Abstract
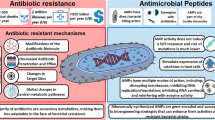
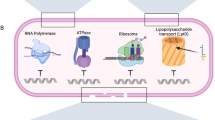
Currently, antimicrobial drug resistance is a global problem that threatens to precipitate a ‘Post-antibiotic era’ in which the ability of common infections and minor injuries to kill is a very real possibility. A potential solution to this problem is the development of host defence peptides, which are endogenous antibiotics that kill microbes via membranolytic action, based in part on the belief that microbes were unlikely to develop resistance to this action. However, the incidence of microbes exhibiting resistance to the action of host defence peptides is growing and an increasingly diverse spectrum of mechanisms is being reported to underpin this resistance. These mechanisms can be broadly categorized as those that either: destroy these peptides, such as through the production of bacterial proteases; intercept/shield these peptides, such as by the release of host cell proteoglycans by bacterial enzymes; or export these peptides, such as via the use of bacterial efflux pumps. Here we give an overview of these mechanisms, with a focus on recent developments in this area, and then discuss the potential of inhibitors of these resistance mechanisms to treat infections due to bacterial pathogens.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelsalam M, Asheg A, Eissa AE (2013) Streptococcus dysgalactiae: An emerging pathogen of fishes and mammals. Int J Vet Sci Med 1(1):1–6
Agus A et al (2014) Understanding host-adherent-invasive Escherichia coli interaction in crohn’s disease: opening up new therapeutic strategies. Biomed Res Int 2014:16
Åkesson P, Sjöholm AG, Björck L (1996) Protein SIC, a novel extracellular protein of Streptococcus pyogenes interfering with complement function. J Biol Chem 271(2):1081–1088
Aloia RC, Tian H, Jensen FC (1993) Lipid composition and fluidity of the human immunodeficiency virus envelope and host cell plasma membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci 90(11):5181–5185
Alteri CJ et al (2011) The broadly conserved regulator PhoP links pathogen virulence and membrane potential in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 82(1):145–163
Alvarez-Ortega C, Olivares J, Martinez JL (2013) RND multidrug efflux pumps: what are they good for? Front Microbiol 4
Amaral L et al (2012) Structure, genetic regulation, physiology and function of the AcrAB-TolC efflux pump of Escherichia coli and Salmonella. In: Tegos G, Mylonakis E (ed) Antimicrobial drug discovery: emerging strategies, pp 44–61
Aminov RI (2010) A brief history of the antibiotic era: lessons learned and challenges for the future. Front Microbiol 1:134
Anaya-Lopez JL, Lopez-Meza JE, Ochoa-Zarzosa A (2013) Bacterial resistance to cationic antimicrobial peptides. Crit Rev Microbiol 39(2):180–195
Andersen JL et al (2015) Multidrug efflux pumps from enterobacteriaceae, vibrio cholerae and Staphylococcus aureus bacterial food pathogens. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12(2):1487–1547
Andra J et al (2004) Biophysical characterization of endotoxin inactivation by NK-2, an antimicrobial peptide derived from mammalian NK-lysin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 48(5):1593–1599
Andra J et al (2011) Multiple peptide resistance factor (MprF)-mediated resistance of Staphylococcus aureus against antimicrobial peptides coincides with a modulated peptide interaction with artificial membranes comprising lysyl-phosphatidylglycerol. J Biol Chem 286(21):18692–18700
Anes J et al (2015) The ins and outs of RND efflux pumps in Escherichia coli. Front Microbiol 6:14
Arendt W et al (2012) Resistance phenotypes mediated by aminoacyl-phosphatidylglycerol synthases. J Bacteriol 194(6):1401–1416
