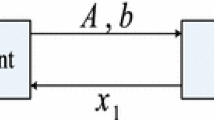Abstract
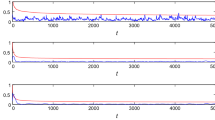
How to use the observation data to build the mathematical models of time-delay systems and how to estimate the parameters of the obtained models are important for studying the laws of motion of systems. This paper presents an auxiliary model-based stochastic gradient parameter estimation algorithm and studies its convergence for the input–output representation for state-space systems with one-step delays, by means of the auxiliary model identification idea. The simulation results indicate that the proposed algorithm can effectively estimate the parameters of the systems.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.S. Ahmad, O. Kukrer, A. Hocanin, Recursive inverse adaptive filtering algorithm. Digit. Signal Process. 21(4), 491–496 (2011)
M. Dehghani, S.K.Y. Nikravesh, Nonlinear state space model identification of synchronous generators. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 78(5), 926–940 (2008)
F. Ding, Hierarchical multi-innovation stochastic gradient algorithm for Hammerstein nonlinear system modeling. Appl. Math. Model. (2012). doi:10.1016/j.apm.2012.04.039
F. Ding, T. Chen, Hierarchical identification of lifted state-space models for general dual-rate systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I, Regul. Pap. 52(6), 1179–1187 (2005)
F. Ding, T. Chen, Parameter estimation of dual-rate stochastic systems by using an output error method. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 50(9), 1436–1441 (2005)
F. Ding, T. Chen, Performance analysis of multi-innovation gradient type identification methods. Automatica 43(1), 1–14 (2007)
F. Ding, J. Ding, Least squares parameter estimation with irregularly missing data. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 24(7), 540–553 (2010)
F. Ding, Y. Gu, Performance analysis of the auxiliary model based least squares identification algorithm for one-step state delay systems. Int. J. Comput. Math. (2012). doi:10.1080/00207160.2012.698008
F. Ding, Y.J. Liu, B. Bao, Gradient based and least squares based iterative estimation algorithms for multi-input multi-output systems. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., Part I, J. Syst. Control Eng. 226(1), 43–55 (2012)
F. Ding, G. Liu, X.P. Liu, Parameter estimation with scarce measurements. Automatica 47(8), 1646–1655 (2011)
F. Ding, G. Liu, X.P. Liu, Partially coupled stochastic gradient identification methods for non-uniformly sampled systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 55(8), 1976–1981 (2010)
F. Ding, X.P. Liu, G. Liu, Auxiliary model based multi-innovation extended stochastic gradient parameter estimation with colored measurement noises. Signal Process. 89(10), 1883–1890 (2009)
F. Ding, X.P. Liu, G. Liu, Identification methods for Hammerstein nonlinear systems. Digit. Signal Process. 21(2), 215–238 (2011)
F. Ding, X.P. Liu, Y. Shi, Convergence analysis of estimation algorithms for dual-rate stochastic systems. Appl. Math. Comput. 176(1), 245–261 (2006)
F. Ding, L. Qiu, T. Chen, Reconstruction of continuous-time systems from their non-uniformly sampled discrete-time systems. Automatica 45(2), 324–332 (2009)
F. Ding, H.Z. Yang, F. Liu, Performance analysis of stochastic gradient algorithms under weak conditions. Sci. China Ser. F 51(9), 1269–1280 (2008)
Y.Y. Du, J.S.H. Tsai, H. Patil, L.S. Shieh, Y.H. Chen, Indirect identification of continuous-time delay systems from step responses. Appl. Math. Model. 35(2), 594–611 (2011)
H. Fang, J. Wu, Y. Shi, Genetic adaptive state estimation with missing input/output data. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., Part I, J. Syst. Control Eng. 224(15), 611–617 (2010)
G.C. Goodwin, K.S. Sin, Adaptive Filtering Prediction and Control (Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, 1984)
Y. Gu, F. Ding, Auxiliary model based least squares identification method for a state space model with a unit time-delay. Appl. Math. Model. (2012). doi:10.1016/j.apm.01.039
H.Q. Han, G.L. Song et al., Performance analysis of the AM-SG parameter estimation for multivariable systems. Appl. Math. Comput. 217(12), 5566–5572 (2011)
M.F. Hassan, M. Zribi, M. Tawfik, State estimation of constrained nonlinear discrete-time dynamical systems. Int. J. Innov. Comput. Inf. Control 6(10), 4449–4470 (2010)
L.L. Han, F. Ding, Multi-innovation stochastic gradient algorithms for multi-input multi-output systems. Digit. Signal Process. 19(4), 545–554 (2009)
J.H. Li, Parameter estimation for Hammerstein CARARMA systems based on the Newton iteration. Appl. Math. Lett. (2012). doi:10.1016/j.aml.2012.03.038
J.H. Li, F. Ding, Maximum likelihood stochastic gradient estimation for Hammerstein systems with colored noise based on the key term separation technique. Comput. Math. Appl. 62(11), 4170–4177 (2011)
J.H. Li, F. Ding, G.W. Yang, Maximum likelihood least squares identification method for input nonlinear finite impulse response moving average systems. Math. Comput. Model. 55(3–4), 442–450 (2012)
Y.J. Liu, F. Ding, Y. Shi, Least squares estimation for a class of non-uniformly sampled systems based on the hierarchical identification principle. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. (2012). doi:10.1007/s00034-012-9421-2
Y.J. Liu, J. Sheng, R.F. Ding, Convergence of stochastic gradient algorithm for multivariable ARX-like systems. Comput. Math. Appl. 59(8), 2615–2627 (2010)
Y.J. Liu, D.Q. Wang et al., Least-squares based iterative algorithms for identifying Box–Jenkins models with finite measurement data. Digit. Signal Process. 20(5), 1458–1467 (2010)
