Abstract
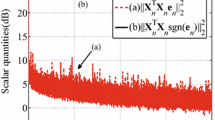
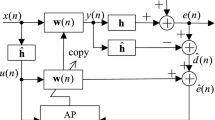
To solve the conflicting requirement of fast convergence and low steady-state misalignment, a variable step-size shrinkage set-membership affine projection algorithm is proposed, which is efficient for the correlated input signal and noisy input environments. The new variable step size is derived by minimizing the square of noise-free a posteriori error, and the shrinkage method is employed to estimate the second-order statistics of the noise-free a priori error vector. Moreover, the stability analysis of the algorithm is conducted. Simulations demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm for various noisy input environments.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Benesty, H. Rey, L.R. Vega, S. Tressens, A nonparametric VSS NLMS algorithm. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 13(10), 581–584 (2006)
M.Z.A. Bhotto, A. Antoniou, Robust set-membership affine-projection adaptive-filtering algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 60(1), 73–81 (2012)
M.Z.A. Bhotto, A. Antoniou, A family of shrinkage adaptive filtering algorithms. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 61(7), 1689–1697 (2013)
M.T. Chen, F. Ding, L. Xu, T. Hayat, A. Alsaedi, Iterative identification algorithms for bilinear-in-parameter systems with autoregressive moving average noise. J. Frankl. Inst. 354(17), 7885–7898 (2017)
J. Cui, H. Shao, A robust set-membership affine projection algorithm based on outlier estimation method, in ISCC (2015), pp. 1–8
R.C. de Lamare, P.S.R. Diniz, Set-membership adaptive algorithms based on time-varying error bounds for CDMA interference suppression. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 58(2), 644–654 (2009)
F. Ding, Y. Gu, Performance analysis of the auxiliary model-based stochastic gradient parameter estimation algorithm for state space systems with one-step state delay. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 32(2), 585–599 (2013)
F. Ding, Y. Gu, Parameter estimation for an input nonlinear state space system with time delay. J. Frankl. Inst. Eng. Appl. Math. 351(12), 5326–5339 (2014)
F. Ding, X.H. Wang, Hierarchical stochastic gradient algorithm and its performance analysis for a class of bilinear-in-parameter systems. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 36(4), 1393–1405 (2017)
F. Ding, Y.J. Wang, J.Y. Dai, Q. Li, Q. Chen, A recursive least squares parameter estimation algorithm for output nonlinear autoregressive systems using the input–output data filtering. J. Frankl. Inst. 354(15), 6938–6955 (2017)
F. Ding, X.H. Wang, L. Mao, L. Xu, Joint state and multi-innovation parameter estimation for time-delay linear systems and its convergence based on the Kalman filtering. Digital Signal Process. 62, 211–223 (2017)
D.L. Duttweiler, Proportionate normalized least-mean-squares adaptation in echo cancellers. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 8(5), 508–518 (2000)
Y. Gu, F. Ding, J.H. Li, States based iterative parameter estimation for a state space model with multi-state delays using decomposition. Signal Process. 106, 294–300 (2015)
S. Haykin, Adaptive Filter Theory, 4th edn. (Prentice-Hall, New Jersey, 2002)
M.H. Li, X.M. Liu, The least squares based iterative algorithms for parameter estimation of a bilinear system with autoregressive noise using the data filtering technique. Signal Process. 147, 23–34 (2018)
M.H. Li, X.M. Liu, F. Ding, The gradient based iterative estimation algorithms for bilinear systems with autoregressive noise. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 36(11), 4541–4568 (2017)
M.V.S. Lima, T.N. Ferreira, W.A. Martins, P.S.R. Diniz, Sparsity-aware data-selective adaptive filters. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 62(17), 4557–4572 (2014)
L. Lu, H. Zhao, Adaptive combination of affine projection sign subband adaptive filters for modeling of acoustic paths in impulsive noise environments. Int. J. Speech Technol. 19(4), 907–917 (2016)
L. Lu, H. Zhao, B. Chen, Collaborative adaptive Volterra filters for nonlinear system identification in α-stable noise environments. J. Frankl. Inst. 353(17), 4500–4525 (2016)