Ashby M, Petkova A, Hilpert K (2014) Cationic antimicrobial peptides as potential new therapeutic agents in neonates and children: a review. Curr Opin Infect Dis 27(3):258–267
Avila-Calderón E et al (2015) Roles of bacterial membrane vesicles. Arch Microbiol 197(1):1–10
Bader MW et al (2003) Regulation of Salmonella typhimurium virulence gene expression by cationic antimicrobial peptides. Mol Microbiol 50(1):219–230
Bader MW et al (2005) Recognition of antimicrobial peptides by a bacterial sensor kinase. Cell 122(3):461–472
Baker J, Wright SH, Tama F (2012) Simulations of substrate transport in the multidrug transporter EmrD. Proteins Struct Funct Bioinf 80(6):1620–1632
Balciunas EM et al (2013) Novel biotechnological applications of bacteriocins: a review. Food Control 32(1):134–142
Band VI, Weiss DS (2015) Mechanisms of antimicrobial peptide resistance in Gram-negative bacteria. Antibiotics (Basel) 4(1):18–41
Barrett AJ, Rawlings ND, Woessner JF (2012) Handbook of proteolytic enzymes, Elsevier Science
Bastos MDD, Coelho MLV, Santos OCD (2015) Resistance to bacteriocins produced by Gram-positive bacteria. Microbiol SGM 161:683–700
Batabyal B, Kundu GKR, Biswas S (2012) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a brief review. International Research Journal of Biological Sciences 1:65–71
Bavro VN, Marshall RL, Symmons MF (2015) Architecture and roles of periplasmic adaptor proteins in tripartite efflux assemblies. Front Microbiol 6
Bayer AS et al (1998) In vitro resistance to thrombin-induced platelet microbicidal protein among clinical bacteremic isolates of Staphylococcus aureus correlates with an endovascular infectious source. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 42(12):3169–3172
Bayer AS et al (2000) In vitro resistance of Staphylococcus aureus to thrombin-induced platelet microbicidal protein is associated with alterations in cytoplasmic membrane fluidity. Infect Immun 68(6):3548–3553
Bayer AS et al (2006) Low-level resistance of Staphylococcus aureus to thrombin-induced platelet microbicidal protein 1 in vitro associated with qacA gene carriage is independent of multidrug efflux pump activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 50(7):2448–2454
Bayer AS, Schneider T, Sahl HG (2013) Mechanisms of daptomycin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: role of the cell membrane and cell wall. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1277:139–158
Belden WJ, Miller SI (1994) Further characterization of the PhoP regulon—identification of new PhoP-activated virulence loci. Infect Immun 62(11):5095–5101
Bellm L, Lehrer RI, Ganz T (2000) Protegrins: new antibiotics of mammalian origin. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 9(8):1731–1742
Bengoechea JA, Skurnik M (2000) Temperature-regulated efflux pump/potassium antiporter system mediates resistance to cationic antimicrobial peptides in Yersinia. Mol Microbiol 37(1):67–80
Bentley R (2009) Different roads to discovery; Prontosil (hence sulfa drugs) and penicillin (hence beta-lactams). J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36(6):775–786
Bhardwaj AK, Mohanty P (2012) Bacterial efflux pumps involved in multidrug resistance and their inhibitors: rejuvinating the antimicrobial chemotherapy. Recent Pat Anti-Infect Drug Discov 7(1):73–89
Bialvaei AZ, Kafil HS (2015) Colistin, mechanisms and prevalence of resistance. Curr Med Res Opin 31(4):707–721
Bisno AL, Brito MO, Collins CM (2003) Molecular basis of group A streptococcal virulence. Lancet Infect Dis 3(4):191–200
Bjarnsholt T (2013) The role of bacterial biofilms in chronic infections. APMIS 121:1–58
Blair JMA, Richmond GE, Piddock LJV (2014) Multidrug efflux pumps in Gram-negative bacteria and their role in antibiotic resistance. Future Microbiology 9(10):1165–1177
Bostanci N, Belibasakis GN (2012) Porphyromonas gingivalis: an invasive and evasive opportunistic oral pathogen. FEMS Microbiol Lett 333(1):1–9
