Abstract
Objective and design
This study attempted to clarify the roles of endothelins and mechanisms associated with ETA/ETB receptors in mouse models of colitis.
Materials and methods
Colitis was induced by intracolonic administration of 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS, 1.5 mg/animal) or dextran sulfate sodium (DSS, 3%). After colitis establishment, mice received Atrasentan (ETA receptor antagonist, 10 mg/kg), A-192621 (ETB receptor antagonist, 20 mg/kg) or Dexamethasone (1 mg/kg) and several inflammatory parameters were assessed, as well as mRNA levels for ET-1, ET-2 and ET receptors.
Results
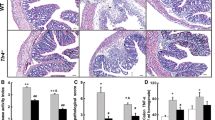
Atrasentan treatment ameliorates TNBS- and DSS-induced colitis. In the TNBS model was observed reduction in macroscopic and microscopic score, colon weight, neutrophil influx, IL-1β, MIP-2 and keratinocyte chemoattractant (KC) levels, inhibition of adhesion molecules expression and restoration of IL-10 levels. However, A192621 treatment did not modify any parameter. ET-1 and ET-2 mRNA was decreased 24 h, but ET-2 mRNA was markedly increased at 48 h after TNBS. ET-2 was able to potentiate LPS-induced KC production in vitro. ETA and ETB receptors mRNA were increased at 24, 48 and 72 h after colitis induction.
Conclusions
Atrasentan treatment was effective in reducing the severity of colitis in DSS- and TNBS-treated mice, suggesting that ETA receptors might be a potential target for inflammatory bowel diseases.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wallace KL, Zheng LB, Kanazawa Y, Shih DQ. Immunopathology of inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:6–21.
Sartor RB. Mechanisms of disease: pathogenesis of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;3:390–407.
Masaki T. Historical review: endothelin. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2004;25:219–24.
Letizia C, Boirivant M, De Toma G, Cerci S, Subioli S, Scuro L, et al. Plasma levels of endothelin-1 in patients with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Ital J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1998;30:266–9.
Kanazawa S, Tsunoda T, Onuma E, Majima T, Kagiyama M, Kikuchi K. VEGF, basic-FGF, and TGF-beta in Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis: a novel mechanism of chronic intestinal inflammation. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96:822–8.
Murch SH, Braegger CP, Sessa WC, MacDonald TT. High endothelin-1 immunoreactivity in Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Lancet. 1992;339:381–5.
Cheluvappa R. A novel model of appendicitis and appendectomy to investigate inflammatory bowel disease pathogenesis and remediation. Biol Proced Online. 2014;16:10.
Cheluvappa R, Eri R, Luo AS, Grimm MC. Endothelin and vascular remodelling in colitis pathogenesis–appendicitis and appendectomy limit colitis by suppressing endothelin pathways. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2014;29:1321–8.
Hogaboam CM, Muller MJ, Collins SM, Hunt RH. An orally active non-selective endothelin receptor antagonist, bosentan, markedly reduces injury in a rat model of colitis. Eur J Pharmacol. 1996;309:261–9.
Gulluoglu BM, Kurtel H, Gulluoglu MG, Yegen C, Aktan AO, Dizdaroglu F, et al. Role of endothelins in trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced colitis in rats. Digestion. 1999;60:484–92.
Padol I, Huang JQ, Hogaboam CM, Hunt RH. Therapeutic effects of the endothelin receptor antagonist Ro 48-5695 in the TNBS/DNBS rat model of colitis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2000;12:257–65.
Anthoni C, Mennigen RB, Rijcken EJ, Laukotter MG, Spiegel HU, Senninger N, et al. Bosentan, an endothelin receptor antagonist, reduces leucocyte adhesion and inflammation in a murine model of inflammatory bowel disease. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2006;21:409–18.
Buanne P, Di Carlo E, Caputi L, Brandolini L, Mosca M, Cattani F, et al. Crucial pathophysiological role of CXCR2 in experimental ulcerative colitis in mice. J Leukoc Biol. 2007;82:1239–46.
Wallace JL, McKnight W, Asfaha S, Liu DY. Reduction of acute and reactivated colitis in rats by an inhibitor of neutrophil activation. Am J Physiol. 1998;274:G802–8.
Peterson CG, Sangfelt P, Wagner M, Hansson T, Lettesjo H, Carlson M. Fecal levels of leukocyte markers reflect disease activity in patients with ulcerative colitis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2007;67:810–20.
