Abstract
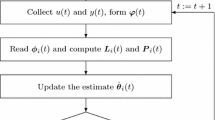
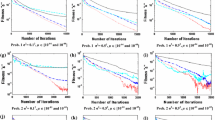
For a dual-rate sampled Hammerstein controlled autoregressive moving average (CARMA) system, this paper uses the polynomial transformation technology to obtain its dual-rate bilinear identification model which is suitable for the available dual-rate sampled-data, uses the maximum likelihood principle to construct a unified parameter vector of all parameters and an information vector formed by the derivative of the noise variable to the unified parameter vector, and directly identifies the parameters of the linear block and the nonlinear block for the dual-rate Hammerstein CARMA system. The unified parameter vector contains the minimum number of the unknown parameters, and the proposed maximum likelihood estimation algorithm has higher computational efficiency than the over-parameterization model based least squares algorithm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Kim and S. J. Kwon, “Dynamic modeling of a twowheeled inverted pendulum balancing mobile robot,” International Journal of Control, Automation, and Systems, vol. 13, no. 4, pp. 926–933, 2015. [click]
P. Shi and F. B. Li, “A Survey on Markovian Jump Systems: Modeling and Design,” International Journal of Control, Automation, and Systems, vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 1–16, 2015. [click]
Y. Shi, J. Huang, and B. Yu, “Robust tracking control of networked control systems: Application to a networked DC motor,” IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 60, no. 12, pp. 5864–5874, 2013.
Y. J. Wang and F. Ding, “Novel data filtering based parameter identification for multiple-input multiple-output systems using the auxiliary model,” Automatica, vol. 71, pp. 308–313, 2016. [click]
F. Ding, X. M. Liu, and Y. Gu, “An auxiliary model based least squares algorithm for a dual-rate state space system with time-delay using the data filtering,” Journal of the Franklin Institute, vol. 353, no. 2, pp. 398–408, 2016.
X. G. Liu and J. Lu, “Least squares based iterative identification for a class of multirate systems,” Automatica, vol. 46, no. 3, pp. 549–554, 2010. [click]
J. Chen, “Several gradient parameter estimation algorithms for dual-rate sampled systems,” Journal of the Franklin Institute, vol. 351, no. 1, pp. 543–554, 2014. [click]
Y. Liu and E. W. Bai, “Iterative identification of Hammerstein systems,” Automatica, vol. 43, no. 2, pp. 346–354, 2007. [click]
M. Salimifard, M. Jafari, and M. Dehghani, “Identification of nonlinear MIMO block-oriented systems with moving average noises using gradient based and least squares based iterative algorithms,” Neurocomputing, vol. 94, pp. 22–31, 2012. [click]
G. Q. Li and C. Y. Wen, “Convergence of fixed-point iteration for the identification of Hammerstein and Wiener systems,” International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, vol. 23, no. 13, pp. 1510–1523, 2013. [click]
B. Zhang and Z. Z. Mao, “Consistent parameter estimation and convergence properties analysis of hammerstein output-error models,” International Journal of Control, Automation, and Systems, vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 302–310, 2015. [click]
F. Ding, Y. Shi, and T. Chen, “Auxiliary model based leastsquares identification methods for Hammerstein outputerror systems,” Systems & Control Letters, vol. 56, no. 5, pp. 373–380, 2007.
M. Jafari, M. Salimifard, and M. Dehghani, “Identification of multivariable nonlinear systems in the presence of colored noises using iterative hierarchical least squares algorithm,” ISA Transactions, vol. 53, no. 4, pp. 1243–1252, 2014. [click]
Y. W. Mao and F. Ding, “Adaptive filtering parameter estimation algorithms for Hammerstein nonlinear systems,” Signal Processing, vol. 128, pp. 417–425, 2016. [click]
J. Vörös, “Identification of nonlinear cascade systems with time-varying backlash,” Journal of Electrical Engineering, vol. 62, no. 2, pp. 87–92, 2011. [click]
Q. Y. Shen and F. Ding, “Iterative identification methods for input nonlinear multivariable systems using the keyterm separation principle,” Journal of the Franklin Institute–Engineering and Applied Mathematics, vol. 352, no. 7, pp. 2847–2865, 2015.
