Abstract
Key message
An enhanced-grain number per spike locus from Agropyron cristatum 6PL was mapped onto 6PL (0.27–0.51) via deletion mapping, and its effect was further verified by evaluating a newly created translocation line.
Abstract
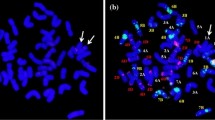
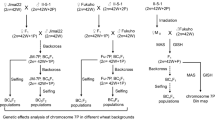
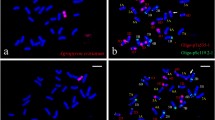
Agropyron cristatum (2n = 4x = 28, PPPP) is an important wild relative of common wheat and carries many desirable yield-related traits. The wheat-A. cristatum 6P disomic addition line 4844-12 exhibited high grain number per spike (GNS), high spikelet number per spike (SNS), and high kernel number per spikelet (KNS). In this study, five A. cristatum 6P deletion lines, five wheat-A. cristatum 6P translocation lines, and genetic populations of these lines were used to map the enhanced-GNS locus from A. cristatum chromosome 6P, which were genotyped via genomic in situ hybridization, fluorescence in situ hybridization, or molecular markers. According to the evaluation of the agronomic traits in four growing seasons (2014–2015, 2015–2016, 2016–2017, and 2017–2018), we found that the deletion lines and the translocation lines carrying the long arm of A. cristatum chromosome 6P (6PL) exhibited high GNS, SNS, and KNS, and the enhanced-GNS locus was ultimately mapped onto 6PL (0.27–0.51). To verify the localization results, we created a new translocation line WAT650a (T5BL•5BS-6PL) that carried 6PL (0.35–0.42); this line exhibited higher GNS and SNS than the recipient parent Fukuhokomugi (Fukuho). Collectively, the enhanced-GNS locus of A. cristatum 6PL can be important for improving yield traits in common wheat; the translocation lines with the enhanced-GNS locus can serve as novel and valuable germplasm resources for wheat breeding.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GNS:
-
Grain number per spike
- SNS:
-
Spikelet number per spike
- KNS:
-
Kernel number per spikelet
- GISH:
-
Genomic in situ hybridization
- FISH:
-
Fluorescence in situ hybridization
- TGW:
-
Thousand-grain weight
References
Bevan MW, Uauy C, Wulff BBH, Zhou J, Krasileva K, Clark MD (2017) Genomic innovation for crop improvement. Nature 543:346–354
Boden SA, Cavanagh C, Cullis BR, Ramm K, Greenwood J, Jean Finnegan E, Trevaskis B, Swain SM (2015) Ppd-1 is a key regulator of inflorescence architecture and paired spikelet development in wheat. Nat Plants 1:14016
Cao AZ, Xing LP, Wang XY, Yang XM, Wang W, Sun YL, Qian C, Ni JL, Chen YP, Liu DJ, Wang XE, Chen PD (2011) Serine/threonine kinase gene Stpk-V, a key member of powdery mildew resistance gene Pm21, confers powdery mildew resistance in wheat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:7727–7732
Chen PD, You CF, Hu Y, Chen SW, Zhou B, Cao AZ, Wang XE (2013) Radiation-induced translocations with reduced Haynaldia villosa chromatin at the Pm21 locus for powdery mildew resistance in wheat. Mol Breed 31:477–484
Copete A, Cabrera A (2017) Chromosomal location of genes for resistance to powdery mildew in Agropyron cristatum and mapping of conserved orthologous set molecular markers. Euphytica 213:189
Cuadrado A, Schwarzacher T, Jouve N (2000) Identification of different chromatin classes in wheat using in situ hybridization with simple sequence repeat oligonucleotides. Theor Appl Genet 101:711–717
Cuthbert JL, Somers DJ, Brûlé-Babel AL, Brown PD, Crow GH (2008) Molecular mapping of quantitative trait loci for yield and yield components in spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 117:595–608
