Abstract
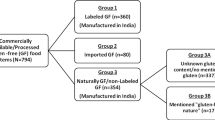
Patients with celiac disease have to rely on the safety of gluten-free foods (GFF), which are frequently contaminated by gluten. Hence, the evaluation of the gluten level in these foods is important. The aim of this study was to assess the gluten content in GFF available in Morocco. It was carried out on 84 food samples including 52 labelled gluten-free foods (L-GFF) and 32 naturally gluten-free foods (N-GFF), belonging to six categories (pasta, cookies and cakes, baker's yeast, dried vegetables, dried fruits, and cereals). To quantify their gluten content, samples were analysed using a sandwich enzyme immunosorbent assay (R5 ELISA Ridascreen® gliadin Mendez), considering 20 mg/kg (ppm) as the contamination threshold. The overall contamination rate was 23.8% (L-GFF: 21.9%, N-GFF: 25%). Among the six analysed categories, three did not show any contamination (pasta, cookies, and baker's yeast). The contamination rate was 5.3% in dried vegetables, 25% in dried fruits, and 42.1% in cereals. All oat samples were affected. L-GFF locally manufactured were more often contaminated than those imported (28.6 vs. 16.7%). Our data show a high prevalence of gluten contamination of GFF, affecting both N-GFF and L-GFF, and oats were the most contaminated food. Therefore, regular checks of GFF by the competent authorities are necessary in order to avoid the sale of unsafe GFF for celiac patients. Likewise, manufacturers should be encouraged to adopt adequate quality management systems.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agakidis C, Karagiozoglou-Lampoudi T, Kalaitsidou M, Papadopoulos T, Savvidou A, Daskalou E, Dimitrios T (2011) Enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay gliadin assessment in processed food products available for persons with celiac disease: a feasibility study for developing a gluten-free food database. Nutr Clin Pract 26(6):695–699. https://doi.org/10.1177/0884533611418784
Alaedini A, Green PH (2005) Narrative review: celiac disease: understanding a complex autoimmune disorder. Ann Intern Med 142(4):289–298. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-142-4-200502150-00011
Atasoy G, Kurt Gokhisar O, Turhan M (2020) Gluten contamination in manufactured gluten-free foods in Turkey. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess 37(3):363–373. https://doi.org/10.1080/19440049.2019.1696021
Ben Houmich T, Admou B (2021) Celiac disease: understandings in diagnostic, nutritional, and medicinal aspects. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 35:20587384211008708. https://doi.org/10.1177/20587384211008709
Bustamante MÁ, Fernández-Gil MP, Churruca I, Miranda J, Lasa A, Navarro V, Simón E (2017) Evolution of gluten content in cereal-based gluten-free products: an overview from 1998 to 2016. Nutrients 9(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9010021
Cawthorn DM, Steinman HA, Witthuhn RC (2010) Wheat and gluten in South African food products. Food Agric Immunol 21(2):91–102. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540100903443725
Codex Alimentarius Commission (2006) Joint Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations/World Health Organization Food Standards Program. Report of the Twenty-Seventh Session of the Codex Committee on Methods of Analysis and Sampling. ALINORM 06/29/23
CODEX STAN WHO/FAO (2008) Standard for foods for special dietary use for persons intolerant to gluten. CODEX STAN 118–1979. Adopted in 1979. Amendment: 1983 and 2015. Revision. https://www.fao.org/fao-who-codexalimentarius/sh-proxy/en/?lnk=1&url=https%253A%252F%252Fworkspace.fao.org%252Fsites%252Fcodex%252FStandards%252FCXS%2B118-1979%252FCXS_118e_2015.pdf Accessed Sep 2021
Cohen IS, Day AS, Shaoul R (2019) Gluten in celiac disease—more or less? Rambam Maimonides Med J 10(1):e0007. https://doi.org/10.5041/RMMJ.10360
Collin P, Thorell L, Kaukinen K, Mäki M (2004) The safe threshold for gluten contamination in gluten-free products. Can trace amounts be accepted in the treatment of celiac disease? Aliment Pharmacol Ther 19(12):1277–1283. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2036.2004.01961.x