L. Lu, H. Zhao, K. Li, B. Chen, A novel normalized sign algorithm for system identification under impulsive noise interference. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 35(9), 3244–3265 (2016)
U. Mahbub, S.A. Fattah, A single-channel acoustic echo cancellation scheme using gradient-based adaptive filtering. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 33(5), 1541–1572 (2014)
V.J. Mathews, Z. Xie, A stochastic gradient adaptive filter with gradient adaptive step size. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 41(6), 2075–2087 (1993)
K. Ozeki, T. Umeda, An adaptive filtering algorithm using an orthogonal projection to an affine subspace and its properties. Electron. Commun. Jpn. 67(5), 19–27 (1984)
L. Shi, H. Zhao, Variable step-size distributed incremental normalised LMS algorithm. Electron. Lett. 52(7), 519–521 (2016)
L. Shi, H. Zhao, L1-norm constrained normalized subband adaptive filter algorithm with variable norm-bound parameter and improved version. Signal Image Video Process. 11(5), 865–871 (2017)
D.Q. Wang, W. Zhang, Improved least squares identification algorithm for multivariable Hammerstein systems. J. Frankl. Inst. Eng. Appl. Math. 352(11), 5292–5370 (2015)
D.Q. Wang, Z. Zhang, J.Y. Yuan, Maximum likelihood estimation method for dual-rate Hammerstein systems. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 15, 698–705 (2017)
Y.J. Wang, F. Ding, L. Xu, Some new results of designing an IIR filter with colored noise for signal processing. Digital Signal Process. 72, 44–58 (2018)
H.X. Wen, X.H. Lai, L. Chen, Z. Cai, Nonparametric VSS-APA based on precise background noise power estimate. J. Cent. South Univ. 22, 251–260 (2015)
S. Werner, P.S.R. Diniz, Set-membership affine projection algorithm. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 8(8), 231–235 (2001)
Y. Yu, H. Zhao, An improved variable step-size NLMS algorithm based on a Versiera function, in IEEE ICSPCC (2013), pp. 1–4
Y. Yu, H. Zhao, Novel sign subband adaptive filter algorithms with individual weighting factors. Signal Process. 122, 14–23 (2016)
Y. Yu, H. Zhao, Robust incremental normalized least mean square algorithm with variable step sizes over distributed networks. Signal Process. 144, 1–6 (2018)
Y. Yu, H. Zhao, B. Chen, Sparseness-controlled proportionate affine projection sign algorithms for acoustic echo cancellation. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 34(12), 3933–3948 (2015)
Z. Zheng, H. Zhao, Proportionate affine projection algorithm based on coefficient difference, in IEEE ICSPCC (2014), pp. 115–119
X. Zhang, F. Ding, A. Alsaadi, T. Hayat, Recursive parameter identification of the dynamical models for bilinear state space systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 89(4), 2415–2429 (2017)
S. Zhang, J. Zhang, H. Han, Robust shrinkage normalized sign algorithm in an impulsive noise environment. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II: Express Briefs 64(1), 91–95 (2017)
H. Zhao, Z. Zheng, Bias-compensated affine-projection-like algorithms with noisy input. Electron. Lett. 52(9), 712–714 (2016)
H. Zhao, Z. Zheng, L0 norm constraint set-membership affine projection algorithm with coefficient vector reuse. Electron. Lett. 52(7), 560–562 (2016)
Z. Zheng, H. Zhao, Memory improved proportionate M-estimate affine projection algorithm. Electron. Lett. 51(6), 525–526 (2015)
Z. Zheng, H. Zhao, Bias-compensated normalized subband adaptive filter algorithm. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 23(6), 809–813 (2016)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. Lu Lu (Southwest Jiaotong University) for polishing the language. This work was partially supported by National Science Foundation of People’s Republic of China (Grants 61571374, 61271340, 61433011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, K., Zhao, H. A Variable Step-Size Shrinkage Set-Membership Affine Projection Algorithm for Noisy Input. Circuits Syst Signal Process 38, 455–469 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-018-0851-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-018-0851-3