X. H. Wang and F. Ding, “Recursive parameter and state estimation for an input nonlinear state space system using the hierarchical identification principle,” Signal Processing, vol. 117, pp. 208–218, 2015. [click]
F. Ding, X. H. Wang, Q. J. Chen, and Y. S. Xiao, “Recursive least squares parameter estimation for a class of output nonlinear systems based on the model decomposition,” Circuits, Systems and Signal Processing, vol. 35, no. 9, pp. 3323–3338, 2016.
D. Q. Wang, “Hierarchical parameter estimation for a class of MIMO Hammerstein systems based on the reframed models,” Applied Mathematics Letters, vol. 57, pp. 13–19, 2016. [click]
D. Q. Wang and F. Ding, “Parameter estimation algorithms for multivariable Hammerstein CARMA systems,” Information Sciences, vol. 355-356, pp. 237–248, 2016. [click]
J. H. Li, “Parameter estimation for Hammerstein CARARMA systems based on the Newton iteration,” Applied Mathematics Letters, vol. 26, no. 1, pp. 91–96, 2013.
L. Ma and X. G. Liu, “Recursive maximum likelihood method for the identification of Hammerstein ARMAX system,” Applied Mathematical Modelling, vol. 40, no. 13–14, pp. 6523–6535, 2016. [click]
D. Q. Wang and W. Zhang, “Improved least squares identification algorithm for multivariable Hammerstein systems,” Journal of the Franklin Institute, vol. 352, no. 11, pp. 5292–5307, 2015. [click]
D. Q. Wang, H. B. Liu, and F. Ding, “Highly efficient identification methods for dual-rate Hammerstein systems,” IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, vol. 23, no. 5, pp. 1952–1960, 2015.
X. H. Wang and F. Ding, “Convergence of the recursive identification algorithms for multivariate pseudo-linear regressive systems,” International Journal of Adaptive Control and Signal Processing, vol. 30, no. 6, pp. 824–842, 2016. [click]
Y. J. Wang and F. Ding, “The filtering based iterative identification for multivariable systems,” IET Control Theory and Applications, vol. 10, no. 8, pp. 894–902, 2016.
F. Ding, “Hierarchical estimation algorithms for multivariable systems using measurement information,” Information Sciences, vol. 277, pp. 396–405, 2014. [click]
D. Q. Wang, L. Mao, and F. Ding, “Recasted models based hierarchical extended stochastic gradient method for MIMO nonlinear systems,” IET Control Theory and Applications, vol. 11, no. 4, pp. 476–485, 2017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Associate Editor Choon Ki Ahn under the direction of Editor Yoshito Ohta. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under grant 61573205, 61403217, and the Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China under grant ZR2015FM017.
Dong-Qing Wang received the Ph.D. degree from the School of Electrical Engineering and Automation, Tianjin University, China in 2006. She was a Visiting Scholar in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at the University of Tennessee, Knoxville, USA during 2004. Since December 2010, she has been a Full Professor in the College of Automation and Electrical Engineering at Qingdao University, China. Her research interests include process modeling, system identification, and adaptive control.
Zhen Zhang received the Ph.D. degree from the Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China in 2013. He is currently a Lecturer in the College of Automation and Electrical Engineering at Qingdao University, China. His research interests cover reinforcement learning, multiagent reinforcement learning, and intelligent urban traffic signal control.
Jin-Yun Yuan received the M.S. degree from the College of Automation and Electrical Engineering at Qingdao University, China in 2016. Her research interests include nonlinear system identification and adaptive control.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, DQ., Zhang, Z. & Yuan, JY. Maximum likelihood estimation method for dual-rate Hammerstein systems. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 15, 698–705 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12555-015-0371-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12555-015-0371-x