Daniewski W, Wojtasik A, Kunachowicz H (2010) Gluten content in special dietary use gluten-free products and other food products. Rocz Panstw Zakl Hig 61(1):51–55
Dewar DH, Amato M, Ellis HJ, Pollock EL, Gonzalez-Cinca N, Wieser H, Ciclitira PJ (2006) The toxicity of high molecular weight glutenin subunits of wheat to patients with coeliac disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 18(5):483–491. https://doi.org/10.1097/00042737-200605000-00005
EFSA (2011) The European Union summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in 2009. EFSA J 9:2090
El Fakiri K, Bourahouate A, Hadi A, Sab IA, Sbihi M (2016) Celiac disease in infants and children at the Marrakech University Hospital. J De Pediatrie Et De Pueric 29(6):289–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpp.2016.08.004
EUR-Lex (2018) Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) No 828/2014 of 30 July 2014 on the requirements for the provision of information to consumers on the absence or reduced presence of gluten in food. https://eurlex.europa.eu/eli/reg_impl/2014/828/oj. Accessed 20 June 2021
European Commision (2011) Regulation (EU) No 1169/2011 of The European Parliament and of the Council of 25 October 2011 on the provision of food information to consumers, amending Regulations (EC) No 1924/2006 and (EC) No 1925/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council, and repealing Commission Directive 87/250/EEC, Council Directive 90/496/EEC, Commission Directive 1999/10/EC, Directive 2000/13/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council, Commission Directives 2002/67/EC and 2008/5/EC and Commission Regulation (EC) No 608/2004. Off J Eur Union L 54(304):18–63
Farage P, de Medeiros Nóbrega YK, Pratesi R, Gandolfi L, Assunção P, Zandonadi RP (2017) Gluten contamination in gluten-free bakery products: a risk for celiac disease patients. Public Health Nutr 20(3):413–416. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1368980016002433
Faulkner-Hogg K, Hodge L, Swain A (2009) Coeliac disease. Aust Fam Phys 38(10):785–786
Federal Register of Legislation (2020) Federal Register of Legislation. Australia and New Zealand Food Standards Code. Available online: https://www.legislation.gov.au/Details/F2016C00189. Accessed 25 Oct 2019
Gibert A, Kruizinga AG, Neuhold S, Houben GF, Canela MA, Fasano A, Catassi C (2013) Might gluten traces in wheat substitutes pose a risk in patients with celiac disease? A population-based probabilistic approach to risk estimation. Am J Clin Nutr 97(1):109–116. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.112.047985
Grand View Research, Inc.[US] (2017) Gluten-free products market analysis by product (bakery, dairy alternatives, desserts and ice-creams, prepared foods, pasta & rice), by distribution (grocery stores, mass merchandiser, club stores), and segment forecasts, 2018–2025. https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/gluten-free-products-market. Accessed June 2021
Guennouni M, El Khoudri N, Bourrhouat A, Hilali A (2020a) Nutritional quality of gluten-free products in Moroccan supermarkets and e-commerce platforms. Cereal Chem 97(5):912–920. https://doi.org/10.1002/cche.10313
Guennouni M, El Khoudri N, Bourrouhouate A, Hilali A (2020b) Availability and cost of gluten-free products in Moroccan supermarkets and e-commerce platforms. Br Food J. https://doi.org/10.1108/BFJ-06-2019-0411 (ahead-of-print)
Guennouni M, Admou B, Bourrhouate A, Elkhoudri N, Fguirouche A, Nibaruta JC, Hilali A (2021a) Quality of life of Moroccan children with celiac disease: Arabic translation and validation of a specific celiac disease instrument. J Pediatr Nurs 62:e1–e6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pedn.2021.06.011
Guennouni M, Admou B, Bourrhouat A, Zogaam LG, Elmoumou L, Hilali A (2021b) Gluten contamination in labelled gluten-free, naturally gluten-free and meals in food services in low-, middle-and high-income countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114521002488
Halmos EP, Di Bella CA, Webster R, Deng M, Tye-Din JA (2018) Gluten in “gluten-free” food from food outlets in Melbourne: a cross-sectional study. Med J Aust 209(1):42–43. https://doi.org/10.5694/mja17.00883
