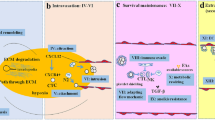
Abstract
Metabolic adaptations are intimately associated with changes in cell behavior. Cancers are characterized by a high metabolic plasticity resulting from mutations and the selection of metabolic phenotypes conferring growth and invasive advantages. While metabolic plasticity allows cancer cells to cope with various microenvironmental situations that can be encountered in a primary tumor, there is increasing evidence that metabolism is also a major driver of cancer metastasis. Rather than a general switch promoting metastasis as a whole, a succession of metabolic adaptations is more likely needed to promote different steps of the metastatic process. This review addresses the contribution of pH, glycolysis and the pentose phosphate pathway, and a companion paper summarizes current knowledge regarding the contribution of mitochondria, lipids and amino acid metabolism. Extracellular acidification, intracellular alkalinization, the glycolytic enzyme phosphoglucose isomerase acting as an autocrine cytokine, lactate and the pentose phosphate pathway are emerging as important factors controlling cancer metastasis.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 6PGD:
-
6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase
- AE2:
-
Anion exchanger 2
- AMF:
-
Autocrine motility factor = PGI
- AP-1:
-
Activator protein-1
- CA:
-
Carbonic anhydrase
- CTC:
-
Circulating tumor cell
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- EMT:
-
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
- ETC:
-
Electron transport chain
- HGF:
-
Hepatocyte growth factor
- HIF-1:
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1
- Hyal-2:
-
Hyaluronidase 2
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- LDH:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MCT:
-
Monocarboxylate transporter
- MIBG:
-
Metaiodobenzylguanidine
- MMP:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase
- MT1-MMP:
-
Membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor-κB
- NHE:
-
Sodium-proton exchanger
- PGI:
-
Phosphoglucose isomerase = AMF
- PHD2:
-
Prolyl-hydroxylase 2
- pHe:
-
Extracellular pH
- pHi:
-
Intracellular pH
- PKM:
-
Pyruvate kinase M
- PPP:
-
Pentose phosphate pathway
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- TKT:
-
Transketolase
- TKTL1:
-
Transketolase-like 1
- uPA:
-
Urokinase
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
References
Gupta GP, Massague J (2006) Cancer metastasis: building a framework. Cell 127:679–695
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2000) The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100:57–70
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144:646–674
Warburg O, Wind F, Negelein E (1927) The metabolism of tumors in the body. J Gen Physiol 8:519–530
Tennant DA, Duran RV, Gottlieb E (2010) Targeting metabolic transformation for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 10:267–277
Porporato PE, Dhup S, Dadhich RK, Copetti T, Sonveaux P (2011) Anticancer targets in the glycolytic metabolism of tumors: a comprehensive review. Front Pharmacol 2:49
Thiery JP, Sleeman JP (2006) Complex networks orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:131–142
Tiwari N, Gheldof A, Tatari M, Christofori G (2012) EMT as the ultimate survival mechanism of cancer cells. Semin Cancer Biol 22:194–207
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan A, Zhou AY, Brooks M, Reinhard F, Zhang CC, Shipitsin M, Campbell LL, Polyak K, Brisken C, Yang J, Weinberg RA (2008) The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell 133:704–715
Frisch SM, Francis H (1994) Disruption of epithelial cell-matrix interactions induces apoptosis. J Cell Biol 124:619–626
Paoli P, Giannoni E, Chiarugi P (2013) Anoikis molecular pathways and its role in cancer progression. Biochim Biophys Acta 1833:3481–3498
Podsypanina K, Du YC, Jechlinger M, Beverly LJ, Hambardzumyan D, Varmus H (2008) Seeding and propagation of untransformed mouse mammary cells in the lung. Science 321:1841–1844
Sieuwerts AM, Kraan J, Bolt J, van der Spoel P, Elstrodt F, Schutte M, Martens JW, Gratama JW, Sleijfer S, Foekens JA (2009) Anti-epithelial cell adhesion molecule antibodies and the detection of circulating normal-like breast tumor cells. J Natl Cancer Inst 101:61–66
Lu J, Fan T, Zhao Q, Zeng W, Zaslavsky E, Chen JJ, Frohman MA, Golightly MG, Madajewicz S, Chen WT (2010) Isolation of circulating epithelial and tumor progenitor cells with an invasive phenotype from breast cancer patients. Int J Cancer 126:669–683
Mimeault M, Batra SK (2014) Molecular biomarkers of cancer stem/progenitor cells associated with progression, metastases, and treatment resistance of aggressive cancers. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 23:234–254
Nieto MA (2013) Epithelial plasticity: a common theme in embryonic and cancer cells. Science 342:1234850
Langley RR, Fidler IJ (2011) The seed and soil hypothesis revisited–the role of tumor-stroma interactions in metastasis to different organs. Int J Cancer 128:2527–2535
Valastyan S, Weinberg RA (2011) Tumor metastasis: molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell 147:275–292
Vanharanta S, Massague J (2013) Origins of metastatic traits. Cancer Cell 24:410–421
Vaupel P, Kallinowski F, Okunieff P (1989) Blood flow, oxygen and nutrient supply, and metabolic microenvironment of human tumors: a review. Cancer Res 49:6449–6465
Griffiths JR (1991) Are cancer cells acidic? Br J Cancer 64:425–427
Gerweck LE, Seetharaman K (1996) Cellular pH gradient in tumor versus normal tissue: potential exploitation for the treatment of cancer. Cancer Res 56:1194–1198
Mookerjee SA, Goncalves RL, Gerencser AA, Nicholls DG, Brand MD (2015) The contributions of respiration and glycolysis to extracellular acid production. Biochim Biophys Acta 1847:171–181
