfide phases and hydrous basanite melt at upper mantle conditions. Earth Planet Sci Lett 355–356:327–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2012.08.008
Li CS, Ripley EM (2005) Empirical equations to predict the sulfur content of mafic magmas at sulfide saturation and applications to magmatic sulfide deposits. Miner Deposita 40:218–230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-005-0478-8
Li CS, Barnes SJ, Makovicky E, RoseHansen J, Makovicky M (1996) Partitioning of nickel, copper, iridium, rhenium, platinum, and palladium between monosulfide solid solution and sulfide liquid: effects of composition and temperature. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 60:1231–1238
Li CS, Xu ZH, de Waal SA, Ripley EM, Maier WD (2004) Compositional variations of olivine from the Jinchuan Ni-Cu sulfide deposit, western China: implications for ore genesis. Miner Deposita 39:159–172
Li XH, Su L, Chung SL, Li ZX, Liu Y, Song B, Liu DY (2005) Formation of the Jinchuan ultramafic intrusion and the world’s third largest Ni-Cu sulfide deposit: Associated with the ∼825 Ma south China mantle plume? Geochem Geophys Geosyst 6:1–6
Liang QL, Song XY, Wirth R, Chen LM, Dai ZH (2019) Implications of nano- and micrometer-size platinum-group element minerals in base metal sulfides of the Yangliuping Ni-Cu-PGE sulfide deposit, SW China. Chem Geol 517:7–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.04.015
Liu Y, Brenan J (2015) Partitioning of platinum-group elements (PGE) and chalcogens (Se, Te, As, Sb, Bi) between monosulfide-solid solution (MSS), intermediate solid solution (ISS) and sulfide liquid at controlled fO2–fS2 conditions. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 159:139–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2015.03.021
Lu YG, Lesher CM, Deng J (2019) Geochemistry and genesis of magmatic Ni-Cu-(PGE) and PGE-(Cu)-(Ni) deposits in China. Ore Geol Rev 107:863–887
Maier WD, Barnes SJ, Chinyepi G, Barton JM, Eglington B, Setshedi I (2008) The composition of magmatic Ni-Cu-(PGE) sulfide deposits in the Tati and Selebi-Phikwe belts of eastern Botswana. Miner Deposita 43:37–60
Mansur ET, Barnes S-J, Duran CJ (2019) Textural and compositional evidence for the formation of pentlandite via peritectic reaction: Implications for the distribution of highly siderophile elements. Geology 47:351–354
Mansur ET, Barnes S-J, Duran CJ (2021) An overview of chalcophile element contents of pyrrhotite, pentlandite, chalcopyrite, and pyrite from magmatic Ni-Cu-PGE sulfide deposits. Miner Deposita 56:179–204
Mao YJ, Barnes SJ, Duan J, Qin KZ, Godel BM, Jiao JG (2018) Morphology and Particle Size Distribution of Olivines and Sulphides in the Jinchuan Ni-Cu Sulphide Deposit: Evidence for Sulphide Percolation in a Crystal Mush. J Petrol 59:1701–1729. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/egy077
Mavrogenes JA, O’Neill HSC (1999) The relative effects of pressure, temperature and oxygen fugacity on the solubility of sulfide in mafic magmas. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 63:1173–1180. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7037(98)00289-0
Mungall JE (2002) Late-stage sulfide liquid mobility in the main mass of the Sudbury Igneous Complex: examples from the Victor Deep, McCreedy East, and Trillabelle deposits. Econ Geol 97:1563–1576
Mungall JE, Brenan JM (2014) Partitioning of platinum-group elements and Au between sulfide liquid and basalt and the origins of mantle-crust fractionation of the chalcophile elements. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 125:265–289
Mungall JE, Andrews DRA, Cabri LJ, Sylvester PJ, Tubrett M (2005) Partitioning of Cu, Ni, Au, and platinum-group elements between monosulfide solid solution and sulfide melt under controlled oxygen and sulfur fugacities. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 69:4349–4360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2004.11.025
Pearce TH (1968) A contribution to the theory of variation diagrams. Contrib Miner Petrol 19:142–157
Prichard HM, Knight RD, Fisher PC, McDonald I, Zhou M-F, Wang CY (2013) Distribution of platinum-group elements in magmatic and altered ores in the Jinchuan intrusion, China: an example of selenium remobilization by postmagmatic fluids. Miner Deposita 48:767–786. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-013-0454-7
Puchtel IS, Humayun M (2001) Platinum group element fractionation in a komatiitic basalt lava lake. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 65:2979–2993
Qi L, Zhou M, Wang C (2004) Determination of low concentrations of platinum group elements in geological samples by ID-ICP-MS. J Anal at Spectrom 19:1335–1339
Qi L, Gao J, Huang X, Hu J, Zhou M-F, Zhong H (2011) An improved digestion technique for determination of platinum group elements in geological samples. J Anal at Spectrom 26:1900–1904
Righter K, Campbell AJ, Humayun M, Hervig RL (2004) Partitioning of Ru, Rh, Pd, Re, Ir, and Au between Cr-bearing spinel, olivine, pyroxene and silicate melts. Associate editor: C. R Neal Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta 68:867–880