Heidemann J, Ogawa H, Dwinell MB, Rafiee P, Maaser C, Gockel HR, et al. Angiogenic effects of interleukin 8 (CXCL8) in human intestinal microvascular endothelial cells are mediated by CXCR2. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:8508–15.
Hipkin RW, Deno G, Fine J, Sun Y, Wilburn B, Fan X, et al. Cloning and pharmacological characterization of CXCR1 and CXCR2 from Macaca fascicularis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004;310:291–300.
Fan X, Patera AC, Pong-Kennedy A, Deno G, Gonsiorek W, Manfra DJ, et al. Murine CXCR1 is a functional receptor for GCP-2/CXCL6 and interleukin-8/CXCL8. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:11658–66.
Romagnani P, Lasagni L, Annunziato F, Serio M, Romagnani S. CXC chemokines: the regulatory link between inflammation and angiogenesis. Trends Immunol. 2004;25:201–9.
Deniz M, Cetinel S, Kurtel H. Blood flow alterations in TNBS-induced colitis: role of endothelin receptors. Inflamm Res. 2004;53:329–36.
Morris GP, Beck PL, Herridge MS, Depew WT, Szewczuk MR, Wallace JL. Hapten-induced model of chronic inflammation and ulceration in the rat colon. Gastroenterology. 1989;96:795–803.
Bento AF, Leite DF, Claudino RF, Hara DB, Leal PC, Calixto JB. The selective nonpeptide CXCR2 antagonist SB225002 ameliorates acute experimental colitis in mice. J Leukoc Biol. 2008;84:1213–21.
Wirtz S, Neufert C, Weigmann B, Neurath MF. Chemically induced mouse models of intestinal inflammation. Nat Protoc. 2007;2:541–6.
Wessale JL, Adler AL, Novosad EI, Calzadilla SV, Dayton BD, Marsh KC, et al. Pharmacology of endothelin receptor antagonists ABT-627, ABT-546, A-182086 and A-192621: ex vivo and in vivo studies. Clin Sci (Lond). 2002;103(Suppl 48):112S–7S.
Claudino RF, Marcon R, Bento AF, Chichorro JG, Rae GA. Endothelins implicated in referred mechanical hyperalgesia associated with colitis induced by TNBS in mice. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010;88:661–7.
Rosano L, Spinella F, Di Castro V, Nicotra MR, Albini A, Natali PG, et al. Endothelin receptor blockade inhibits molecular effectors of Kaposi’s sarcoma cell invasion and tumor growth in vivo. Am J Pathol. 2003;163:753–62.
Cooper HS, Murthy SN, Shah RS, Sedergran DJ. Clinicopathologic study of dextran sulfate sodium experimental murine colitis. Lab Invest. 1993;69:238–49.
Wallace JL, MacNaughton WK, Morris GP, Beck PL. Inhibition of leukotriene synthesis markedly accelerates healing in a rat model of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1989;96:29–36.
Neurath MF, Fuss I, Kelsall BL, Stuber E, Strober W. Antibodies to interleukin 12 abrogate established experimental colitis in mice. J Exp Med. 1995;182:1281–90.
Kimball ES, Wallace NH, Schneider CR, D’Andrea MR, Hornby PJ. Vanilloid receptor 1 antagonists attenuate disease severity in dextran sulphate sodium-induced colitis in mice. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2004;16:811–8.
Rath HC, Herfarth HH, Ikeda JS, Grenther WB, Hamm TE Jr, Balish E, et al. Normal luminal bacteria, especially Bacteroides species, mediate chronic colitis, gastritis, and arthritis in HLA-B27/human beta2 microglobulin transgenic rats. J Clin Invest. 1996;98:945–53.
Van der Sluis M, De Koning BA, De Bruijn AC, Velcich A, Meijerink JP, Van Goudoever JB, et al. Muc2-deficient mice spontaneously develop colitis, indicating that MUC2 is critical for colonic protection. Gastroenterology. 2006;131:117–29.
Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–54.
Talati M, West J, Blackwell TR, Loyd JE, Meyrick B. BMPR2 mutation alters the lung macrophage endothelin-1 cascade in a mouse model and patients with heritable pulmonary artery hypertension. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010;299:L363–73.
Ruetten H, Thiemermann C. Endothelin-1 stimulates the biosynthesis of tumour necrosis factor in macrophages: ET-receptors, signal transduction and inhibition by dexamethasone. J Physiol Pharmacol. 1997;48:675–88.
