Abstract
Introduction
The use of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT) is controversial in Ultra-Central lung tumors, a subset of central lung tumors characterized by proximity to critical mediastinal structures. This is of interest in oligometastatic (≤3 metastases) patients, who can yield survival benefit from local treatments. The aim of our study is to assess the determinants of efficacy and toxicity in this setting.
Materials and methods
Clinical and dosimetric parameters were reviewed in a cohort of oligometastatic patients treated with SBRT for ultra-central tumors. Local control rate (LC) and toxicity were assessed. Statistical Analysis was carried out to assess the impact of those predictors on local recurrence and adverse events.
Results
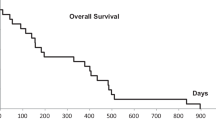
One-hundred-nine consecutive patients were included. A median Biologic Effective Dose (BED) of 105 (75–132) Gy10 was prescribed. At a median follow-up of 17 (range 3–78) months, 2-year LC was 87%. Improved LC was correlated to Planning Treatment Volume (PTV) covered by 95% of the prescription dose (V95% PTV) > 85% (HR 0.15, 95%CI 0.05–0.49, p = 0.0017) and to Gross Tumor Volume (GTV) < 90 cm3 (HR 0.2, 95%CI 0.07–0.56, p = 0.0021). Overall and grade ≥ 3 toxicity incidence was 20% and 5%, respectively. Patients experiencing acute and late toxicities received significantly higher dose to 1 cm3 (D1cm3) of esophagus and lung volume receiving ≥5 Gy (V5Gy) (p = 0.016 and p = 0.013), and higher dose to 0.1 cm3 (D0.1cm3) of heart (p = 0.036), respectively.
Conclusion
V95% PTV > 85% and GTV < 90 cm3 are independent predictors of LC. Dose to esophagus, lung and heart should be carefully assessed to minimize treatment-related toxicities.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Timmerman R, Paulus R, Galvin J, Michalski J, Straube W, Bradley J, Fakiris A, Bezjak A, Videtic G, Johnstone D, Fowler J, Gore E, Choy H (2010) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for inoperable early stage lung cancer. JAMA 303(11):1070–1076. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2010.261
Onishi H, Araki T, Shirato H, Nagata Y, Hiraoka M, Gomi K, Yamashita T, Niibe Y, Karasawa K, Hayakawa K, Takai Y, Kimura T, Hirokawa Y, Takeda A, Ouchi A, Hareyama M, Kokubo M, Hara R, Itami J, Yamada K (2004) Stereotactic hypofractionated high-dose irradiation for stage I nonsmall cell lung carcinoma: clinical outcomes in 245 subjects in a Japanese multiinstitutional study. Cancer 101(7):1623–1631
Palma DA, Olson R, Harrow S, Gaede S, Louie AV, Haasbeek C, Mulroy L, Lock M, Rodrigues GB, Yaremko BP, Schellenberg D, Ahmad B, Griffioen G, Senthi S, Swaminath A, Kopek N, Liu M, Moore K, Currie S, Bauman GS, Warner A, Senan S (2019) Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy versus standard of care palliative treatment in patients with oligometastatic cancers (SABR-COMET): a randomised, phase 2, open-label trial. Lancet 393(10185):2051–2058. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32487-5
Timmerman R, McGarry R, Yiannoutsos C, Papiez L, Tudor K, DeLuca J, Ewing M, Abdulrahman R, DesRosiers C, Williams M, Fletcher J (2006) Excessive toxicity when treating central tumors in a phase II study of stereotactic body radiation therapy for medically inoperable early-stage lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 24(30):4833–4839
Park HS, Harder EM, Mancini BR, Decker RH (2015) Central versus peripheral tumor location: influence on survival, local control, and toxicity following stereotactic body radiotherapy for primary non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 10(5):832–837. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0000000000000484
Mangona VS, Aneese AM, Marina O, Hymas RV, Ionascu D, Robertson JM, Gallardo LJ, Grills IS (2015) Toxicity after central versus peripheral lung stereotactic body radiation therapy: a propensity score matched-pair analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 91(1):124–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2014.08.345
Modh A, Rimner A, Williams E, Foster A, Shah M, Shi W, Zhang Z, Gelblum DY, Rosenzweig KE, Yorke ED, Jackson A, Wu AJ (2014) Local control and toxicity in a large cohort of central lung tumors treated with stereotactic body radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 90(5):1168–1176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2014.08.008
Chang JY, Li QQ, Xu QY, Allen PK, Rebueno N, Gomez DR, Balter P, Komaki R, Mehran R, Swisher SG, Roth JA (2014) Stereotactic ablative radiation therapy for centrally located early stage or isolated parenchymal recurrences of non-small cell lung cancer: how to fly in a “no fly zone”. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 88(5):1120–1128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2014.01.022