Hassan H, Elaridi J, Bassil M (2017) Evaluation of gluten in gluten-free-labeled foods and assessment of exposure level to gluten among celiac patients in Lebanon. Int J Food Sci Nutr 68(7):881–886. https://doi.org/10.1080/09637486.2017.1303461
Howdle PD (2006) Gliadin, glutenin or both? The search for the Holy Grail in coeliac disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 18(7):703–706
Kemppainen TA, Heikkinen MT, Ristikankare MK, Kosma VM, Julkunen RJ (2010) Nutrient intakes during diets including unkilned and large amounts of oats in celiac disease. Eur J Clin Nutr 64(1):62–67. https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2009.113
Koerner TB, Cleroux C, Poirier C, Cantin I, Alimkulov A, Elamparo H (2011) Gluten contamination in the Canadian commercial oat supply. Food Addit Contam 28(6):705–710. https://doi.org/10.1080/19440049.2011.579626
Koerner TB, Cleroux C, Poirier C, Cantin I, La Vieille S, Hayward S, Dubois S (2013) Gluten contamination of naturally gluten-free flours and starches used by Canadians with celiac disease. Food Addit Contam Part A 30(12):2017–2021. https://doi.org/10.1080/19440049.2013.840744
La Vieille S, Dubois S, Hayward S, Koerner TB (2014) Estimated levels of gluten incidentally present in a Canadian gluten-free diet. Nutrients 6(2):881–896. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6020881
Lee HJ, Anderson Z, Ryu D (2014) Gluten contamination in foods labeled as “gluten free” in the United States. J Food Prot 77(10):1830–1833. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-14-149
Losio MN, Dalzini E, Pavoni E, Merigo D, Finazzi G, Daminelli P (2017) A survey study on safety and microbial quality of “gluten-free” products made in Italian pasta factories. Food Control 73:316–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2016.08.020
Malvano F, Albanese D, Pilloton R, Di Matteo M (2017) A new label-free impedimetric aptasensor for gluten detection. Food Control 79:200–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.03.033
Mattioni B, Scheuer PM, Antunes AL, Paulino N, de Francisco A (2016) Compliance with gluten-free labelling regulation in the Brazilian Food Industry. Cereal Chem 93(5):518–522. https://doi.org/10.1094/CCHEM-08-15-0158-R
McAllister BP, Williams E, Clarke K (2019) A comprehensive review of celiac disease/gluten-sensitive enteropathies. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 57(2):226–243. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-018-8691-2
Mehtab W, Sachdev V, Singh A, Agarwal S, Singh N, Malik R, Malhotra A, Ahuja V, Makharia G (2021) Gluten content in labeled and unlabeled gluten-free food products used by patients with celiac disease. Eur J Clin Nutr 18:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-020-00854-6
Mena M, Sousa C (2015) Analytical tools for gluten detection. Policies and regulation. In: Arranz E, Fernández-Bañares F, Rosell CM, Rodrigo L, Peña AS (eds) Advances in the understanding of gluten related pathology and the evolution of gluten-free foods, 1st edn. OmniaScience, Barcelona, pp 527–564. https://doi.org/10.3926/oms.264
National Office for Food Safety (2018) Regulations: labelling of food products. Decree no. aw 78-10, 2013. Décret n°2-12-389. Retrieved from http://www.onssa.gov.ma/fr/reglementation-etiquetage-des-produitsalimentaires
Nerín C, Aznar M, Carrizo D (2016) Food contamination during food process. Trends Food Sci Technol 48:63–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2015.12.004
Osorio CE, Mejías JH, Rustgi S (2019) Gluten detection methods and their critical role in assuring safe diets for celiac patients. Nutrients 11(12):2920. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11122920
Oujamaa I, Sebbani M, Elmoumou L, Bourrahouate A, El Qadiry R, El Moussaoui S, Ait Sab I, Sbihi M, Ennazk L, Mghari-Tabib E, El Ansari N (2019) The prevalence of celiac disease-specific auto-antibodies in type 1 diabetes in a Moroccan population. Int J Endocrinol 19:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7895207
Panda R, Garber EA (2019) Detection and quantitation of gluten in fermented-hydrolyzed foods by antibody-based methods: challenges, progress, and a potential path forward. Front Nutr 28(6):97. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2019.00097