Brannon JR et al (2013) Role of uropathogenic Escherichia coli OmpT in the resistance against human cathelicidin LL-37. FEMS Microbiol Lett 345(1):64–71
Breidenstein EBM, de la Fuente-Nunez C, Hancock REW (2011) Pseudomonas aeruginosa: all roads lead to resistance. Trends Microbiol 19(8):419–426
Brincat JP et al (2011) Discovery of novel inhibitors of the NorA multidrug transporter of Staphylococcus aureus. J Med Chem 54(1):354–365
Brinkmann V, Zychlinsky A (2012) Neutrophil extracellular traps: Is immunity the second function of chromatin? J Cell Biol 198(5):773–783
Brogden KA (2005) Antimicrobial peptides: Pore formers or metabolic inhibitors in bacteria? Nat Rev Microbiol 3(3):238–250
Brown MH, Skurray RA (2002) Structure, function and regulation of the staphylococcal multidrug efflux protein QacA. In: Paulsen IT, Lewis K (eds) JMMB symposium series, microbial multidrug efflux, vol 4, pp 49–66
Carlisle MD, Srikantha RN, Brogden KA (2009) Degradation of human alpha- and beta-defensins by culture supernatants of Porphyromonas gingivalis strain 381. J Innate Immun 1(2):118–122
Chen YC et al (2004) A K + yptake protein, TrkA, is required for serum, protamine, and polymyxin B resistance in Vibrio vulnificus. Infect Immun 72(2):629–636
Cheng H-Y, Chen Y-F, Peng H-L (2010) Molecular characterization of the PhoPQ-PmrD-PmrAB mediated pathway regulating polymyxin B resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae CG43. J Biomed Sci 17
Cipolla L et al (2011) New targets for antibacterial design: Kdo biosynthesis and LPS machinery transport to the cell surface. Curr Med Chem 18(6):830–852
ClinicalTrials.gov (2014) Pexiganan versus placebo control for the treatment of mild infections of diabetic foot ulcers (OneStep-1). Accessed 6 April 15. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01590758
Coetzer THT, Goldring JPD, Huson LEJ (2008) Oligopeptidase B: A processing peptidase involved in pathogenesis. Biochimie 90(2):336–344
Cole ST (2014) Who will develop new antibacterial agents? Philos Trans R Soc B Biol Sci 369(1645):7
Cole JN et al (2010) M protein and hyaluronic acid capsule are essential for in vivo selection of covRS mutations characteristic of invasive serotype M1T1 group A Streptococcus. MBio 1(4)
Collu F, Cascella M (2013) Multidrug resistance and efflux pumps: insights from molecular dynamics simulations. Curr Top Med Chem 13(24):3165–3183
Cooper PR, Palmer LJ, Chapple ILC (2000) Neutrophil extracellular traps as a new paradigm in innate immunity: friend or foe? Periodontology 2000, 2013. 63(1):165–197
Costa SS et al (2013) Multidrug efflux pumps in Staphylococcus aureus: an update. Open Microbiol J 7:59–71
Costa TRD et al (2015) Secretion systems in Gram-negative bacteria: structural and mechanistic insights. Nat Rev Micro 13(6):343–359
Cotter PD, Ross RP, Hill C (2013) Bacteriocins—a viable alternative to antibiotics? Nat Rev Microbiol 11(2):95–105
Cruz J et al (2014) Antimicrobial peptides: promising compounds against pathogenic microorganisms. Curr Med Chem 21(20):2299–2321
da Costa JP et al (2015) Antimicrobial peptides: an alternative for innovative medicines? Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(5):2023–2040
Dalebroux ZD, Miller SI (2014) Salmonellae PhoPQ regulation of the outer membrane to resist innate immunity. Curr Opin Microbiol 17:106–113
Dalebroux ZD et al (2014) PhoPQ regulates acidic glycerophospholipid content of the Salmonella typhimurium outer membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111(5):1963–1968
Danne C, Dramsi S (2012) Pili of Gram-positive bacteria: roles in host colonization. Res Microbiol 163(9–10):645–658
Davidson AL et al (2008) Structure, function, and evolution of bacterial ATP-binding cassette systems. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 72(2):317–364