Dhup S, Dadhich RK, Porporato PE, Sonveaux P (2012) Multiple biological activities of lactic acid in cancer: influences on tumor growth, angiogenesis and metastasis. Curr Pharm Des 18:1319–1330
Spugnini EP, Sonveaux P, Stock C, Perez-Sayans M, De MA, Avnet S, Garcia AG, Harguindey S, Fais S (2014) Proton channels and exchangers in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1848:2715–2726
Dimmer KS, Friedrich B, Lang F, Deitmer JW, Broer S (2000) The low-affinity monocarboxylate transporter MCT4 is adapted to the export of lactate in highly glycolytic cells. Biochem J 350(Pt 1):219–227
Ullah MS, Davies AJ, Halestrap AP (2006) The plasma membrane lactate transporter MCT4, but not MCT1, is up-regulated by hypoxia through a HIF-1alpha-dependent mechanism. J Biol Chem 281:9030–9037
Sonveaux P, Vegran F, Schroeder T, Wergin MC, Verrax J, Rabbani ZN, De Saedeleer CJ, Kennedy KM, Diepart C, Jordan BF, Kelley MJ, Gallez B, Wahl ML, Feron O, Dewhirst MW (2008) Targeting lactate-fueled respiration selectively kills hypoxic tumor cells in mice. J Clin Invest 118:3930–3942
DeBerardinis RJ, Lum JJ, Hatzivassiliou G, Thompson CB (2008) The biology of cancer: metabolic reprogramming fuels cell growth and proliferation. Cell Metab 7:11–20
Robergs RA, Ghiasvand F, Parker D (2004) Biochemistry of exercise-induced metabolic acidosis. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 287:R502–R516
Tomasetti C, Vogelstein B (2015) Cancer etiology. Variation in cancer risk among tissues can be explained by the number of stem cell divisions. Science 347:78–81
Morita T, Nagaki T, Fukuda I, Okumura K (1992) Clastogenicity of low pH to various cultured mammalian cells. Mutat Res 268:297–305
Yuan J, Glazer PM (1998) Mutagenesis induced by the tumor microenvironment. Mutat Res 400:439–446
Yuan J, Narayanan L, Rockwell S, Glazer PM (2000) Diminished DNA repair and elevated mutagenesis in mammalian cells exposed to hypoxia and low pH. Cancer Res 60:4372–4376
Park HJ, Makepeace CM, Lyons JC, Song CW (1996) Effect of intracellular acidity and ionomycin on apoptosis in HL-60 cells. Eur J Cancer 32A:540–546
Park HJ, Lyons JC, Ohtsubo T, Song CW (1999) Acidic environment causes apoptosis by increasing caspase activity. Br J Cancer 80:1892–1897
Williams AC, Collard TJ, Paraskeva C (1999) An acidic environment leads to p53 dependent induction of apoptosis in human adenoma and carcinoma cell lines: implications for clonal selection during colorectal carcinogenesis. Oncogene 18:3199–3204
Lardner A (2001) The effects of extracellular pH on immune function. J Leukoc Biol 69:522–530
Bosticardo M, Ariotti S, Losana G, Bernabei P, Forni G, Novelli F (2001) Biased activation of human T lymphocytes due to low extracellular pH is antagonized by B7/CD28 costimulation. Eur J Immunol 31:2829–2838
Wojtkowiak JW, Verduzco D, Schramm KJ, Gillies RJ (2011) Drug resistance and cellular adaptation to tumor acidic pH microenvironment. Mol Pharm 8:2032–2038
Chen KH, Tung PY, Wu JC, Chen Y, Chen PC, Huang SH, Wang SM (2008) An acidic extracellular pH induces Src kinase-dependent loss of beta-catenin from the adherens junction. Cancer Lett 267:37–48
Donowitz M, Ming TC, Fuster D (2013) SLC9/NHE gene family, a plasma membrane and organellar family of Na(+)/H(+) exchangers. Mol Aspects Med 34:236–251
Benej M, Pastorekova S, Pastorek J (2014) Carbonic anhydrase IX: regulation and role in cancer. Subcell Biochem 75:199–219
Alper SL, Chernova MN, Stewart AK (2002) How pH regulates a pH regulator: a regulatory hot spot in the N-terminal cytoplasmic domain of the AE2 anion exchanger. Cell Biochem Biophys 36:123–136
Klein M, Seeger P, Schuricht B, Alper SL, Schwab A (2000) Polarization of Na(+)/H(+) and Cl(-)/HCO (3)(-) exchangers in migrating renal epithelial cells. J Gen Physiol 115:599–608
Lagana A, Vadnais J, Le PU, Nguyen TN, Laprade R, Nabi IR, Noel J (2000) Regulation of the formation of tumor cell pseudopodia by the Na(+)/H(+) exchanger NHE1. J Cell Sci 113(Pt 20):3649–3662
Svastova E, Witarski W, Csaderova L, Kosik I, Skvarkova L, Hulikova A, Zatovicova M, Barathova M, Kopacek J, Pastorek J, Pastorekova S (2012) Carbonic anhydrase IX interacts with bicarbonate transporters in lamellipodia and increases cell migration via its catalytic domain. J Biol Chem 287:3392–3402
Denker SP, Barber DL (2002) Cell migration requires both ion translocation and cytoskeletal anchoring by the Na-H exchanger NHE1. J Cell Biol 159:1087–1096
Stock C, Gassner B, Hauck CR, Arnold H, Mally S, Eble JA, Dieterich P, Schwab A (2005) Migration of human melanoma cells depends on extracellular pH and Na+/H+ exchange. J Physiol 567:225–238
Riemann A, Schneider B, Gundel D, Stock C, Thews O, Gekle M (2014) Acidic priming enhances metastatic potential of cancer cells. Pflugers Arch 466:2127–2138
Reshkin SJ, Bellizzi A, Albarani V, Guerra L, Tommasino M, Paradiso A, Casavola V (2000) Phosphoinositide 3-kinase is involved in the tumor-specific activation of human breast cancer cell Na(+)/H(+) exchange, motility, and invasion induced by serum deprivation. J Biol Chem 275:5361–5369
Stuwe L, Muller M, Fabian A, Waning J, Mally S, Noel J, Schwab A, Stock C (2007) pH dependence of melanoma cell migration: protons extruded by NHE1 dominate protons of the bulk solution. J Physiol 585:351–360
Shin HJ, Rho SB, Jung DC, Han IO, Oh ES, Kim JY (2011) Carbonic anhydrase IX (CA9) modulates tumor-associated cell migration and invasion. J Cell Sci 124:1077–1087
Maciewicz RA, Wotton SF, Etherington DJ, Duance VC (1990) Susceptibility of the cartilage collagens types II, IX and XI to degradation by the cysteine proteinases, cathepsins B and L. FEBS Lett 269:189–193
Buck MR, Karustis DG, Day NA, Honn KV, Sloane BF (1992) Degradation of extracellular-matrix proteins by human cathepsin B from normal and tumour tissues. Biochem J 282(Pt 1):273–278
