Abstract
Key message
Through a map-based cloning approach, a gene coding for an R2R3-MYB transcription factor was identified as a causal gene for the I locus controlling the dominant white bulb color in onion.
Abstract
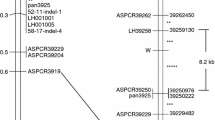
White bulb colors in onion (Allium cepa L.) are determined by either the C or I loci. The causal gene for the C locus was previously isolated, but the gene responsible for the I locus has not been identified yet. To identify candidate genes for the I locus, an approximately 7-Mb genomic DNA region harboring the I locus was obtained from onion and bunching onion (A. fistulosum) whole genome sequences using two tightly linked molecular markers. Within this interval, the AcMYB1 gene, known as a positive regulator of anthocyanin production, was identified. No polymorphic sequences were found between white and red AcMYB1 alleles in the 4,860-bp full-length genomic DNA sequences. However, a 4,838-bp LTR-retrotransposon was identified in the white allele, in the 79-bp upstream coding region from the stop codon. The insertion of this LTR-retrotransposon created a premature stop codon, resulting in the replacement of 26 amino acids with seven different residues. A molecular marker was developed based on the insertion of this LTR-retrotransposon to genotype the I locus. A perfect linkage between bulb color phenotypes and marker genotypes was observed among 5,303 individuals of segregating populations. The transcription of AcMYB1 appeared to be normal in both red and white onions, but the transcription of CHS-A, which encodes chalcone synthase and is involved in the first step of the anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway, was inactivated in the white onions. Taken together, an aberrant AcMYB1 protein produced from the mutant allele might be responsible for the dominant white bulb color in onions.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Nucleotide sequences of AcMYB1 alleles are accessible at NCBI database under the accession numbers of PP095636 and PP095637. Detailed information of the onion genome sequence (DHW30006) is available at NCBI under the BioProject number of PRJNA912256. The raw sequences of RNA-Seq reads are available upon request.
References
Albert NW, Davies KM, Lewis DH, Zhang H, Montefiori M, Brendolise C, Boase MR, Ngo H, Jameson PE, Schwinn KE (2014) A conserved network of transcriptional activators and repressors regulates anthocyanin pigmentation in eudicots. Plant Cell 26:962–980
Anders S, Huber W (2010) Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol 11:R106
Andersen SL, Jensen TH (2015) Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay: an intricate machinery that shapes transcriptomes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 16:665–677
Antonescu C, Antonescu V, Sultana R, Quackenbush J (2010) Using the DFCI gene index batabases for biological discovery. Curr Protoc Bioinform 29:1.6.1-1.6.36
Baek G, Kim C, Kim S (2017) Development of a molecular marker tightly linked to the C locus conferring a white bulb color in onion (Allium cepa L.) using bulked segregant analysis and RNA-seq. Mol Breed 37:94
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics, btu170
Brewster JL (2008) Onions And Other Vegetable Alliums. CAB international, Wallingford, UK
Cao J, Chen W, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Zhao X (2010) Content of selected flavonoids in 100 edible vegetables and fruits. Food Sci Technol Res 16:395–402
Castresana J (2000) Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol Biol Evol 17:540–552
Chin S, Behm CA, Mathesius U (2018) Functions of flavonoids in plant-nematode interactions. Plants 7:85
Clarke AE, Jones HA, Little TM (1944) Inheritance of bulb color in the onion. Genetics 29:569–575
Dixon RA, Pasinetti GM (2010) Flavonoids and isoflavonoids: from plant biology to agriculture and neuroscience. Plant Physiol 154:453–457
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem Bull 19:11–15
Du H, Liang Z, Zhao S, Nan M, Tran LP, Lu K, Huang Y, Li J (2015) The evolutionary history of R2R3-MYB proteins across 50 eukaryotes: new insights into subfamily classification and expansion. Sci Rep 5:11037