Davies J (2006) Where have all the antibiotics gone? Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol (Journal canadien des maladies infectieuses et de la microbiologie medicale/AMMI Canada) 17(5):287–90
Delmar JA, Su C-C, Yu EW (2014) Bacterial multidrug efflux transporters. Annu Rev Biophys 43(1):93–117
Dennison SR, Harris F, Phoenix DA (2005) Are oblique orientated alpha-helices used by antimicrobial peptides for membrane invasion? Protein Pept Lett 12(1):27–29
Dennison SR et al (2013) A novel form of bacterial resistance to the action of eukaryotic host defense peptides, the use of a lipid receptor. Biochemistry 52(35):6021–6029
Dennison SR et al (2015) Use of the antimicrobial peptide, maximin H5 to protect against Staphylococcus aureus. In: 5th international meeting of antimicrobial peptides 2015. Royal Society for Chemistry, London
Dennison SR et al (2015) The role of C-terminal amidation in the membrane interactions of the anionic antimicrobial peptide, maximin H5. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Biomembr 1848(5):1111–1118
Destoumieux-Garzón D et al (2014) Resistance to antimicrobial peptides in vibrios. Antibiotics 3(4):540–563
Devine DA et al (1999) Modulation of antibacterial peptide activity by products of Porphyromonas Gingivalis and Prevotella spp. Microbiol UK 145:965–971
Dhawan VK, Bayer AS, Yeaman MR (1998) In vitro resistance to thrombin-induced platelet microbicidal protein is associated with enhanced progression and hematogenous dissemination in experimental Staphylococcus aureus infective endocarditis. Infect Immun 66(7):3476–3479
Dobson AJ et al (2013) Comparing selection on S. aureus between antimicrobial peptides and common antibiotics. PLoS ONE 8(10):5
Dobson AJ, Purves J, Rolff J (2014) Increased survival of experimentally evolved antimicrobial peptide-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in an animal host. Evol Appl 7(8):905–912
Dorner F, Lienkamp K (2014) Chapter 5 polymer-based synthetic mimics of antimicrobial peptides (SMAMPs)—a new class of nature-inspired antimicrobial agents with low bacterial resistance formation potential, in polymeric materials with antimicrobial activity: from synthesis to applications. R Soc Chem 97–138
Dorotkiewicz-Jach A et al (2015) Modern therapeutic approaches against Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Curr Med Chem 22(14):1642–1664
Draper LA et al (2015) Lantibiotic resistance. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev MMBR 79(2):171–191
Drider D, Rebuffat S (2011) Prokaryotic antimicrobial peptides: from genes to applications. Springer, New York
Duperthuy M et al (2013) Role of the Vibrio cholerae matrix protein Bap1 in cross-resistance to antimicrobial peptides. PLoS Pathog 9(10):e1003620
Duquesne S et al (2007) Microcins, gene-encoded antibacterial peptides from enterobacteria. Nat Prod Rep 24(4):708–734
Eckert R (2011) Road to clinical efficacy: challenges and novel strategies for antimicrobial peptide development. Future Microbiol 6(6):635–651
Elkins CA, Mullis LB (2006) Mammalian steroid hormones are substrates for the major RND- and MFS-type tripartite multidrug efflux pumps of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 188(3):1191–1195
Epand RM, Epand RF (2011) Bacterial membrane lipids in the action of antimicrobial agents. J Pept Sci 17(5):298–305
Ernst CM, Peschel A (2011) Broad-spectrum antimicrobial peptide resistance by MprF-mediated aminoacylation and flipping of phospholipids. Mol Microbiol 80(2):290–299
Escaich S (2010) Novel agents to inhibit microbial virulence and pathogenicity. Expert Opin Ther Pat 20(10):1401–1418
Eswarappa SM et al (2008) The yejABEF operon of Salmonella confers resistance to antimicrobial peptides and contributes to its virulence. Microbiology 154(2):666–678