Ostad M, Weiss R, Droller M, Liu B (1992) Ha-ras oncogene induction of invasion and metastasis is associated with the activation and redistribution of protease(s) in rat-kidney cells. Int J Oncol 1:765–771
Kobayashi H, Moniwa N, Sugimura M, Shinohara H, Ohi H, Terao T (1993) Effects of membrane-associated cathepsin B on the activation of receptor-bound prourokinase and subsequent invasion of reconstituted basement membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1178:55–62
Rozhin J, Sameni M, Ziegler G, Sloane BF (1994) Pericellular pH affects distribution and secretion of cathepsin B in malignant cells. Cancer Res 54:6517–6525
Bourguignon LY, Singleton PA, Diedrich F, Stern R, Gilad E (2004) CD44 interaction with Na + -H + exchanger (NHE1) creates acidic microenvironments leading to hyaluronidase-2 and cathepsin B activation and breast tumor cell invasion. J Biol Chem 279:26991–27007
Rofstad EK, Mathiesen B, Kindem K, Galappathi K (2006) Acidic extracellular pH promotes experimental metastasis of human melanoma cells in athymic nude mice. Cancer Res 66:6699–6707
Glunde K, Guggino SE, Solaiyappan M, Pathak AP, Ichikawa Y, Bhujwalla ZM (2003) Extracellular acidification alters lysosomal trafficking in human breast cancer cells. Neoplasia 5:533–545
Steffan JJ, Snider JL, Skalli O, Welbourne T, Cardelli JA (2009) Na+/H+ exchangers and RhoA regulate acidic extracellular pH-induced lysosome trafficking in prostate cancer cells. Traffic 10:737–753
Steffan JJ, Williams BC, Welbourne T, Cardelli JA (2010) HGF-induced invasion by prostate tumor cells requires anterograde lysosome trafficking and activity of Na + -H + exchangers. J Cell Sci 123:1151–1159
Busco G, Cardone RA, Greco MR, Bellizzi A, Colella M, Antelmi E, Mancini MT, Dell’Aquila ME, Casavola V, Paradiso A, Reshkin SJ (2010) NHE1 promotes invadopodial ECM proteolysis through acidification of the peri-invadopodial space. FASEB J 24:3903–3915
Briozzo P, Morisset M, Capony F, Rougeot C, Rochefort H (1988) In vitro degradation of extracellular matrix with Mr 52,000 cathepsin D secreted by breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 48:3688–3692
Smith SM, Gottesman MM (1989) Activity and deletion analysis of recombinant human cathepsin L expressed in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 264:20487–20495
Rowan AD, Mason P, Mach L, Mort JS (1992) Rat procathepsin B. Proteolytic processing to the mature form in vitro. J Biol Chem 267:15993–15999
Kato Y, Ozono S, Shuin T, Miyazaki K (1996) Slow induction of gelatinase B mRNA by acidic culture conditions in mouse metastatic melanoma cells. Cell Biol Int 20:375–377
Kato Y, Lambert CA, Colige AC, Mineur P, Noel A, Frankenne F, Foidart JM, Baba M, Hata R, Miyazaki K, Tsukuda M (2005) Acidic extracellular pH induces matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in mouse metastatic melanoma cells through the phospholipase D-mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. J Biol Chem 280:10938–10944
Kato Y, Ozawa S, Tsukuda M, Kubota E, Miyazaki K, St Pierre Y, Hata R (2007) Acidic extracellular pH increases calcium influx-triggered phospholipase D activity along with acidic sphingomyelinase activation to induce matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in mouse metastatic melanoma. FEBS J 274:3171–3183
Martinez-Zaguilan R, Seftor EA, Seftor RE, Chu YW, Gillies RJ, Hendrix MJ (1996) Acidic pH enhances the invasive behavior of human melanoma cells. Clin Exp Metastasis 14:176–186
Jang A, Hill RP (1997) An examination of the effects of hypoxia, acidosis, and glucose starvation on the expression of metastasis-associated genes in murine tumor cells. Clin Exp Metastasis 15:469–483
Lin Y, Chang G, Wang J, Jin W, Wang L, Li H, Ma L, Li Q, Pang T (2011) NHE1 mediates MDA-MB-231 cells invasion through the regulation of MT1-MMP. Exp Cell Res 317:2031–2040
Lin Y, Wang J, Jin W, Wang L, Li H, Ma L, Li Q, Pang T (2012) NHE1 mediates migration and invasion of HeLa cells via regulating the expression and localization of MT1-MMP. Cell Biochem Funct 30:41–46
Nakajima M, Irimura T, Di FD, Di FN, Nicolson GL (1983) Heparan sulfate degradation: relation to tumor invasive and metastatic properties of mouse B16 melanoma sublines. Science 220:611–613
Nakajima M, Irimura T, Di FN, Nicolson GL (1984) Metastatic melanoma cell heparanase. Characterization of heparan sulfate degradation fragments produced by B16 melanoma endoglucuronidase. J Biol Chem 259:2283–2290
Cuvier C, Jang A, Hill RP (1997) Exposure to hypoxia, glucose starvation and acidosis: effect on invasive capacity of murine tumor cells and correlation with cathepsin (L + B) secretion. Clin Exp Metastasis 15:19–25
Parkkila S, Rajaniemi H, Parkkila AK, Kivela J, Waheed A, Pastorekova S, Pastorek J, Sly WS (2000) Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor suppresses invasion of renal cancer cells in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:2220–2224
Schlappack OK, Zimmermann A, Hill RP (1991) Glucose starvation and acidosis: effect on experimental metastatic potential, DNA content and MTX resistance of murine tumour cells. Br J Cancer 64:663–670
Moellering RE, Black KC, Krishnamurty C, Baggett BK, Stafford P, Rain M, Gatenby RA, Gillies RJ (2008) Acid treatment of melanoma cells selects for invasive phenotypes. Clin Exp Metastasis 25:411–425
Kalliomaki T, Hill RP (2004) Effects of tumour acidification with glucose + MIBG on the spontaneous metastatic potential of two murine cell lines. Br J Cancer 90:1842–1849
Porporato PE, Payen VL, Perez-Escuredo J, De Saedeleer CJ, Danhier P, Copetti T, Dhup S, Tardy M, Vazeille T, Bouzin C, Feron O, Michiels C, Gallez B, Sonveaux P (2014) A mitochondrial switch promotes tumor metastasis. Cell Rep 8:754–766