Y.J. Liu, Y.S. Xiao, X.L. Zhao, Multi-innovation stochastic gradient algorithm for multiple-input single-output systems using the auxiliary model. Appl. Math. Comput. 215(4), 1477–1483 (2009)
Y.J. Liu, L. Xie et al., An auxiliary model based recursive least squares parameter estimation algorithm for non-uniformly sampled multirate systems. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., Part I, J. Syst. Control Eng. 223(4), 445–454 (2009)
Y.J. Liu, L. Yu et al., Multi-innovation extended stochastic gradient algorithm and its performance analysis. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 29(4), 649–667 (2010)
L. Ljung, System Identification: Theory for the User, 2nd edn. (Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, 1999)
J.X. Ma, F. Ding, Recursive relations of the cost functions for the least squares algorithms for multivariable systems. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. (2012). doi:10.1007/s00034-012-9448-4
N.V. Nguyen, G. Shevlyakov, V. Shin, Robust state estimation fusion in power system. Int. J. Innov. Comput. Inf. Control 6(12), 5771–5784 (2010)
Q. Qu, M.L. Jin, Parameter estimation of a quadratic FM signal based on FRFT. ICIC Express Lett. 3(3), 385–390 (2009)
T.B. Schön, A. Wills, B. Ninness, System identification of nonlinear state-space models. Automatica 47(1), 39–49 (2011)
Y. Shi, F. Ding, T. Chen, 2-Norm based recursive design of transmultiplexers with designable filter length. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 25(4), 447–462 (2006)
Y. Shi, H.Z. Fang, Kalman filter-based identification for systems with randomly missing measurements in a network environment. Int. J. Control 83(3), 538–551 (2010)
Y. Shi, H. Fang, M. Yan, Kalman filter-based adaptive control for networked systems with unknown parameters and randomly missing outputs. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 19(18), 1976–1992 (2009)
X. Su, P. Shi, L. Wu, Y.D. Song, A novel approach to filter design for T-S fuzzy discrete-time systems with time-varying delay. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. (2012). doi:10.1109/TFUZZ.2196522
D.Q. Wang, F. Ding, Least squares based and gradient based iterative identification for wiener nonlinear systems. Signal Process. 91(5), 1182–1189 (2011)
D.Q. Wang, F. Ding, Performance analysis of the auxiliary models based multi-innovation stochastic gradient estimation algorithm for output error systems. Digit. Signal Process. 20(3), 750–762 (2010)
W. Wang, J.H. Li, R.F. Ding, Maximum likelihood parameter estimation algorithm for controlled autoregressive autoregressive models. Int. J. Comput. Math. 88(16), 3458–3467 (2011)
F. Wang, H.L. Li, J.J. Zhou, Joint multiple parameters estimation for vector-sensor array using biquaternions. ICIC Express Lett. 4(5B), 2039–2044 (2010)
L.L. Xiang, L.B. Xie et al., Hierarchical least squares algorithms for single-input multiple-output systems based on the auxiliary model. Math. Comput. Model. 52(5–6), 918–924 (2010)
B. Yu, Y. Shi, H.N. Huang, l 2−l ∞ filtering for multirate systems based on lifted models. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 27(5), 699–711 (2008)
M. Yan, Y. Shi, Robust discrete-time sliding mode control for uncertain systems with time-varying state delay. IET Control Theory Appl. 2(8), 662–674 (2008)
X. Su, L. Wu, P. Shi, Y.D. Song, H-infinity model reduction of T-S fuzzy stochastic systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern., Part B, Cybern. (2012). doi:10.1109/TSMCB.2195723
D.Q. Wang, Least squares-based recursive and iterative estimation for output error moving average (OEMA) systems using data filtering. IET Control Theory Appl. 5(14), 1648–1657 (2011)
W. Wang, F. Ding, J.Y. Dai, Maximum likelihood least squares identification for systems with autoregressive moving average noise. Appl. Math. Model. 36(5), 1842–1853 (2012)
D.Q. Wang, G.W. Yang, R.F. Ding, Gradient-based iterative parameter estimation for Box–Jenkins systems. Comput. Math. Appl. 60(5), 1200–1208 (2010)
L. Wu, X. Su, P. Shi, J. Qiu, Model approximation for discrete-time state-delay systems in the T-S fuzzy framework. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 19(2), 366–378 (2011)
L. Wu, X. Su, P. Shi, J. Qiu, A new approach to stability analysis and stabilization of discrete-time T-S fuzzy time-varying delay systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern., Part B, Cybern. 41(1), 273–286 (2011)
L. Xie, Y.J. Liu et al., Modelling and identification for non-uniformly periodically sampled-data systems. IET Control Theory Appl. 4(5), 784–794 (2010)
W. Yin, A.S. Mehr, Identification of LPTV systems in the frequency domain. Digit. Signal Process. 21(1), 25–35 (2011)
Y. Zhang, Unbiased identification of a class of multi-input single-output systems with correlated disturbances using bias compensation methods. Math. Comput. Model. 53(9–10), 1810–1819 (2011)
Y. Zhang, G.M. Cui, Bias compensation methods for stochastic systems with colored noise. Appl. Math. Model. 35(4), 1709–1716 (2011)
Z.N. Zhang, F. Ding, X.G. Liu, Hierarchical gradient based iterative parameter estimation algorithm for multivariable output error moving average systems. Comput. Math. Appl. 61(3), 672–682 (2011)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 60973043), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (China) and the 111 Project (B12018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, F., Gu, Y. Performance Analysis of the Auxiliary Model-Based Stochastic Gradient Parameter Estimation Algorithm for State-Space Systems with One-Step State Delay. Circuits Syst Signal Process 32, 585–599 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-012-9463-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-012-9463-5