Ripley EM, Li C (2003) Sulfur isotope exchange and metal enrichment in the formation of magmatic Cu-Ni-(PGE) deposits. Econ Geol 98:635–641
Ripley EM, Sarkar A, Li CS (2005) Mineralogic and stable isotope studies of hydrothermal alteration at the Jinchuan Ni-Cu deposit, China. Econ Geol 100:1349–1361
Savard D, Barnes SJ, Meisel T (2010) Comparison between nickel-sulfur fire assay Te Co-precipitation and isotope dilution with high-pressure asher acid digestion for the determination of platinum-group elements, rhenium and gold. Geostand Geoanal Res 34:281–291
Sixth Geological Unit (1984) Geology of the Baijiaozuizi Cu-Ni sulfide deposit. Geological Survey of Gansu Province, Geological publishing House, Beijing, Sixth Geological Unit
Song XY, Zhou MF, Wang CY, Qi L, Zhang CJ (2006) Role of crustal contamination in formation of the Jinchuan intrusion and its world-class Ni-Cu-(PGE) sulfide deposit, northwest China. Int Geol Rev 48:1113–1132
Song XY, Keays RR, Zhou MF, Qi L, IhIenfeld C, Xiao JF (2009) Siderophile and chalcophile elemental constraints on the origin of the Jinchuan Ni-Cu-(PGE) sulfide deposit, NW China. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 73:404–424
Song XY, Danyushevsky LV, Keays RR, Chen LM, Wang YS, Tian YL, Xiao JF (2012) Structural, lithological, and geochemical constraints on the dynamic magma plumbing system of the Jinchuan Ni-Cu sulfide deposit, NW China. Miner Deposita 47:277–297
Song XY, Wang KY, Barnes SJ, Yi JN, Chen LM, Schoneveld LE (2020) Petrogenetic insights from chromite in ultramafic cumulates of the Xiarihamu intrusion, northern Tibet Plateau, China. Am Miner 105:479–497
Stanley CR, Russell JK (1989) Petrologic hypothesis testing with Pearce element ratio diagrams: derivation of diagram axes. Contrib Miner Petrol 103:78–89
Su SG, Li CS, Zhou MF, Ripley EM, Qi L (2008) Controls on variations of platinum-group element concentrations in the sulfide ores of the Jinchuan Ni-Cu deposit, western China. Miner Deposita 43:609–622
Sullivan NA, Zajacz Z, Brenan JM, Hinde JC, Tsay A, Yin Y (2022a) The solubility of gold and palladium in magmatic brines: Implications for PGE enrichment in mafic-ultramafic and porphyry environments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 316:230–252
Sullivan NA, Zajacz Z, Brenan JM, Tsay A (2022b) The solubility of platinum in magmatic brines: Insights into the mobility of PGE in ore-forming environments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 316:253–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2021.09.014
Tang ZL, Li WY (1995) Mineralization model and geology of the Jinchuan deposit bearing PGE. Geological Publishing House (in Chinese), Beijing
Tang ZL (1991) Formation of the Jinchuan Cu–Ni sulfide deposit. Modern Geol (in Chinese) 4:55–64
Tonnelier NJ (2010) Geology and genesis of the Jinchuan Ni-Cu-(PGE) deposit, China: Unpublished Ph.D. thesis, Sudbury, Canada, Laurentian University, pp 1–192
Waal SD, Xu Z, Li C, Mouri H (2004) Emplacement of viscous mushes in the Jinchuan ultramafic intrusion, western China. Can Mineral 42:371–392
Waldner P, Pelton AD (2004) Critical thermodynamic assessment and modeling of the Fe-Ni-S system. Metall and Mater Trans B 35:897–907. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-004-0084-7
Xie W, Song XY, Chen LM, Deng YF, Zheng WQ, Wang YS, Ba DH, Yin MH, Luan Y (2014) Geochemistry insights on the genesis of the subduction-related Heishan magmatic Ni-Cu-(PGE) deposit, Gansu, northwestern China, at the Southern Margin of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Econ Geol 109:1563–1583
Yang S, Qu W, Tian Y, Chen J, Yang G, Du A (2008) Origin of the inconsistent apparent Re–Os ages of the Jinchuan Ni–Cu sulfide ore deposit, China: Post-segregation diffusion of Os. Chem Geol 247:401–418
Zhang M, Kamo SL, Li C, Hu P, Ripley EM (2010) Precise U-Pb zircon–baddeleyite age of the Jinchuan sulfide ore-bearing ultramafic intrusion, western China. Miner Deposita 45:3–9
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Science Foundation of China projects (42121003, 41772067, and 41630316) to X.-Y. Song. We thank Chusi Li of Indiana University for useful discussion, plus editing the abstract and conclusions of the first draft. We are indebted to Mr. Ya-Lin Gao, Mei-Lin Xiao and Yuan-Zhi Meng of Jinchuan Company for their logistic support in sampling, and to Dr. Da-Peng Wang and Ms. Yi-Fan Yin for their assistance in PGE analysis. Constructive reviews from MC Lesher, David Evans and Wolfgang Maier are greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interest.
Additional information
Editorial handling: W. D. Maier
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Long, TM., Song, XY., Kang, J. et al. Genesis of No. 2 orebody of the Jinchuan magmatic Ni-Cu-(PGE) sulfide deposit, NW China: New constraints from the newly discovered deep extension. Miner Deposita 58, 1317–1332 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-023-01184-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-023-01184-w