Tan AS, Baty JW, Dong LF, Bezawork-Geleta A, Endaya B, Goodwin J, Bajzikova M, Kovarova J, Peterka M, Yan B, Pesdar EA, Sobol M, Filimonenko A, Stuart S, Vondrusova M, Kluckova K, Sachaphibulkij K, Rohlena J, Hozak P, Truksa J, Eccles D, Haupt LM, Griffiths LR, Neuzil J, Berridge MV (2015) Mitochondrial genome acquisition restores respiratory function and tumorigenic potential of cancer cells without mitochondrial DNA. Cell Metab 21:81–94
Shi Q, Abbruzzese JL, Huang S, Fidler IJ, Xiong Q, Xie K (1999) Constitutive and inducible interleukin 8 expression by hypoxia and acidosis renders human pancreatic cancer cells more tumorigenic and metastatic. Clin Cancer Res 5:3711–3721
Shi Q, Le X, Wang B, Xiong Q, Abbruzzese JL, Xie K (2000) Regulation of interleukin-8 expression by cellular pH in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. J Interferon Cytokine Res 20:1023–1028
Xu L, Fidler IJ (2000) Acidic pH-induced elevation in interleukin 8 expression by human ovarian carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 60:4610–4616
Shi Q, Le X, Wang B, Abbruzzese JL, Xiong Q, He Y, Xie K (2001) Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression by acidosis in human cancer cells. Oncogene 20:3751–3756
Fukumura D, Xu L, Chen Y, Gohongi T, Seed B, Jain RK (2001) Hypoxia and acidosis independently up-regulate vascular endothelial growth factor transcription in brain tumors in vivo. Cancer Res 61:6020–6024
Xu L, Fukumura D, Jain RK (2002) Acidic extracellular pH induces vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in human glioblastoma cells via ERK1/2 MAPK signaling pathway: mechanism of low pH-induced VEGF. J Biol Chem 277:11368–11374
Roberts WG, Palade GE (1995) Increased microvascular permeability and endothelial fenestration induced by vascular endothelial growth factor. J Cell Sci 108(Pt 6):2369–2379
Olsson AK, Dimberg A, Kreuger J, Claesson-Welsh L (2006) VEGF receptor signalling - in control of vascular function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:359–371
Unemori EN, Ferrara N, Bauer EA, Amento EP (1992) Vascular endothelial growth factor induces interstitial collagenase expression in human endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol 153:557–562
Mandriota SJ, Seghezzi G, Vassalli JD, Ferrara N, Wasi S, Mazzieri R, Mignatti P, Pepper MS (1995) Vascular endothelial growth factor increases urokinase receptor expression in vascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 270:9709–9716
Bar-Eli M (1999) Role of interleukin-8 in tumor growth and metastasis of human melanoma. Pathobiology 67:12–18
Pacchiano F, Carta F, McDonald PC, Lou Y, Vullo D, Scozzafava A, Dedhar S, Supuran CT (2011) Ureido-substituted benzenesulfonamides potently inhibit carbonic anhydrase IX and show antimetastatic activity in a model of breast cancer metastasis. J Med Chem 54:1896–1902
Lou Y, McDonald PC, Oloumi A, Chia S, Ostlund C, Ahmadi A, Kyle A, dem Auf KU, Leung S, Huntsman D, Clarke B, Sutherland BW, Waterhouse D, Bally M, Roskelley C, Overall CM, Minchinton A, Pacchiano F, Carta F, Scozzafava A, Touisni N, Winum JY, Supuran CT, Dedhar S (2011) Targeting tumor hypoxia: suppression of breast tumor growth and metastasis by novel carbonic anhydrase IX inhibitors. Cancer Res 71:3364–3376
Robey IF, Baggett BK, Kirkpatrick ND, Roe DJ, Dosescu J, Sloane BF, Hashim AI, Morse DL, Raghunand N, Gatenby RA, Gillies RJ (2009) Bicarbonate increases tumor pH and inhibits spontaneous metastases. Cancer Res 69:2260–2268
Ibrahim HA, Cornnell HH, Coelho Ribeiro ML, Abrahams D, Cunningham J, Lloyd M, Martinez GV, Gatenby RA, Gillies RJ (2011) Reduction of metastasis using a non-volatile buffer. Clin Exp Metastasis 28:841–849
Ibrahim-Hashim A, Wojtkowiak JW, de Lourdes Coelho RM, Estrella V, Bailey KM, Cornnell HH, Gatenby RA, Gillies RJ (2011) Free base lysine increases survival and reduces metastasis in prostate cancer model. J Cancer Sci Ther Suppl 1(4): JCST-S1-004
Bailey KM, Wojtkowiak JW, Cornnell HH, Ribeiro MC, Balagurunathan Y, Hashim AI, Gillies RJ (2014) Mechanisms of buffer therapy resistance. Neoplasia 16:354–364
Liotta LA, Mandler R, Murano G, Katz DA, Gordon RK, Chiang PK, Schiffmann E (1986) Tumor cell autocrine motility factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 83:3302–3306
Watanabe H, Carmi P, Hogan V, Raz T, Silletti S, Nabi IR, Raz A (1991) Purification of human tumor cell autocrine motility factor and molecular cloning of its receptor. J Biol Chem 266:13442–13448
Timar J, Trikha M, Szekeres K, Bazaz R, Tovari J, Silletti S, Raz A, Honn KV (1996) Autocrine motility factor signals integrin-mediated metastatic melanoma cell adhesion and invasion. Cancer Res 56:1902–1908
Torimura T, Ueno T, Kin M, Harada R, Nakamura T, Kawaguchi T, Harada M, Kumashiro R, Watanabe H, Avraham R, Sata M (2001) Autocrine motility factor enhances hepatoma cell invasion across the basement membrane through activation of beta1 integrins. Hepatology 34:62–71
Niizeki H, Kobayashi M, Horiuchi I, Akakura N, Chen J, Wang J, Hamada JI, Seth P, Katoh H, Watanabe H, Raz A, Hosokawa M (2002) Hypoxia enhances the expression of autocrine motility factor and the motility of human pancreatic cancer cells. Br J Cancer 86:1914–1919
Tsutsumi S, Yanagawa T, Shimura T, Kuwano H, Raz A (2004) Autocrine motility factor signaling enhances pancreatic cancer metastasis. Clin Cancer Res 10:7775–7784
Yanagawa T, Watanabe H, Takeuchi T, Fujimoto S, Kurihara H, Takagishi K (2004) Overexpression of autocrine motility factor in metastatic tumor cells: possible association with augmented expression of KIF3A and GDI-beta. Lab Invest 84:513–522
Funasaka T, Yanagawa T, Hogan V, Raz A (2005) Regulation of phosphoglucose isomerase/autocrine motility factor expression by hypoxia. FASEB J 19:1422–1430
Tsutsumi S, Fukasawa T, Yamauchi H, Kato T, Kigure W, Morita H, Asao T, Kuwano H (2009) Phosphoglucose isomerase enhances colorectal cancer metastasis. Int J Oncol 35:1117–1121