Bezjak A, Paulus R, Gaspar LE, Timmerman RD, Straube WL, Ryan WF, Garces YI, Pu AT, Singh AK, Videtic GM, McGarry RC, Iyengar P, Pantarotto JR, Urbanic JJ, Sun AY, Daly ME, Grills IS, Sperduto P, Normolle DP, Bradley JD, Choy H (2019) Safety and efficacy of a five-fraction stereotactic body radiotherapy schedule for centrally located non-small-cell lung cancer: NRG oncology/RTOG 0813 trial. J Clin Oncol 37(15):1316–1325. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.18.00622
Haseltine JM, Rimner A, Gelblum DY, Modh A, Rosenzweig KE, Jackson A, Yorke ED, Wu AJ (2016) Fatal complications after stereotactic body radiation therapy for central lung tumors abutting the proximal bronchial tree. Pract Radiat Oncol 6(2):e27–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prro.2015.09.012
Tekatli H, Haasbeek N, Dahele M, De Haan P, Verbakel W, Bongers E, Hashemi S, Nossent E, Spoelstra F, de Langen AJ, Slotman B, Senan S (2016) Outcomes of hypofractionated high-dose radiotherapy in poor-risk patients with “ultra-central” non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 11(7):1081–1089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2016.03.008
Chaudhuri AA, Tang C, Binkley MS, Jin M, Wynne JF, von Eyben R, Hara WY, Trakul N, Loo BW Jr, Diehn M (2015) Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR) for treatment of central and ultra-central lung tumors. Lung Cancer 89(1):50–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2015.04.014
Raman S, Yau V, Pineda S, Le LW, Lau A, Bezjak A, Cho BCJ, Sun A, Hope AJ, Giuliani M (2018) Ultra-central tumors treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy: single-institution experience. Clin Lung Cancer 19(5):e803–e810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cllc.2018.06.001
Giuliani M, Mathew AS, Bahig H, Bratman SV, Filion E, Glick D, Louie AV, Raman S, Swaminath A, Warner A, Yau V, Palma D (2018) SUNSET: stereotactic radiation for ultra-central non-small-cell lung cancer-A safety and efficacy trial. Clin Lung Cancer 19(4):e529–e532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cllc.2018.04.001
Lischalk JW, Malik RM, Collins SP, Collins BT, Matus IA, Anderson ED (2016) Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for high-risk central pulmonary metastases. Radiat Oncol 11:28. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-016-0608-8
Duncker-Rohr V, Nestle U, Momm F, Prokic V, Heinemann F, Mix M, Reusch J, Messmer MB, Marschner N, Waller CF, Weber WA, Grosu AL (2013) Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for small lung tumors with a moderate dose. Favorable results and low toxicity. Strahlenther Onkol 189(1):33–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-012-0224-y
Lischalk JW, Malik RM, Collins SP, Collins BT, Matus IA, Anderson ED (2016) Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for high-risk central pulmonary metastases. Radiat Oncol 11:28. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-016-0608-8
Martini N, Melamed MR (1975) Multiple primary lung cancers. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 70(4):606–612
Cong Y, Sun B, Wang J, Meng X, Xuan L, Zhang J, Liu J, Shen G, Wu S (2019) Outcomes and toxicity of stereotactic body radiation therapy for advanced stage ultra-central non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac Cancer 10(7):1567–1575. https://doi.org/10.1111/1759-7714.13105
Guckenberger M, Wulf J, Mueller G, Krieger T, Baier K, Gabor M, Richter A, Wilbert J, Flentje M (2009) Dose-response relationship for image-guided stereotactic body radiotherapy of pulmonary tumors: relevance of 4D dose calculation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 74(1):47–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.06.1939
Onishi H, Araki T, Shirato H, Nagata Y, Hiraoka M, Gomi K, Yamashita T, Niibe Y, Karasawa K, Hayakawa K, Takai Y, Kimura T, Hirokawa Y, Takeda A, Ouchi A, Hareyama M, Kokubo M, Hara R, Itami J, Yamada K (2004) Stereotactic hypofractionated high-dose irradiation for stage I nonsmall cell lung carcinoma: clinical outcomes in 245 subjects in a Japanese multiinstitutional study. Cancer 101(7):1623–1631
Sharma A, Duijm M, Oomen-de Hoop E, Aerts JG, Verhoef C, Hoogeman M, Nuyttens JJ (2018) Factors affecting local control of pulmonary oligometastases treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy. Acta Oncol 57(8):1031–1037. https://doi.org/10.1080/0284186X.2018.1445285
Parker SM, Siochi RA, Wen S, Mattes MD (2019) Impact of tumor size on local control and pneumonitis after stereotactic body radiation therapy for lung tumors. Pract Radiat Oncol 9(1):e90–e97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prro.2018.09.003
Dunlap NE, Larner JM, Read PW, Kozower BD, Lau CL, Sheng K, Jones DR (2010) Size matters: a comparison of T1 and T2 peripheral non-small-cell lung cancers treated with stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT). J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 140(3):583–589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2010.01.046