Dewey DR (1984) The genomic system of classification as a guide to intergeneric hybridization with the perennial Triticeae. In: Gustafson JP (ed) Gene manipulation in plant improvement. Plenum Press, New York, pp 209–279
Dong YC, Zhou RH, Xu SJ, Li LH, Cauderon Y, Wang RRC (1992) Desirable characteristics in perennial Triticeae collected in China for wheat improvement. Hereditas 116:175–178
Dubcovsky J, Dvorak J (2007) Genome plasticity a key factor in the success of polyploid wheat under domestication. Science 316:1862–1866
Han HM, Liu WH, Lu YQ, Zhang JP, Yang XM, Li X, Hu Z, Li LH (2017) Isolation and application of P genome-specific DNA sequences of Agropyron Gaertn. in Triticeae. Planta 245:425–437
Kang HY, Zhang ZJ, Xu LL, Qi WL, Tang Y, Wang H, Zhu W, Li DY, Zeng J, Wang Y, Fan X, Sha LN, Zhang HQ, Zhou YH (2016) Characterization of wheat-Psathyrostachys huashanica small segment translocation line with enhanced kernels per spike and stripe rust resistance. Genome 59:221–229
Kato K, Miura H, Sawada S (2000) Mapping QTLs controlling grain yield and its components on chromosome 5A of wheat. Theor Appl Genet 101:1114–1121
Li WL, Li ZS, Mu SM (1990) A cytological study of chromosomal structure changes in a common wheat variety, Xiaoyan No. 6. Acta Genet Sin 17:430–437
Li LH, Dong YC, Zhou RH, Li XQ, Li P (1995) Cytogenetics and self-fertility of hybrids between Triticum aestivum L. and Agropyron cristatum (L.) Gaertn. Acta Genet Sin 22:109–114
Li LH, Li XQ, Li P, Dong YC, Zhao GS (1997) Establishment of wheat-Agropyron cristatum alien addition lines. I. Cytology of F3, F2BC1, BC4, and BC3F1 progenies. Acta Genet Sin 24:154–159
Li HH, Jiang B, Wang JC, Lu YQ, Zhang JP, Pan CL, Yang XM, Li XQ, Liu WH, Li LH (2017) Mapping of novel powdery mildew resistance gene(s) from Agropyron cristatum chromosome 2P. Theor Appl Genet 130:109–121
Limin AE, Fowler DB (1990) An interspecific hybrid and amphiploid produced from Triticum aestivum crosses with Agropyron cristatum and Agropyron desertorum. Genome 33:581–584
Lu MJ, Lu YQ, Li HH, Pan CL, Guo Y, Zhang JP, Yang XM, Li XQ, Liu WH, Li LH (2017) Transferring desirable genes from Agropyron cristatum 7P chromosome into common wheat. PLoS ONE 11:e0159577
Lukaszewski AJ (2001) Breeding behavior of the cytogenetically engineered wheat-rye translocation chromosome 1RS•1BL. Crop Sci 41:1062–1065
Miura K, Ikeda M, Matsubara A, Song XJ, Ito M, Asano K, Matsuoka M, Kitano H, Ashikari M (2010) OsSPL14 promotes panicle branching and higher grain productivity in rice. Nat Genet 42:545–549
Ochoa V, Madrid E, Said M, Rubiales D, Cabrera A (2015) Molecular and cytogenetic characterization of a common wheat-Agropyron cristatum chromosome translocation conferring resistance to leaf rust. Euphytica 201:89–95
Pu J, Wang Q, Shen YF, Zhuang LF, Li CX, Tan MF, Bie TD, Chu CG, Qi ZJ (2015) Physical mapping of chromosome 4J of Thinopyrum bessarabicum using gamma radiation-induced aberrations. Theor Appl Genet 128:1319–1328
Sears ER, Gustafson JP (1993) Use of radiation to transfer alien chromosome segments to wheat. Crop Sci 33:897–901
Song LQ, Lu YQ, Zhang JP, Pan CL, Yang XM, Li XQ, Liu W, Li LH (2016a) Physical mapping of Agropyron cristatum chromosome 6P using deletion lines in common wheat background. Theor Appl Genet 129:1023–1034
Song LQ, Lu YQ, Zhang JP, Pan CL, Yang XM, Li XQ, Liu WH, Li LH (2016b) Cytological and molecular analysis of wheat-Agropyron cristatum translocation lines with 6P chromosome fragments conferring superior agronomic traits in common wheat. Genome 59:840–850