Tsutsumi S, Hogan V, Nabi IR, Raz A (2003) Overexpression of the autocrine motility factor/phosphoglucose isomerase induces transformation and survival of NIH-3T3 fibroblasts. Cancer Res 63:242–249
Kho DH, Zhang T, Balan V, Wang Y, Ha SW, Xie Y, Raz A (2014) Autocrine motility factor modulates EGF-mediated invasion signaling. Cancer Res 74:2229–2237
Tsutsumi S, Gupta SK, Hogan V, Collard JG, Raz A (2002) Activation of small GTPase Rho is required for autocrine motility factor signaling. Cancer Res 62:4484–4490
Funasaka T, Hogan V, Raz A (2009) Phosphoglucose isomerase/autocrine motility factor mediates epithelial and mesenchymal phenotype conversions in breast cancer. Cancer Res 69:5349–5356
Ahmad A, Aboukameel A, Kong D, Wang Z, Sethi S, Chen W, Sarkar FH, Raz A (2011) Phosphoglucose isomerase/autocrine motility factor mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transition regulated by miR-200 in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 71:3400–3409
Funasaka T, Haga A, Raz A, Nagase H (2001) Tumor autocrine motility factor is an angiogenic factor hat stimulates endothelial cell motility. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 284:1116–1125
Funasaka T, Haga A, Raz A, Nagase H (2002) Autocrine motility factor secreted by tumor cells upregulates vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (Flt-1) expression in endothelial cells. Int J Cancer 101:217–223
Funasaka T, Haga A, Raz A, Nagase H (2002) Tumor autocrine motility factor induces hyperpermeability of endothelial and mesothelial cells leading to accumulation of ascites fluid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 293:192–200
Filella X, Molina R, Jo J, Mas E, Ballesta AM (1991) Serum phosphohexose isomerase activities in patients with colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol 12:360–367
Nakamori S, Watanabe H, Kameyama M, Imaoka S, Furukawa H, Ishikawa O, Sasaki Y, Kabuto T, Raz A (1994) Expression of autocrine motility factor receptor in colorectal cancer as a predictor for disease recurrence. Cancer 74:1855–1862
Maruyama K, Watanabe H, Shiozaki H, Takayama T, Gofuku J, Yano H, Inoue M, Tamura S, Raz A, Monden M (1995) Expression of autocrine motility factor receptor in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer 64:316–321
Takanami I, Takeuchi K, Naruke M, Kodaira S, Tanaka F, Watanabe H, Raz A (1998) Autocrine motility factor in pulmonary adenocarcinomas: results of an immunohistochemical study. Tumour Biol 19:384–389
Attanasio F, Caldieri G, Giacchetti G, van HR, Wieringa B, Buccione R (2011) Novel invadopodia components revealed by differential proteomic analysis. Eur J Cell Biol 90:115–127
Beckner ME, Stracke ML, Liotta LA, Schiffmann E (1990) Glycolysis as primary energy source in tumor cell chemotaxis. J Natl Cancer Inst 82:1836–1840
Schafer ZT, Grassian AR, Song L, Jiang Z, Gerhart-Hines Z, Irie HY, Gao S, Puigserver P, Brugge JS (2009) Antioxidant and oncogene rescue of metabolic defects caused by loss of matrix attachment. Nature 461:109–113
Danhier P, Copetti T, De PG, Leveque P, Feron O, Jordan BF, Sonveaux P, Gallez B (2013) Influence of cell detachment on the respiration rate of tumor and endothelial cells. PLoS One 8:e53324
Payen VL, Brisson L, Dewhirst MW, Sonveaux P (2015) Common responses of tumors and wounds to hypoxia. Cancer J 21:75–87
Halestrap AP (2012) The monocarboxylate transporter family–Structure and functional characterization. IUBMB Life 64:1–9
DeBerardinis RJ, Mancuso A, Daikhin E, Nissim I, Yudkoff M, Wehrli S, Thompson CB (2007) Beyond aerobic glycolysis: transformed cells can engage in glutamine metabolism that exceeds the requirement for protein and nucleotide synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:19345–19350
Walenta S, Schroeder T, Mueller-Klieser W (2004) Lactate in solid malignant tumors: potential basis of a metabolic classification in clinical oncology. Curr Med Chem 11:2195–2204
Shime H, Yabu M, Akazawa T, Kodama K, Matsumoto M, Seya T, Inoue N (2008) Tumor-secreted lactic acid promotes IL-23/IL-17 proinflammatory pathway. J Immunol 180:7175–7183
Yabu M, Shime H, Hara H, Saito T, Matsumoto M, Seya T, Akazawa T, Inoue N (2011) IL-23-dependent and -independent enhancement pathways of IL-17A production by lactic acid. Int Immunol 23:29–41
Gottfried E, Kunz-Schughart LA, Ebner S, Mueller-Klieser W, Hoves S, Andreesen R, Mackensen A, Kreutz M (2006) Tumor-derived lactic acid modulates dendritic cell activation and antigen expression. Blood 107:2013–2021
Fischer K, Hoffmann P, Voelkl S, Meidenbauer N, Ammer J, Edinger M, Gottfried E, Schwarz S, Rothe G, Hoves S, Renner K, Timischl B, Mackensen A, Kunz-Schughart L, Andreesen R, Krause SW, Kreutz M (2007) Inhibitory effect of tumor cell-derived lactic acid on human T cells. Blood 109:3812–3819
Dietl K, Renner K, Dettmer K, Timischl B, Eberhart K, Dorn C, Hellerbrand C, Kastenberger M, Kunz-Schughart LA, Oefner PJ, Andreesen R, Gottfried E, Kreutz MP (2010) Lactic acid and acidification inhibit TNF secretion and glycolysis of human monocytes. J Immunol 184:1200–1209
Goetze K, Walenta S, Ksiazkiewicz M, Kunz-Schughart LA, Mueller-Klieser W (2011) Lactate enhances motility of tumor cells and inhibits monocyte migration and cytokine release. Int J Oncol 39:453–463
Sattler UG, Hirschhaeusera F, Mueller-Klieser WF (2010) Manipulation of glycolysis in malignant tumors: fantasy or therapy? Curr Med Chem 17:96–108
Walenta S, Salameh A, Lyng H, Evensen JF, Mitze M, Rofstad EK, Mueller-Klieser W (1997) Correlation of high lactate levels in head and neck tumors with incidence of metastasis. Am J Pathol 150:409–415
Brizel DM, Schroeder T, Scher RL, Walenta S, Clough RW, Dewhirst MW, Mueller-Klieser W (2001) Elevated tumor lactate concentrations predict for an increased risk of metastases in head-and-neck cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 51:349–353