Petruzzelli A, Foglini M, Paolini F, Framboas M, Serena Altissimi M, Naceur Haouet M, Mangili P, Osimani A, Clementi F, Cenci T, Tonucci F (2014) Evaluation of the quality of foods for special diets produced in a school catering facility within a HACCP-based approach: a case study. Int J Environ Health Res 24(1):73–81. https://doi.org/10.1080/09603123.2013.782605
Raju N, Joshi AK, Vahini R, Deepika T, Bhaskarachari K, Devindra S (2020) Gluten contamination in labelled and naturally gluten-free grain products in southern India. Food Addit Contam Part A 37(4):531–538. https://doi.org/10.1080/19440049.2020.1711970
Rosell CM, Barro F, Sousa C, Mena MC (2014) Cereals for developing gluten-free products and analytical tools for gluten detection. J Cereal Sci 59:354–364
Rysová J, Mašková E, Šmídová Z (2019) The gluten content in oat products available on the Czech market. Czech J Food Sci 37(5):345–350. https://doi.org/10.17221/114/2018-CJFS
Sansotta N, Amirikian K, Guandalini S, Jericho H (2018) Celiac disease symptom resolution: effectiveness of the gluten-free diet. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 66(1):48–52. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0000000000001634
Sewell AM, Farber JM (2001) Foodborne outbreaks in Canada linked to produce. J Food Prot 64(11):1863–1877. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X-64.11.1863
Sharma GM, Pereira M, Williams KM (2015) Gluten detection in foods available in the United States—a market survey. Food Chem 169:120–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.07.134
Singh P, Arora A, Strand TA, Leffler DA, Catassi C, Green PH, Kelly CP, Ahuja V, Makharia GK (2018) Global prevalence of celiac disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 16(6):823–836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2017.06.037
Størsrud S, Hulthen LR, Lenner RA (2003) Beneficial effects of oats in the gluten-free diet of adults with special reference to nutrient status, symptoms and subjective experiences. Br J Nutr 90(1):101–107. https://doi.org/10.1079/BJN2003872
Thompson T (2004) Gluten contamination of commercial oat products in the United States. N Engl J Med 351(19):2021–2022. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM200411043511924
Vader W, Kooy Y, Van Veelen P, De Ru A, Harris D, Benckhuijsen W, Peña S, Mearin L, Drijfhout JW, Koning F (2002) The gluten response in children with celiac disease is directed toward multiple gliadin and glutenin peptides. Gastroenterology 122(7):1729–1737. https://doi.org/10.1053/gast.2002.33606
Verma AK, Gatti S, Galeazzi T, Monachesi C, Padella L, Baldo GD, Annibali R, Lionetti E, Catassi C (2017) Gluten contamination in naturally or labeled gluten-free products marketed in Italy. Nutrients 9(2):115. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9020115
Vukman D, Viličnik P, Vahčić N, Lasić D, Niseteo T, Krbavčić IP, Bituh M (2020) Design and evaluation of an HACCP gluten-free protocol in a children’s hospital. Food Control 120:107527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2020.107527
Wieser H (2007) Chemistry of gluten proteins. Food Microbiol 24(2):115–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2006.07.004
Xhakollari V, Canavari M, Osman M (2019) Factors affecting consumers’ adherence to gluten-free diet, a systematic review. Trends Food Sci Technol 85:23–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2018.12.005
Zuidmeer L, Goldhahn K, Rona RJ, Gislason D, Madsen C, Summers C, Sodergren E, Dahlstrom J, Lindner T, Sigurdardottir ST, McBride D (2008) The prevalence of plant food allergies: a systematic review. J Allergy Clin Immunol 121(5):1210–1218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2008.02.019
Funding
This study did not receive any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guennouni, M., Elmoumou, L., Admou, B. et al. Detection of gluten content in both naturally and labelled gluten-free products available in Morocco. J Consum Prot Food Saf 17, 137–144 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00003-022-01374-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00003-022-01374-0