Dubos C, Stracke R, Grotewold E, Weisshaar B, Martin C, Lepiniec L (2010) MYB transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trend Plant Sci 15:573–581
Edae EA, Rouse MN (2019) Bulked segregant analysis RNA-seq (BSR-Seq) validated a stem resistance locus in Aegilops umbellulata, a wild relative of wheat. PLoS ONE 14:e0215492
El-Shafie MW, Davis GN (1967) Inheritance of bulb color in the onion (Allium cepa L.). Hilgardia 38:607–622
Fini A, Brunetti C, Di Ferdinando M, Ferrini F, Tattini M (2011) Stress-induced flavonoid biosynthesis and the antioxidant machinery of plants. Plant Signal Behav 6:709–711
Finkers R, van Kaauwen M, Ament K, Burger-Meijer K, Egging R, Huits H, Kodde L, Kroon L, Shigyo M, Sato S, Vosman B, van Workum W, Scholten O (2021) Insights from the first genome assembly of Onion (Allium cepa). G3 11:jkab243
Fujito S, Akyol TY, Mukae T, Wako T, Yamashita K, Tsukazaki H, Hirakawa H, Tanaka K, Mine Y, Sato S, Shigyo M (2021) Construction of a high-density linkage map and graphical representation of the arrangement of transcriptome-based unigene markers on the chromosomes of onion. Allium Cepa l BMC Genom 22:481
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Window 95/98/NT. Nucl Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Han J, Kim C, Kim S (2023) Genetic analysis of the interaction between G and R loci involved in the determination of bulb colors in onion (Allium cepa L.). Hortic Environ Biotechnol 64:801–810
Heppel SC, Jaffé FW, Takos AM, Schellmann S, Rausch T, Walker AR, Bogs J (2013) Identification of key amino acids for the evolution of promoter target specificity of anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin regulating MYB factors. Plant Mol Biol 82:457–471
Hichri I, Barrieu F, Bogs J, Kappel C, Delrot S, Lauvergeat V (2011) Recent advances in the transcriptional regulation of the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway. J Exp Bot 62:2465–2483
Holton TA, Cornish EC (1995) Genetics and biochemistry of anthocyanin biosynthesis. Plant Cell 7:1070–1083
Jaakola L (2013) New insights into the regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in fruits. Trends Plant Sci 18:477–483
Jeon S, Han J, Kim C, Kim J, Moon J, Kim S (2022) Identification of a candidate gene responsible for the G locus determining chartreuse bulb color in onion (Allium cepa L.) using bulked segregant RNA-Seq. Theor Appl Genet 135:1025–1036
Jo C, Kim S (2020) Transposition of a non-autonomous DNA transposon in the gene coding for a bHLH transcription factor results in a white bulb color of onions (Allium cepa L.). Theor Appl Genet 133:317–328
Khandagale K, Gawande S (2019) Genetic of bulb colour variation and flavonoids in onion. J Hortic Sci Biotech 94:522–532
Kim B, Kim S (2019) Identification of a variant of CMS-T cytoplasm and development of high resolution melting markers for distinguishing cytoplasm types and genotyping a restorer-of-fertility locus in onion (Allium cepa L.). Euphytica 215:164
Kim S, Binzel ML, Yoo K, Park S, Pike LM (2004) Pink (P), a new locus responsible for pink trait in onions (Allium cepa) resulting from natural mutations of anthocyanidin synthase. Mol Gen Genom 272:18–27
Kim S, Jones R, Yoo K, Pike LM (2005a) The L locus, one of complementary genes required for anthocyanin production in onions (Allium cepa), encodes anthocyanidin synthase. Theor Appl Genet 111:120–127
Kim S, Yoo K, Pike LM (2005b) Development of a PCR-based marker utilizing a deletion mutation in the DFR (dihydroflavonol 4-reductase) gene responsible for the lack of anthocyanin production in yellow onions (Allium cepa). Theor Appl Genet 110:588–595
Kim S, Yoo K, Pike LM (2005c) The basic color factor, the C locus, encodes a regulatory gene controlling transcription of chalcone synthase genes in onions (Allium cepa). Euphytica 142:273–282
Kim S, Park JY, Yang T (2015) Characterization of three active transposable elements recently inserted in three independent DFR-A alleles and one high-copy DNA transposon isolated from the Pink allele of the ANS gene in onion (Allium cepa L.). Mol Genet Genom 290:1027–1037
Kim E, Kim C, Kim S (2016) Identification of two novel mutant ANS alleles responsible for inactivation of anthocyanidin synthase and failure of anthocyanin production in onion (Allium cepa L.). Euphytica 212:427–437