Walenta S, Chau TV, Schroeder T, Lehr HA, Kunz-Schughart LA, Fuerst A, Mueller-Klieser W (2003) Metabolic classification of human rectal adenocarcinomas: a novel guideline for clinical oncologists? J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 129:321–326
Schwickert G, Walenta S, Sundfor K, Rofstad EK, Mueller-Klieser W (1995) Correlation of high lactate levels in human cervical cancer with incidence of metastasis. Cancer Res 55:4757–4759
Walenta S, Wetterling M, Lehrke M, Schwickert G, Sundfor K, Rofstad EK, Mueller-Klieser W (2000) High lactate levels predict likelihood of metastases, tumor recurrence, and restricted patient survival in human cervical cancers. Cancer Res 60:916–921
Stern R, Shuster S, Neudecker BA, Formby B (2002) Lactate stimulates fibroblast expression of hyaluronan and CD44: the Warburg effect revisited. Exp Cell Res 276:24–31
Baumann F, Leukel P, Doerfelt A, Beier CP, Dettmer K, Oefner PJ, Kastenberger M, Kreutz M, Nickl-Jockschat T, Bogdahn U, Bosserhoff AK, Hau P (2009) Lactate promotes glioma migration by TGF-beta2-dependent regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-2. Neuro Oncol 11:368–380
Bonuccelli G, Tsirigos A, Whitaker-Menezes D, Pavlides S, Pestell RG, Chiavarina B, Frank PG, Flomenberg N, Howell A, Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Sotgia F, Lisanti MP (2010) Ketones and lactate “fuel” tumor growth and metastasis: evidence that epithelial cancer cells use oxidative mitochondrial metabolism. Cell Cycle 9:3506–3514
Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Prisco M, Ertel A, Tsirigos A, Lin Z, Pavlides S, Wang C, Flomenberg N, Knudsen ES, Howell A, Pestell RG, Sotgia F, Lisanti MP (2011) Ketones and lactate increase cancer cell “stemness,” driving recurrence, metastasis and poor clinical outcome in breast cancer: achieving personalized medicine via Metabolo-Genomics. Cell Cycle 10:1271–1286
Lu H, Forbes RA, Verma A (2002) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 activation by aerobic glycolysis implicates the Warburg effect in carcinogenesis. J Biol Chem 277:23111–23115
Lu H, Dalgard CL, Mohyeldin A, McFate T, Tait AS, Verma A (2005) Reversible inactivation of HIF-1 prolyl hydroxylases allows cell metabolism to control basal HIF-1. J Biol Chem 280:41928–41939
Vegran F, Boidot R, Michiels C, Sonveaux P, Feron O (2011) Lactate influx through the endothelial cell monocarboxylate transporter MCT1 supports an NF-kappaB/IL-8 pathway that drives tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Res 71:2550–2560
De Saedeleer CJ, Copetti T, Porporato PE, Verrax J, Feron O, Sonveaux P (2012) Lactate activates HIF-1 in oxidative but not in Warburg-phenotype human tumor cells. PLoS One 7:e46571
Porporato PE, Payen VL, De Saedeleer CJ, Preat V, Thissen JP, Feron O, Sonveaux P (2012) Lactate stimulates angiogenesis and accelerates the healing of superficial and ischemic wounds in mice. Angiogenesis 15:581–592
Sonveaux P, Copetti T, De Saedeleer CJ, Vegran F, Verrax J, Kennedy KM, Moon EJ, Dhup S, Danhier P, Frerart F, Gallez B, Ribeiro A, Michiels C, Dewhirst MW, Feron O (2012) Targeting the lactate transporter MCT1 in endothelial cells inhibits lactate-induced HIF-1 activation and tumor angiogenesis. PLoS ONE 7:e33418
Vegran F, Seront E, Sonveaux P, Feron O (2012) Lactate-induced IL-8 pathway in endothelial cells–response. Cancer Res 72:1903–1904
Andela VB, Schwarz EM, Puzas JE, O’Keefe RJ, Rosier RN (2000) Tumor metastasis and the reciprocal regulation of prometastatic and antimetastatic factors by nuclear factor kappaB. Cancer Res 60:6557–6562
Lu X, Kang Y (2010) Hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factors: master regulators of metastasis. Clin Cancer Res 16:5928–5935
Kennedy KM, Scarbrough PM, Ribeiro A, Richardson R, Yuan H, Sonveaux P, Landon CD, Chi JT, Pizzo S, Schroeder T, Dewhirst MW (2013) Catabolism of exogenous lactate reveals it as a legitimate metabolic substrate in breast cancer. PLoS ONE 8:e75154
Gallagher SM, Castorino JJ, Wang D, Philp NJ (2007) Monocarboxylate transporter 4 regulates maturation and trafficking of CD147 to the plasma membrane in the metastatic breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231. Cancer Res 67:4182–4189
Izumi H, Takahashi M, Uramoto H, Nakayama Y, Oyama T, Wang KY, Sasaguri Y, Nishizawa S, Kohno K (2011) Monocarboxylate transporters 1 and 4 are involved in the invasion activity of human lung cancer cells. Cancer Sci 102:1007–1013
De Saedeleer CJ, Porporato PE, Copetti T, Perez-Escuredo J, Payen VL, Brisson L, Feron O, Sonveaux P (2014) Glucose deprivation increases monocarboxylate transporter 1 (MCT1) expression and MCT1-dependent tumor cell migration. Oncogene 33:4060–4068
Zhao Z, Wu MS, Zou C, Tang Q, Lu J, Liu D, Wu Y, Yin J, Xie X, Shen J, Kang T, Wang J (2014) Downregulation of MCT1 inhibits tumor growth, metastasis and enhances chemotherapeutic efficacy in osteosarcoma through regulation of the NF-kappaB pathway. Cancer Lett 342:150–158
Lee GH, Kim DS, Chung MJ, Chae SW, Kim HR, Chae HJ (2011) Lysyl oxidase-like-1 enhances lung metastasis when lactate accumulation and monocarboxylate transporter expression are involved. Oncol Lett 2:831–838
Nakayama Y, Torigoe T, Inoue Y, Minagawa N, Izumi H, Kohno K, Yamaguchi K (2012) Prognostic significance of monocarboxylate transporter 4 expression in patients with colorectal cancer. Exp Ther Med 3:25–30
Chen JL, Lucas JE, Schroeder T, Mori S, Wu J, Nevins J, Dewhirst M, West M, Chi JT (2008) The genomic analysis of lactic acidosis and acidosis response in human cancers. PLoS Genet 4:e1000293
Kanekura T, Chen X, Kanzaki T (2002) Basigin (CD147) is expressed on melanoma cells and induces tumor cell invasion by stimulating production of matrix metalloproteinases by fibroblasts. Int J Cancer 99:520–528