Evans ML, Chapman MR (2014) Curli biogenesis: Order out of disorder. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1843(8):1551–1558
Falord M et al (2011) Investigation of the Staphylococcus aureus GraSR regulon reveals novel links to virulence, stress response and cell wall signal transduction pathways. PLoS ONE 6(7):e21323
Falord M et al (2012) GraXSR proteins interact with the VraFG ABC transporter to form a five-component system required for cationic antimicrobial peptide sensing and resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56(2):1047–1058
Fernández L, Hancock REW (2012) Adaptive and mutational resistance: role of porins and efflux pumps in drug resistance. Clin Microbiol Rev 25(4):661–681
Fernández-Fuentes MA et al (2014) Genetic determinants of antimicrobial resistance in Gram positive bacteria from organic foods. Int J Food Microbiol 172:49–56
Fernando D, Kumar A (2013) Resistance-nodulation-division multidrug efflux pumps in Gram-negative bacteria: role in virulence. Antibiotics 2(1):163
Fernie-King BA, Seilly DJ, Lachmann PJ (2004) The interaction of streptococcal inhibitor of complement (SIC) and its proteolytic fragments with the human beta defensins. Immunology 111(4):444–452
Fernie-King BA et al (2007) Streptococcal DRS (distantly related to SIC) and SIC inhibit antimicrobial peptides, components of mucosal innate immunity: a comparison of their activities. Microbes Infect 9(3):300–307
Ferreira M, Costa J, Reis-Henriques MA (2014) ABC transporters in fish species: a review. Front Physiol 5
Forrest LR, Krämer R, Ziegler C (2011) The structural basis of secondary active transport mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Bioenerg 1807(2):167–188
Fox JL (2013) Antimicrobial peptides stage a comeback. Nat Biotechnol 31(5):379–382
Franco OL, Parachin NS (2014) New edge of antibiotic development: antimicrobial peptides and corresponding resistance. Frontiers E-books
Frees D, Brøndsted L, Ingmer H (2013) Bacterial proteases and virulence. In: Dougan DA (ed) Regulated proteolysis in microorganisms. Springer, Netherlands, pp 161–192
Frick I-M et al (2003) SIC, a secreted protein of Streptococcus pyogenes that inactivates antibacterial peptides. J Biol Chem 278(19):16561–16566
Frick I-M et al (2008) Identification of a novel protein promoting the colonization and survival of Finegoldia magna, a bacterial commensal and opportunistic pathogen. Mol Microbiol 70(3):695–708
Frick I-M et al (2011a) Antibacterial activity of the contact and complement systems is blocked by SIC, a protein secreted by Streptococcus pyogenes. J Biol Chem 286(2):1331–1340
Frick I-M et al (2011b) Constitutive and inflammation-dependent antimicrobial peptides produced by epithelium are differentially processed and inactivated by the commensal finegoldia magna and the pathogen Streptococcus pyogenes. J Immunol 187(8):4300–4309
Fronzes R, Remaut H, Waksman G (2008) Architectures and biogenesis of non-flagellar protein appendages in Gram-negative bacteria. The EMBO J 27(17):2271–2280
Gabrielli L et al (2012) Recent approaches to novel antibacterials designed after LPS structure and biochemistry. Curr Drug Targets 13(11):1458–1471
Ganz T et al (1985) Defensins—natural peptide antibiotics of human-neutrophils. J Clin Invest 76(4):1427–1435
Gebhard S (2012) ABC transporters of antimicrobial peptides in Firmicutes bacteria—phylogeny, function and regulation. Mol Microbiol 86(6):1295–1317
Gela A et al (2014) Midkine in host defence. Br J Pharmacol 171(4):859–869
German N, Wei P, Kaatz GW, Kerns RJ (2008) Synthesis and evaluation of fluoroquinolone derivatives as substrate-based inhibitors of bacterial efflux pumps. Eur J Med Chem. 43(11):2453–63
Ghosh P (2011) The nonideal coiled coil of M protein and its multifarious functions in pathogenesis. In: Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, pp 197–211