Kranz HD, Denekamp M, Greco R, Jin H, Leyva A, Meissner RC, Petroni K, Urzainqui A, Bevan M, Martin C, Smeekens S, Tonelli C, Paz-Ares J, Weisshaar B (1998) Towards functional characterization of the members of the R2R3-MYB gene family from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:263–276
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874
Kurtz S, Phillippy A, Delcher AL, Smoot M, Shumway M, Antonescu C, Salzberg SL (2004) Versatile and open software for comparing large genomes. Genome Biol 5:R12
LaFountain AM, Yuan Y (2021) Repressors of anthocyanin biosynthesis. New Phytol 231:933–949
Li X, Cao L, Jiao B, Yang H, Ma C, Liang Y (2022) The bHLH transcription factor AcB2 regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis in onion (Allium cepa L.). Hortic Res 9:128
Liao N, Hu Z, Miao J et al (2022) Chromosome-level genome assembly of bunching onion illuminates genome evolution and flavor formation in Allium crops. Nat Commun 13:6690
Liu S, Yeh C, Tang HM, Nettleton D, Schnable PS (2012) Gene mapping via bulked segregant RNA-Seq (BSR-Seq). PLoS ONE 7:e36406
Naing AH, Kim CK (2018) Roles of R2R3-MYB transcription factors in transcriptional regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in horticultural plants. Plant Mol Biol 98:1–18
Neumann P, Novák P, Hoštáková N, Macas J (2019) Systematic survey of plant LTR-retrotransposons elucidates phylogenetic relationships of their polyprotein domains and provides a reference for element classification. Mob DNA 10:1
Nickless A, Bailis JM, You Z (2017) Control of gene expression through the nonsense-mediated RNA decay pathway. Cell Biosci 7:26
Passeri V, Koes R, Quattrocchio FM (2016) New challenges for the design of high value plant products: stabilization of anthocyanins in plant vacuoles. Front Plant Sci 7:153
Petroni K, Tonelli C (2011) Recent advances on the regulation of anthocyanin synthesis in reproductive organs. Plant Sci 181:219–229
Ramsay NA, Glover BJ (2005) MYB-bHLH-WD40 protein complex and the evolution of cellular diversity. Trends Plant Sci 10:63–70
Ricroch A, Yockteng R, Brown SC, Nadot S (2005) Evolution of genome size across some cultivated Allium species. Genome 48:511–520
Scarano A, Chieppa M, Santino A (2018) Looking at flavonoid biodiversity in horticultural crops: a colored mine with nutritional benefits. Plants 7:98
Schwinn KE, Ngo H, Kenel F, Brummell DA, Albert NW, McCallum JA, Pither-Joyce M, Crowhurst RN, Eady C, Davies KM (2016) The onion (Allium cepa L.) R2R3-MYB gene MYB1 regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis. Front Plant Sci 7:1865
Seo I, Kim J, Moon J, Kim S (2020) Construction of a linkage map flanking the I locus controlling dominant white bulb color and analysis of differentially expressed genes between dominant white and red bulbs in onion (Allium cepa L.). Euphytica 216:97
Slimestad R, Fossen T, Vågen IM (2007) Onions: a source of unique dietary flavonoids. J Agric Food Chem 55:10067–10080
Sohn S, Ahn Y, Lee T, Lee J, Jeong M, Seo C, Chandra R, Kwon Y, Kim C, Kim D, Won S, Kim JS, Choi D (2016) Construction of a draft reference transcripts of onion (Allium cepa) using long-read sequencing. Plant Biotechnol Rep 10:383–390
Song S, Kim C, Moon JS, Kim S (2014) At least nine independent natural mutations of the DFR-A gene are responsible for appearance of yellow onions (Allium cepa L.) from red progenitors. Mol Breed 33:173–186
Stracke R, Werber M, Weisshaar B (2001) The R2R3-MYB gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr Opin Plant Biol 4:447–456
Van der Auwera GA, O’Connor BD (2020) Genomics in the cloud: using Docker, GATK, and WDL in Terra. In: O'Reilly Media
Voorrips RE (2002) MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Hered 93:77–78
Waterhouse AM, Procter JB, Martin DMA, Clamp M, Barton GJ (2009) Jalview Version 2—a multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench. Bioinformatics 25:1189–1191
Wicker T, Sabot F, Hua-Van A, Bennetzen JL, Capy P, Chalhoub B, Flavell A, Leroy P, Morgante M, Panaud O, Paux E, SanMiguel P, Schulman AH (2007) A unified classification system for eukaryotic transposable elements. Nat Rev Genet 8:973–982