Peterson J, Niles C, Patel A, Boujaoude Z, Abouzgheib W, Goldsmith B, Asbell S, Xu Q, Khrizman P, Kubicek GJ (2017) Stereotactic body radiotherapy for large (> 5 cm) non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer 18(4):396–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cllc.2016.11.020
Woody NM, Stephans KL, Marwaha G, Djemil T, Videtic GM (2015) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for non-small cell lung cancer tumors greater than 5 cm: safety and efficacy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 92(2):325–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.01.045
Verma V, Shostrom VK, Kumar SS, Zhen W, Hallemeier CL, Braunstein SE, Holland J, Harkenrider MM, Iskhanian AS, Neboori HJ, Jabbour SK, Attia A, Lee P, Alite F, Walker JM, Stahl JM, Wang K, Bingham BS, Hadzitheodorou C, Decker RH, McGarry RC, Simone CB 2nd (2017) Multi-institutional experience of stereotactic body radiotherapy for large (≥5 centimeters) non-small cell lung tumors. Cancer 123(4):688–696. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.30375
Murrell DH, Laba JM, Erickson A, Millman B, Palma DA, Louie AV (2018) Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for ultra-central lung tumors: prioritize target coverage or organs at risk? Radiat Oncol 13(1):57. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-018-1001-6
Adebahr S, Collette S, Shash E, Lambrecht M, Le Pechoux C, Faivre-Finn C, De Ruysscher D, Peulen H, Belderbos J, Dziadziuszko R, Fink C, Guckenberger M, Hurkmans C, Nestle U (2015) LungTech, an EORTC phase II trial of stereotactic body radiotherapy for centrally located lung tumours: a clinical perspective. Br J Radiol 88(1051):20150036. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20150036
Sharma A, Baker S, Duijm M, Oomen-de Hoop E, Cornelissen R, Verhoef C, Hoogeman M, Nuyttens JJ (2020) Prognostic factors for local control and survival for inoperable pulmonary colorectal oligometastases treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol 144:23–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2019.10.004
Franceschini D, Cozzi L, De Rose F, Navarria P, Franzese C, Comito T, Iftode C, Tozzi A, Di Brina L, Ascolese AM, Clerici E, D’Agostino G, Fogliata A, Scorsetti M (2017) Role of stereotactic body radiation therapy for lung metastases from radio-resistant primary tumours. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 143(7):1293–1299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-017-2373-y
Chen H, Laba JM, Zayed S, Boldt RG, Palma DA, Louie AV (2019) Safety and effectiveness of stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for ultra-central lung lesions: a systematic review. J Thorac Oncol 14(8):1332–1342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2019.04.018
Tekatli H, Duijm M, Oomen-de Hoop E, Verbakel W, Schillemans W, Slotman BJ, Nuyttens JJ, Senan S (2018) Normal tissue complication probability modeling of pulmonary toxicity after stereotactic and hypofractionated radiation therapy for central lung tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 100(3):738–747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.11.022
Duijm M, Tekatli H, Oomen-de Hoop E, Verbakel W, Schillemans W, Slotman BJ, Senan S, Nuyttens JJ (2018) Esophagus toxicity after stereotactic and hypofractionated radiotherapy for central lung tumors: normal tissue complication probability modeling. Radiother Oncol 127(2):233–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2018.02.004
Chang JY, Liu H, Balter P, Komaki R, Liao Z, Welsh J, Mehran RJ, Roth JA, Swisher SG (2012) Clinical outcome and predictors of survival and pneumonitis after stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Radiat Oncol 7:152
Huang EX, Hope AJ, Lindsay PE, Trovo M, El Naqa I, Deasy JO, Bradley JD (2011) Heart irradiation as a risk factor for radiation pneumonitis. Acta Oncol 50(1):51–60. https://doi.org/10.3109/0284186X.2010.521192
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the conception and design of the retrospective study as well as data acquisition, analysis, and interpretation. All authors were involved in drafting and revising the manuscript. All authors have given their approval for the submission of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
M. Loi, D. Franceschini, L. Dominici, I. Chiola, C. Franzese, G.R. D’Agostino, P. Navarria, M. Marzo, L. Paganini, T. Comito, P. Mancosu, S. Tomatis, L. Cozzi, M. Alifano, and M. Scorsetti declare that they have no competing interests.
Caption Electronic Supplementary Material
66_2020_1687_MOESM1_ESM.doc
Supplementary Material: Dose constraints for organs at risk, detailed statistical analysis for outcome and related figures
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Loi, M., Franceschini, D., Dominici, L. et al. Dose coverage impacts local control in ultra-central lung oligometastases treated with stereotactic radiotherapy. Strahlenther Onkol 197, 396–404 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-020-01687-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-020-01687-9