Goldberg K et al (2013) Sensitization of gram-negative bacteria by targeting the membrane potential. Faseb Journal 27(9):3818–3826
Gomes F, Teixeira P, Oliveira R (2014) Mini-review: Staphylococcus epidermidis as the most frequent cause of nosocomial infections: old and new fighting strategies. Biofouling 30(2):131–141
Goyita M, Kandler JL, Shafer WM (2013) Mechanisms and significance of bacterial resistance to human cationic antimicrobial peptides. In: Hiemstra PS, Zaat SAJ (eds) Antimicrobial peptides and innate immunity. Springer, Basel, pp 219–255
Grenier D, La VD (2011) Proteases of Porphyromonas gingivalis as important virulence factors in periodontal disease and potential targets for plant-derived compounds: a review article. Curr Drug Targets 12(3):322–331
Groisman EA (2001) The pleiotropic two-component regulatory system PhoP-PhoQ. J Bacteriol 183(6):1835–1842
Gruenheid S, Le Moual H (2012) Resistance to antimicrobial peptides in Gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 330(2):81–89
Gudhka RK, Neilan BA, Burns BP (2015) Adaptation, ecology, and evolution of the halophilic stromatolite archaeon Halococcus hamelinensis inferred through genome analyses. Archaea (Vancouver, B.C.) 2015:241608–241608
Guilhelmelli F et al (2013) Antimicrobial development challenges: the various mechanisms of action of antimicrobial peptides and of bacterial resistance. Front Microbiol 4
Guina T et al (2000) A PhoP-regulated outer membrane protease of Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium promotes resistance to alpha-helical antimicrobial peptides. J Bacteriol 182(14):4077–4086
Gunn JS, Miller SI (1996) PhoP-PhoQ activates transcription of pmrAB, encoding a two-component regulatory system involved in Salmonella typhimurium antimicrobial peptide resistance. J Bacteriol 178(23):6857–6864
Guo L et al (1998) Lipid a acylation and bacterial resistance against vertebrate antimicrobial peptides. Cell 95(2):189–198
Guo Y, Nguyen K-A, Potempa J (2000) Dichotomy of gingipains action as virulence factors: from cleaving substrates with the precision of a surgeon’s knife to a meat chopper-like brutal degradation of proteins. Periodontology 2010(54):15–44
Gupta S et al (2011) DbMDR: a relational database for multidrug resistance genes as potential drug targets. Chem Biol Drug Des 78(4):734–738
Gupta V et al (2015) Detection of Yersinia enterocolitica in food: an overview. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 34(4):641–650
Gutner M et al (2009) Saliva enables the antimicrobial activity of LL-37 in the presence of proteases of Porphyromonas gingivalis. Infect Immun 77(12):5558–5563
Habets MGJL, Brockhurst MA (2012) Therapeutic antimicrobial peptides may compromise natural immunity. Biol Lett 8(3):416–418
Habets M, Rozen DE, Brockhurst MA (2012) Variation in Streptococcus pneumoniae susceptibility to human antimicrobial peptides may mediate intraspecific competition. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 279(1743):3803–3811
Haiko J et al (2009) Invited review: breaking barriers—attack on innate immune defences by omptin surface proteases of enterobacterial pathogens. Innate Immun 15(2):67–80
Halverson TWR et al (2015) DNA is an antimicrobial component of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. Plos Pathog 11(1)
Handzlik J, Matys A, Kieć-Kononowicz K (2013) Recent advances in Multi-Drug Resistance (MDR) efflux pump inhibitors of Gram-positive bacteria S. aureus. Antibiotics 2(1):28
Harris F, Dennison SR, Phoenix DA (2009) Anionic antimicrobial peptides from eukaryotic organisms. Curr Protein Pept Sci 10(6):585–606
Harris F, Dennison S, Phoenix D (2011) Anionic antimicrobial peptides from eukaryotic organisms and their mechanisms of action. Curr Chem Biol 5(2):142–153
Harris JB et al (2012) Cholera. Lancet 379(9835):2466–2476