Sourdille P, Singh S, Cadalen T, Brown-Guedira GL, Gay G, Qi L, Gill BS, Dufour P, Murigneux A, Bernard M (2004) Microsatellite-based deletion bin system for the establishment of genetic–physical map relationships in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Funct Integr Genom 4:12–25
Tang ZX, Yang ZJ, Fu SL (2014) Oligonucleotides replacing the roles of repetitive sequences pAs1, pSc119.2, pTa-535, pTa71, CCS1, and pAWRC.1 for FISH analysis. J Appl Genet 55:313–318
Wang HJ, Yu ZH, Li B, Lang T, Li GR, Yang ZJ (2018) Characterization of new wheat-Dasypyrum breviaristatum introgression lines with superior gene(s) for spike length and stripe rust resistance. Cytogenet Genome Res 156:117–125
Wu J, Yang XM, Wang H, Li HJ, Li LH, Li XQ, Liu WH (2006) The introgression of chromosome 6P specifying for increased numbers of florets and kernels from Agropyron cristatum into wheat. Theor Appl Genet 114:13–20
Xing LP, Hu P, Liu JP et al (2018) Pm21 from Haynaldia villosa encodes a CC-NBS-LRR protein conferring powdery mildew resistance in wheat. Mol Plant 11:874–878
Zhang RQ, Hou F, Feng YG, Zhang W, Zhang MY, Chen PD (2015) Characterization of a Triticum aestivum-Dasypyrum villosum T2VS•2DL translocation line expressing a longer spike and more kernels traits. Theor Appl Genet 128:2415–2425
Zhang J, Zhang JP, Liu WH, Wu XY, Yang XM, Li XQ, Lu YQ, Li LH (2016) An intercalary translocation from Agropyron cristatum 6P chromosome into common wheat confers enhanced kernel number per spike. Planta 244:853–864
Zhang JP, Liu WH, Lu YQ, Liu QX, Yang XM, Li XQ, Li LH (2017a) A resource of large-scale molecular markers for monitoring Agropyron cristatum chromatin introgression in wheat background based on transcriptome sequences. Sci Rep 7:11942
Zhang Z, Song LQ, Han HM, Zhou SH, Zhang JP, Yang XM, Li XQ, Liu WH, Li LH (2017b) Physical localization of a locus from Agropyron cristatum conferring resistance to stripe rust in common wheat. Int J Mol Sci 18:2403
Zhang J, Ma HH, Zhang JP, Zhou SH, Han HM, Liu WH, Li XQ, Yang XM, Li LH (2018) Molecular cytogenetic characterization of an Agropyron cristatum 6PL chromosome segment conferring superior kernel traits in wheat. Euphytica 214:198
Zheng TC, Zhang XK, Yin GH, Wang LN, Han YL, Chen L, Huang F, Tang JW, Xia XC, He ZH (2011) Genetic gains in grain yield, net photosynthesis and stomatal conductance achieved in Henan Province of China between 1981 and 2008. Field Crops Res 122:225–233
Zhou Y, He ZH, Sui XX, Xia XC, Zhang XK, Zhang GS (2007) Genetic improvement of grain yield and associated traits in the northern China winter wheat region from 1960 to 2000. Crop Sci 47:245–253
Zhou SH, Zhang JP, Che YH, Liu WH, Lu YH, Yang XM, Li XQ, Jia JZ, Liu X, Li LH (2018) Construction of Agropyron Gaertn. genetic linkage maps using a wheat 660K SNP array reveals a homoeologous relationship with the wheat genome. Plant Biotechnol J 16:818–827
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS-ASTIP-2017-ICS) and the Chinese Agriculture Research System (CARS-03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by P. Heslop-Harrison.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Han, H., Liu, W. et al. Deletion mapping and verification of an enhanced-grain number per spike locus from the 6PL chromosome arm of Agropyron cristatum in common wheat. Theor Appl Genet 132, 2815–2827 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-019-03390-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-019-03390-5