Wu Y, Wen J, Xia Y, Zhang L, Du H (2022) Evolution and functional diversification of R2R3-MYB transcription factors in plants. Hortic Res 9:uhac058
Xie D, Tan J, Yu Y, Gui L, Su D, Zhou S, He X (2020a) Insight into phylogeny, age and evolution of Allium (Amaryllidaceae) based on the whole plastome sequences. Ann Bot 125:1039–1055
Xie S, Lei Y, Chen H, Li J, Chen H, Zhang Z (2020b) R2R3-MYB transcription factors regulate anthocyanin biosynthesis in grapevine vegetative tissues. Front Plant Sci 11:527
Xu Z, Feng K, Que F, Wang F, Xiong A (2017) A MYB transcription factor, DcMYB6, is involved in regulating anthocyanin biosynthesis in purple carrot taproots. Sci Rep 7:45324
Yamazaki M, Makita Y, Springob K, Saito K (2003) Regulatory mechanisms for anthocyanin biosynthesis in chemotypes of Perilla frutescens var. crispa. Biochem Eng J 14:191–197
Zaynab M, Fatima M, Abbas S, Sharif Y, Umair M, Zafar MH, Bahadar K (2018) Role of secondary metabolites in plant defense against pathogens. Microb Pathog 124:198–202
Zhang M, Huang S, Gao Y, Fu W, Qu G, Zhao Y, Shi F, Liu Z, Feng H (2020) Fine mapping of a leaf flattening gene Bralcm through BSR-Seq in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. spp. pekinensis). Sci Rep 10:13924
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture and Forestry (No. 322067-03-3-HD020) and the BK21 FOUR funded by the Ministry of Education of Korea and National Research Foundation of Korea. The authors thank Ji-wha Hur, Jeong-Ahn Yoo, and Su-jung Kim for their dedicated technical assistance.
Funding
This study was funded by Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, 322067-03-3-HD020, Sunggil Kim.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Geonjoong Kim performed experiments and drafted the manuscript. Heejung Cho assembled the draft whole genome sequence of onion (DHW30006). Sunggil Kim organized and coordinated this research project and edited the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to this study to disclose.
Ethical approval
All experiments performed in this study were in compliance with the current laws of the Republic of Korea.
Additional information
Communicated by Sandra Elaine Branham.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
122_2024_4626_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplementary Fig. 2. Dot plot showing the alignment of 7.52-Mb bunching onion and 6.87-Mb onion sequences (DHW30006) containing the I locus. Blue and red colors indicate parallel and antiparallel orientations of alignments, respectively. (TIF 133 KB)
122_2024_4626_MOESM3_ESM.tif
Supplementary Fig. 3. Alignment of AcMYB1 and two homologs (Ace03g21065 and AfisC3G03591) identified from the whole genome sequences of onion (DHW30006) and bunching onion, respectively. A. Alignment of cDNA sequences of the three genes encoding R2R3-MYB transcription factors. B. Alignment of deduced amino acid sequences of the three genes encoding R2R3-MYB transcription factors. (TIF 399 KB)
122_2024_4626_MOESM4_ESM.tif
Supplementary Fig. 4. Phylogenetic tree of the reverse transcriptase (RT) domains of Ivana-AcMYB1 and 16 families from the Ty1/copia superfamily. An LTR-retrotransposon (Athila) from the Ty3/gypsy superfamily is used as an outgroup. The REXdb identification numbers of the LTR-retrotransposons are shown as taxon names. Detailed information on the LTR-retrotransposons is provided in Supplementary Table 5. (TIF 63 KB)
122_2024_4626_MOESM5_ESM.tif
Supplementary Fig. 5. Bulb color phenotypes of F4 individuals with three distinct genotypes of the I locus. Three representative bulbs were selected for each genotype from the WR15-5 population. (TIF 333 KB)
122_2024_4626_MOESM6_ESM.tif
Supplementary Fig. 6. Phylogenetic tree of R2R3-MYB transcription factors isolated from onion and other plant species. Detailed information about each protein is provided in Supplementary Table 4. (TIF 81 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, G., Cho, H. & Kim, S. Identification of a candidate gene for the I locus determining the dominant white bulb color in onion (Allium cepa L.). Theor Appl Genet 137, 118 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-024-04626-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-024-04626-9