Pan Y, He B, Song G, Bao Q, Tang Z, Tian F, Wang S (2012) CD147 silencing via RNA interference reduces tumor cell invasion, metastasis and increases chemosensitivity in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncol Rep 27:2003–2009
Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC, Thompson CB (2009) Understanding the Warburg effect: the metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science 324:1029–1033
Chen EI, Hewel J, Krueger JS, Tiraby C, Weber MR, Kralli A, Becker K, Yates JR III, Felding-Habermann B (2007) Adaptation of energy metabolism in breast cancer brain metastases. Cancer Res 67:1472–1486
White NM, Newsted DW, Masui O, Romaschin AD, Siu KW, Yousef GM (2014) Identification and validation of dysregulated metabolic pathways in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol 35:1833–1846
Newell K, Franchi A, Pouyssegur J, Tannock I (1993) Studies with glycolysis-deficient cells suggest that production of lactic acid is not the only cause of tumor acidity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:1127–1131
Yamagata M, Hasuda K, Stamato T, Tannock IF (1998) The contribution of lactic acid to acidification of tumours: studies of variant cells lacking lactate dehydrogenase. Br J Cancer 77:1726–1731
Helmlinger G, Sckell A, Dellian M, Forbes NS, Jain RK (2002) Acid production in glycolysis-impaired tumors provides new insights into tumor metabolism. Clin Cancer Res 8:1284–1291
Sun W, Liu Y, Glazer CA, Shao C, Bhan S, Demokan S, Zhao M, Rudek MA, Ha PK, Califano JA (2010) TKTL1 is activated by promoter hypomethylation and contributes to head and neck squamous cell carcinoma carcinogenesis through increased aerobic glycolysis and HIF1alpha stabilization. Clin Cancer Res 16:857–866
Pandolfi PP, Sonati F, Rivi R, Mason P, Grosveld F, Luzzatto L (1995) Targeted disruption of the housekeeping gene encoding glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD): G6PD is dispensable for pentose synthesis but essential for defense against oxidative stress. EMBO J 14:5209–5215
Weinberg F, Hamanaka R, Wheaton WW, Weinberg S, Joseph J, Lopez M, Kalyanaraman B, Mutlu GM, Budinger GR, Chandel NS (2010) Mitochondrial metabolism and ROS generation are essential for Kras-mediated tumorigenicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:8788–8793
Ciou SC, Chou YT, Liu YL, Nieh YC, Lu JW, Huang SF, Chou YT, Cheng LH, Lo JF, Chen MJ, Yang MC, Yuh CH, Wang HD (2015) Ribose-5-phosphate isomerase A regulates hepatocarcinogenesis via PP2A and ERK signaling. Int J Cancer 137:104–115
Mazurek S, Boschek CB, Hugo F, Eigenbrodt E (2005) Pyruvate kinase type M2 and its role in tumor growth and spreading. Semin Cancer Biol 15:300–308
Christofk HR, Vander Heiden MG, Harris MH, Ramanathan A, Gerszten RE, Wei R, Fleming MD, Schreiber SL, Cantley LC (2008) The M2 splice isoform of pyruvate kinase is important for cancer metabolism and tumour growth. Nature 452:230–233
David CJ, Chen M, Assanah M, Canoll P, Manley JL (2010) HnRNP proteins controlled by c-Myc deregulate pyruvate kinase mRNA splicing in cancer. Nature 463:364–368
Mazurek S (2011) Pyruvate kinase type M2: A key regulator of the metabolic budget system in tumor cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 43:969–980
Anastasiou D, Poulogiannis G, Asara JM, Boxer MB, Jiang JK, Shen M, Bellinger G, Sasaki AT, Locasale JW, Auld DS, Thomas CJ, Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC (2011) Inhibition of pyruvate kinase M2 by reactive oxygen species contributes to cellular antioxidant responses. Science 334:1278–1283
Peralta D, Bronowska AK, Morgan B, Doka E, Van LK, Nagy P, Grater F, Dick TP (2015) A proton relay enhances H2O2 sensitivity of GAPDH to facilitate metabolic adaptation. Nat Chem Biol 11:156–163
Jiang P, Du W, Wang X, Mancuso A, Gao X, Wu M, Yang X (2011) p53 regulates biosynthesis through direct inactivation of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Nat Cell Biol 13:310–316
Wen D, Liu D, Tang J, Dong L, Liu Y, Tao Z, Wan J, Gao D, Wang L, Sun H, Fan J, Wu W (2015) Malic enzyme 1 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and indicates poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol 36:6211–6221
Fan J, Ye J, Kamphorst JJ, Shlomi T, Thompson CB, Rabinowitz JD (2014) Quantitative flux analysis reveals folate-dependent NADPH production. Nature 510:298–302
Chan B, VanderLaan PA, Sukhatme VP (2013) 6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase regulates tumor cell migration in vitro by regulating receptor tyrosine kinase c-Met. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 439:247–251
Ramos-Montoya A, Lee WN, Bassilian S, Lim S, Trebukhina RV, Kazhyna MV, Ciudad CJ, Noe V, Centelles JJ, Cascante M (2006) Pentose phosphate cycle oxidative and nonoxidative balance: a new vulnerable target for overcoming drug resistance in cancer. Int J Cancer 119:2733–2741
Coy JF, Dressler D, Wilde J, Schubert P (2005) Mutations in the transketolase-like gene TKTL1: clinical implications for neurodegenerative diseases, diabetes and cancer. Clin Lab 51:257–273
Langbein S, Zerilli M, Zur HA, Staiger W, Rensch-Boschert K, Lukan N, Popa J, Ternullo MP, Steidler A, Weiss C, Grobholz R, Willeke F, Alken P, Stassi G, Schubert P, Coy JF (2006) Expression of transketolase TKTL1 predicts colon and urothelial cancer patient survival: Warburg effect reinterpreted. Br J Cancer 94:578–585
Hu LH, Yang JH, Zhang DT, Zhang S, Wang L, Cai PC, Zheng JF, Huang JS (2007) The TKTL1 gene influences total transketolase activity and cell proliferation in human colon cancer LoVo cells. Anticancer Drugs 18:427–433
Zhang S, Yang JH, Guo CK, Cai PC (2007) Gene silencing of TKTL1 by RNAi inhibits cell proliferation in human hepatoma cells. Cancer Lett 253:108–114
Langbein S, Frederiks WM, Zur HA, Popa J, Lehmann J, Weiss C, Alken P, Coy JF (2008) Metastasis is promoted by a bioenergetic switch: new targets for progressive renal cell cancer. Int J Cancer 122:2422–2428