Zouki C, Baron C, Fournier A, Filep JG. Endothelin-1 enhances neutrophil adhesion to human coronary artery endothelial cells: role of ET(A) receptors and platelet-activating factor. Br J Pharmacol. 1999;127:969–79.
Koseki C, Imai M, Hirata Y, Yanagisawa M, Masaki T. Autoradiographic distribution in rat tissues of binding sites for endothelin: a neuropeptide? Am J Physiol. 1989;256:R858–66.
Inagaki H, Bishop AE, Escrig C, Wharton J, Allen-Mersh TG, Polak JM. Localization of endothelinlike immunoreactivity and endothelin binding sites in human colon. Gastroenterology. 1991;101:47–54.
de la Monte SM, Quertermous T, Hong CC, Bloch KD. Regional and maturation-associated expression of endothelin 2 in rat gastrointestinal tract. J Histochem Cytochem. 1995;43:203–9.
Egidy G, Juillerat-Jeanneret L, Korth P, Bosman FT, Pinet F. The endothelin system in normal human colon. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2000;279:G211–22.
Takizawa S, Uchide T, Adur J, Kozakai T, Kotake-Nara E, Quan J, et al. Differential expression of endothelin-2 along the mouse intestinal tract. J Mol Endocrinol. 2005;35:201–9.
Massai L, Carbotti P, Cambiaggi C, Mencarelli M, Migliaccio P, Muscettola M, et al. Prepro-endothelin-1 mRNA and its mature peptide in human appendix. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2003;284:G340–8.
Takahashi K, Jones PM, Kanse SM, Lam HC, Spokes RA, Ghatei MA, et al. Endothelin in the gastrointestinal tract. Presence of endothelinlike immunoreactivity, endothelin-1 messenger RNA, endothelin receptors, and pharmacological effect. Gastroenterology. 1990;99:1660–7.
Escrig C, Bishop AE, Inagaki H, Moscoso G, Takahashi K, Varndell IM, et al. Localisation of endothelin like immunoreactivity in adult and developing human gut. Gut. 1992;33:212–7.
Baynash AG, Hosoda K, Giaid A, Richardson JA, Emoto N, Hammer RE, et al. Interaction of endothelin-3 with endothelin-B receptor is essential for development of epidermal melanocytes and enteric neurons. Cell. 1994;79:1277–85.
Yoshimura M, Yamashita Y, Kan S, Niwa M, Taniyama K. Localization of endothelin ETB receptors on the myenteric plexus of guinea-pig ileum and the receptor-mediated release of acetylcholine. Br J Pharmacol. 1996;118:1171–6.
McCartney SA, Ballinger AB, Vojnovic I, Farthing MJ, Warner TD. Endothelin in human inflammatory bowel disease: comparison to rat trinitrobenzenesulphonic acid-induced colitis. Life Sci. 2002;71:1893–904.
Lee S, Carter PR, Watts MN, Bao JR, Harris NR. Effects of the endothelin-converting enzyme inhibitor SM-19712 in a mouse model of dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2009;15:1007–13.
Kruschewski M, Anderson T, Loddenkemper C, Buhr HJ. Endothelin-1 receptor antagonist (LU-135252) improves the microcirculation and course of TNBS colitis in rats. Dig Dis Sci. 2006;51:1461–70.
McCarron RM, Wang L, Stanimirovic DB, Spatz M. Endothelin induction of adhesion molecule expression on human brain microvascular endothelial cells. Neurosci Lett. 1993;156:31–4.
Ishizuka T, Takamizawa-Matsumoto M, Suzuki K, Kurita A. Endothelin-1 enhances vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression in tumor necrosis factor alpha-stimulated vascular endothelial cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1999;369:237–45.
Lin CC, Lin WN, Hou WC, Hsiao LD, Yang CM. Endothelin-1 induces VCAM-1 expression-mediated inflammation via receptor tyrosine kinases and Elk/p300 in human tracheal smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015;309:L211–25.
Ohanian J, Forman SP, Katzenberg G, Ohanian V. Endothelin-1 stimulates small artery VCAM-1 expression through p38MAPK-dependent neutral sphingomyelinase. J Vasc Res. 2012;49:353–62.
Sessa WC, Kaw S, Hecker M, Vane JR. The biosynthesis of endothelin-1 by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991;174:613–8.
