Summary
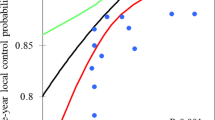
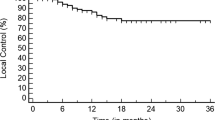
Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) delivers precise concentric radiation to a tumor. It is well established that local control depends on the biologically effective dose (BED) delivered, with BED10 of ≥100 as a significant predictor of local control. The aim of this study was to evaluate factors associated with overall survival (OS) in inoperable lung cancer cases treated with SBRT. From 2013 to 2016, 22 patients with inoperable lung cancer treated with SBRT who could be followed up until their time of death were retrospectively enrolled. Data on sex, age, dose (Gray), number of fractions, BED (α/β = 10), pathology, tumor location, performance status, and background lung disease were collected. The median total dose at the isocenter was 50 Gy, and median BED was 120 Gy. OS was compared in groups with BED of ≥120 Gy (“high-BED”; n = 15) and BED of <120 Gy (“low-BED,” n = 7). Overall, 1‑year OS was 48%. In the univariate analysis, the number of fractions, BED, and pathology were significantly associated with OS. The high-BED group showed better OS, with 1‑ and 2‑year OS of 64% and 21%, respectively, compared with 25% and 0%, respectively, for the low-BED group (p = 0.04). No adverse event of grade 3 or higher occurred. For these inoperable lung cancer cases treated with SBRT, BED was significantly associated with OS. The poor OS rate observed in this case series might be associated with the fact that all the tumors were inoperable.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Timmerman R, Paulus R, Galvin J, Michalski J, Straube W, Bradley J, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for inoperable early stage lung cancer. JAMA. 2010;303:1070–107. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2010.261.
Yu JB, Soulos PR, Cramer LD, Decker RH, Kim AW, Gross CP. Comparative effectiveness of surgery and radiosurgery for stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer. 2015;121:2341–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.29359.
Zhang B, Zhu F, Ma X, Tian Y, Cao D, Luo S, et al. Matched-pair comparisons of stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) versus surgery for the treatment of early stage non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiother Oncol. 2014;112:250–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2014.08.031.
Roesch J, Panje C, Sterzing F, Mantel F, Nestle U, Andratschke N, et al. SBRT for centrally localized NSCLC—what is too central? Radiat Oncol. 2016;11:157.
Videtic GM, Donington J, Giuliani M, Heinzerling J, Karas TZ, Kelsey CR, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer: Executive Summary of an ASTRO Evidence-Based Guideline. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2017;7:295–301.
Chua KLM, Sin I, Fong KW, Chua MLK, Onishi H. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for early stage lung cancer-historical developments and future strategies. Chin Clin Oncol. 2017;6:S20. https://doi.org/10.21037/cco.2017.08.02.
Lu C, Lei Z, Wu H, Lu H. Evaluating risk factors of radiation pneumonitis after stereotactic body radiation therapy in lung tumor: Meta-analysis of 9 observational studies. PLoS ONE. 2018;13(2018):e208637. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0208637.
Onishi H, Araki T, Shirato H. Stereotactic hypofractionated high-dose irradiation for stage I nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Cancer. 2004;101:1623–31. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.20539.
Nagata Y, Hiraoka M, Shibata T, Onishi H, Kokubo M, Karasawa K, et al. Prospective trial of stereotactic body radiation therapy for both operable and inoperable T1N0M0 non-small cell lung cancer: Japan clinical oncology group study JCOG0403. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015;93:989–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.07.2278.
Koshy M, Malik R, Weichselbaum RR, Sher DJ. Increasing radiation therapy dose is associated with improved survival in patients undergoing stereotactic body radiation therapy for stage I non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015;91:344–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2014.10.002.
Eriguchi T, Takeda A, Sanuki N, Nishimura S, Takagawa Y, Enomoto T, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for T3 and T4N0M0 non-small cell lung cancer. J Radiat Res. 2016;57:265–72. https://doi.org/10.1093/jrr/rrw023.
Navarro-Martin A, Aso S, Cacicedo J, Arnaiz M, Navarro V, Rosales S, et al. Phase II Trial of SBRT for Stage I NSCLC: survival, local control, and lung function at 36 Months. J Thorac Oncol. 2016;11:1101–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2016.03.021.
Oshiro Y, Aruga T, Tsuboi K, Marino K, Hara R, Sanayama Y, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for lung tumors at the pulmonary hilum. Strahlenther Onkol. 2010;186:274–9.
Bradley JD, El Naqa I, Drzymala RE, Trovo M, Jones G, Denning MD. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer: the pattern of failure is distant. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010;77:1146–50.
Rowe BP, Boffa DJ, Wilson LD, Kim AW, Detterbeck FC, Decker RH. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for central lung tumors. J Thorac Oncol. 2012;7:1394–9.
Milano MT, Chen Y, Katz AW, Philip A, Schell MC, Okunieff P. Central thoracic lesions treated with hypofractionated stereotactic body radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 2009;91:301–6.
Andratschke N, Zimmermann F, Boehm E, Schill S, Schoenknecht C, Thamm R, et al. Stereotactic radiotherapy of histologically proven inoperable stage I non-small cell lung cancer: patterns of failure. Radiother Oncol. 2011;101:245–9.
Timmerman R, McGarry R, Yiannoutsos C, Papiez L, Tudor K, DeLuca J, et al. Excessive toxicity when treating central tumors in a phase II study of stereotactic body radiation therapy for medically inoperable early-stage lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:4833–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
O. Tanaka, N. Funaguchi, S. Toyoshi, T. Taniguchi, K. Ono, C. Makita, and M. Matsuo declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
National Clinical Trial number: UMIN000034389
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanaka, O., Funaguchi, N., Toyoshi, S. et al. Biologically effective dose and overall survival in stereotactic body radiotherapy for lung tumors. memo 13, 353–356 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12254-020-00617-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12254-020-00617-w