Krockenberger M, Honig A, Rieger L, Coy JF, Sutterlin M, Kapp M, Horn E, Dietl J, Kammerer U (2007) Transketolase-like 1 expression correlates with subtypes of ovarian cancer and the presence of distant metastases. Int J Gynecol Cancer 17:101–106
Zerilli M, Amato MC, Martorana A, Cabibi D, Coy JF, Cappello F, Pompei G, Russo A, Giordano C, Rodolico V (2008) Increased expression of transketolase-like-1 in papillary thyroid carcinomas smaller than 1.5 cm in diameter is associated with lymph-node metastases. Cancer 113:936–944
Diaz-Moralli S, Tarrado-Castellarnau M, Alenda C, Castells A, Cascante M (2011) Transketolase-like 1 expression is modulated during colorectal cancer progression and metastasis formation. PLoS One 6:e25323
Mayer A, Von WA, Vaupel P (2010) Glucose metabolism of malignant cells is not regulated by transketolase-like (TKTL)-1. Int J Oncol 37:265–271
Mayer A, Von WA, Vaupel P (2011) Evidence against a major role for TKTL-1 in hypoxic and normoxic cancer cells. Adv Exp Med Biol 701:123–128
Murray CM, Hutchinson R, Bantick JR, Belfield GP, Benjamin AD, Brazma D, Bundick RV, Cook ID, Craggs RI, Edwards S, Evans LR, Harrison R, Holness E, Jackson AP, Jackson CG, Kingston LP, Perry MW, Ross AR, Rugman PA, Sidhu SS, Sullivan M, Taylor-Fishwick DA, Walker PC, Whitehead YM, Wilkinson DJ, Wright A, Donald DK (2005) Monocarboxylate transporter MCT1 is a target for immunosuppression. Nat Chem Biol 1:371–376
Draoui N, Schicke O, Fernandes A, Drozak X, Nahra F, Dumont A, Douxfils J, Hermans E, Dogne JM, Corbau R, Marchand A, Chaltin P, Sonveaux P, Feron O, Riant O (2013) Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of carboxycoumarins as a new antitumor treatment targeting lactate transport in cancer cells. Bioorg Med Chem 21:7107–7117
Draoui N, Schicke O, Seront E, Bouzin C, Sonveaux P, Riant O, Feron O (2014) Antitumor activity of 7-aminocarboxycoumarin derivatives, a new class of potent inhibitors of lactate influx but not efflux. Mol Cancer Ther 13:1410–1418
Lane AN, Fan TWM, Higashi RM (2009) Metabolic acidosis and the importance of balanced equations. Metabolomics 5:163–165
Wichert M, Krall N (2015) Targeting carbonic anhydrase IX with small organic ligands. Curr Opin Chem Biol 26:48–54
Liu J, Huang Y, Kumar A, Tan A, Jin S, Mozhi A, Liang XJ (2014) pH-sensitive nano-systems for drug delivery in cancer therapy. Biotechnol Adv 32:693–710
Meng F, Zhong Y, Cheng R, Deng C, Zhong Z (2014) pH-sensitive polymeric nanoparticles for tumor-targeting doxorubicin delivery: concept and recent advances. Nanomedicine (Lond) 9:487–499
Koivunen P, Hirsila M, Remes AM, Hassinen IE, Kivirikko KI, Myllyharju J (2007) Inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) hydroxylases by citric acid cycle intermediates: possible links between cell metabolism and stabilization of HIF. J Biol Chem 282:4524–4532
Xiao M, Yang H, Xu W, Ma S, Lin H, Zhu H, Liu L, Liu Y, Yang C, Xu Y, Zhao S, Ye D, Xiong Y, Guan KL (2012) Inhibition of alpha-KG-dependent histone and DNA demethylases by fumarate and succinate that are accumulated in mutations of FH and SDH tumor suppressors. Genes Dev 26:1326–1338
Selak MA, Armour SM, MacKenzie ED, Boulahbel H, Watson DG, Mansfield KD, Pan Y, Simon MC, Thompson CB, Gottlieb E (2005) Succinate links TCA cycle dysfunction to oncogenesis by inhibiting HIF-alpha prolyl hydroxylase. Cancer Cell 7:77–85
Isaacs JS, Jung YJ, Mole DR, Lee S, Torres-Cabala C, Chung YL, Merino M, Trepel J, Zbar B, Toro J, Ratcliffe PJ, Linehan WM, Neckers L (2005) HIF overexpression correlates with biallelic loss of fumarate hydratase in renal cancer: novel role of fumarate in regulation of HIF stability. Cancer Cell 8:143–153
Roland CL, Arumugam T, Deng D, Liu SH, Philip B, Gomez S, Burns WR, Ramachandran V, Wang H, Cruz-Monserrate Z, Logsdon CD (2014) Cell surface lactate receptor GPR81 is crucial for cancer cell survival. Cancer Res 74:5301–5310
Giannoni E, Taddei ML, Morandi A, Comito G, Calvani M, Bianchini F, Richichi B, Raugei G, Wong N, Tang D, Chiarugi P (2015) Targeting stromal-induced pyruvate kinase M2 nuclear translocation impairs oxphos and prostate cancer metastatic spread. Oncotarget 6:24061–24074
Lincet H, Icard P (2015) How do glycolytic enzymes favour cancer cell proliferation by nonmetabolic functions? Oncogene 34:3751–3759
Acknowledgments
Work at the authors’ lab is supported by a Starting Grant from the European Research Council (ERC No. 243188 TUMETABO), Interuniversity Attraction Pole (IAP) grant #UP7-03 from the Belgian Science Policy Office (Belspo), an Action de Recherche Concertée from the Communauté Française de Belgique (ARC 14/19-058), the Belgian Fonds National de la Recherche Scientifique (F.R.S.-FNRS), the Télévie, the Belgian Fondation contre le Cancer (2012-186), the Belgian Federal Agency for Nuclear Control (FANC-AFCN), the Louvain Foundation and the UCL Fonds Spéciaux de la Recherche (FSR). Pierre Sonveaux is a F.R.S.-FNRS Research Associate, Paolo E. Porporato a F.R.S.-FNRS Postdoctoral Fellow and Valéry L. Payen a F.R.S.-FNRS PhD Fellow. Bjorn Baselet is a grantee of the Belgian Nuclear Research Center (SCK∙CEN).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
V. L. Payen and P. E. Porporato equally contributed to this manuscript.
Submitted as a companion paper to “Porporato PE, Payen VL, Baselet B, Sonveaux P. Metabolic changes associated with tumor metastasis, part 2: mitochondria, lipid and amino acid metabolism.”
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Payen, V.L., Porporato, P.E., Baselet, B. et al. Metabolic changes associated with tumor metastasis, part 1: tumor pH, glycolysis and the pentose phosphate pathway. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 73, 1333–1348 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-015-2098-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-015-2098-5