Elferink JG, de Koster BM. Endothelin-induced activation of neutrophil migration. Biochem Pharmacol. 1994;48:865–71.
Elferink JG, de Koster BM. Modulation of human neutrophil chemotaxis by the endothelin-B receptor agonist sarafotoxin S6c. Chem Biol Interact. 1996;101:165–74.
Hofman FM, Chen P, Jeyaseelan R, Incardona F, Fisher M, Zidovetzki R. Endothelin-1 induces production of the neutrophil chemotactic factor interleukin-8 by human brain-derived endothelial cells. Blood. 1998;92:3064–72.
Sampaio AL, Rae GA, Henriques MG. Participation of endogenous endothelins in delayed eosinophil and neutrophil recruitment in mouse pleurisy. Inflamm Res. 2000;49:170–6.
Sampaio AL, Rae GA, Henriques MG. Effects of endothelin ETA receptor antagonism on granulocyte and lymphocyte accumulation in LPS-induced inflammation. J Leukoc Biol. 2004;76:210–6.
Conte Fde P, Barja-Fidalgo C, Verri WA Jr, Cunha FQ, Rae GA, Penido C, et al. Endothelins modulate inflammatory reaction in zymosan-induced arthritis: participation of LTB4, TNF-alpha, and CXCL-1. J Leukoc Biol. 2008;84:652–60.
Verri WA Jr, Cunha TM, Magro DA, Guerrero AT, Vieira SM, Carregaro V, et al. Targeting endothelin ETA and ETB receptors inhibits antigen-induced neutrophil migration and mechanical hypernociception in mice. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2009;379:271–9.
Zarpelon AC, Pinto LG, Cunha TM, Vieira SM, Carregaro V, Souza GR, et al. Endothelin-1 induces neutrophil recruitment in adaptive inflammation via TNFalpha and CXCL1/CXCR2 in mice. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012;90:187–99.
Gomez-Garre D, Guerra M, Gonzalez E, Lopez-Farre A, Riesco A, Caramelo C, et al. Aggregation of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes by endothelin: role of platelet-activating factor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992;224:167–72.
Lopez-Farre A, Caramelo C, Esteban A, Alberola ML, Millas I, Monton M, et al. Effects of aspirin on platelet-neutrophil interactions. Role of nitric oxide and endothelin-1. Circulation. 1995;91:2080–8.
Cunningham ME, Huribal M, Bala RJ, McMillen MA. Endothelin-1 and endothelin-4 stimulate monocyte production of cytokines. Crit Care Med. 1997;25:958–64.
Peng H, Chen P, Cai Y, Chen Y, Wu QH, Li Y, et al. Endothelin-1 increases expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and production of interlukin-8 in hunan pulmonary epithelial cells. Peptides. 2008;29:419–24.
Speciale L, Roda K, Saresella M, Taramelli D, Ferrante P. Different endothelins stimulate cytokine production by peritoneal macrophages and microglial cell line. Immunology. 1998;93:109–14.
Lomas-Neira JL, Chung CS, Grutkoski PS, Miller EJ, Ayala A. CXCR2 inhibition suppresses hemorrhage-induced priming for acute lung injury in mice. J Leukoc Biol. 2004;76:58–64.
Saleem S, Dai Z, Coelho SN, Konieczny BT, Assmann KJ, Baddoura FK, et al. IL-4 is an endogenous inhibitor of neutrophil influx and subsequent pathology in acute antibody-mediated inflammation. J Immunol. 1998;160:979–84.
Kucharzik T, Lugering N, Weigelt H, Adolf M, Domschke W, Stoll R. Immunoregulatory properties of IL-13 in patients with inflammatory bowel disease; comparison with IL-4 and IL-10. Clin Exp Immunol. 1996;104:483–90.
Acknowledgements
The kind donations of Atrasentan and A-192621 by Dr. Terry Opgenorth (Abbott Laboratories, Abbott Park, USA) is gratefully acknowledged. The study was supported by the Brazilian National Research Council (CNPq), Coordenacao de Aperfeicoamento de Pessoal de Nivel Superior (Capes) and Fundacao de Amparo a Ciencia e Tecnologia do Estado de Santa Catarina (Funcitec).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Mauro Teixeira.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Claudino, R.F., Leite, D.F., Bento, A.F. et al. Potential role for ET-2 acting through ETA receptors in experimental colitis in mice. Inflamm. Res. 66, 141–155 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-016-1001-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-016-1001-7