Harris F et al (2013) On the selectivity and efficacy of defense peptides with respect to cancer cells. Med Res Rev 33(1):190–234
Hassan M et al (2012) Natural antimicrobial peptides from bacteria: characteristics and potential applications to fight against antibiotic resistance. J Appl Microbiol 113(4):723–736
Hassan KA et al (2013) Transcriptomic and biochemical analyses identify a family of chlorhexidine efflux proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(50):20254–20259
Hassan KA et al (2015a) Homologs of the Acinetobacter baumannii aceI transporter represent a new family of bacterial multidrug efflux systems. mBio 6(1)
Hassan KA et al (2015b) An ace up their sleeve: a transcriptomic approach exposes the Acel efflux protein of Acinetobacter baumannii and reveals the drug efflux potential hidden in many microbial pathogens. Front Microbiol 6
Hawkey PM (2015) Multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria: a product of globalization. J Hosp Infect 89(4):241–247
Heimlich D, Harrison A, Mason K (2014) Host antimicrobial peptides in bacterial homeostasis and pathogenesis of disease. Antibiotics 3(4):645
Henriques ST, Melo MN, Castanho MARB (2006) Cell-penetrating peptides and antimicrobial peptides: how different are they? Biochem J 399:1–7
Hinchliffe P et al (2013) Structure and operation of bacterial tripartite pumps. Annu Rev Microbiol 67(67):221–242
Hoang KV, Wang Y, Lin J (2012) Identification of genetic loci that contribute to Campylobacter resistance to fowlicidin-1, a chicken host defense peptide. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2:32
Holler JG et al (2012) Novel inhibitory activity of the Staphylococcus aureus NorA efflux pump by a kaempferol rhamnoside isolated from Persea lingue Nees. J Antimicrob Chemother 67(5):1138–1144
Hritonenko V, Stathopoulos C (2007) Omptin proteins: an expanding family of outer membrane proteases in Gram-negative Enterobacteriaceae. Mol Membr Biol 24(5–6):395–406
Huang YW et al (2013) Characterization of a major facilitator superfamily (MFS) tripartite efflux pump EmrCABsm from Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. J Antimicrob Chemother 68(11):2498–2505
Hui C-Y et al (2010) Escherichia coli outer membrane protease OmpT confers resistance to urinary cationic peptides. Microbiol Immunol 54(8):452–459
Hultmark D et al (1980) Insect immunity - purification and properties of 3 inducible bactericidal proteins from hemolymph of immunized pupae of hyalophora-cecropia. Eur J Biochem 106(1):7–16
Hwang B-Y et al (2007) Substrate specificity of the Escherichia coli outer membrane protease OmpP. J Bacteriol 189(2):522–530
Islam D et al (2001) Downregulation of bactericidal peptides in enteric infections: a novel immune escape mechanism with bacterial DNA as a potential regulator. Nat Med 7(2):180–185
Jardetzky O (1966) Simple allosteric model for membrane pumps [27]. Nature 211(5052):969–970
Jerse AE et al (2003) A gonococcal efflux pump system enhances bacterial survival in a female mouse model of genital tract infection. Infect Immun 71(10):5576–5582
Johansson J et al (1998) Conformation-dependent antibacterial activity of the naturally occurring human peptide LL-37. J Biol Chem 273(6):3718–3724
Johansson L et al (2008) Cathelicidin LL-37 in severe Streptococcus pyogenes soft tissue infections in humans. Infect Immun 76(8):3399–3404
Jones JDG, Dangl JL (2006) The plant immune system. Nature 444(7117):323–329
Joo H-S, Otto M (2015) Mechanisms of resistance to antimicrobial peptides in staphylococci. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Biomembr
Kai-Larsen Y et al (2010) Uropathogenic Escherichia coli modulates immune responses and its curli fimbriae interact with the antimicrobial peptide LL-37. PLoS Pathog 6(7):e1001010
Kang S-J et al (2014) Antimicrobial peptides: therapeutic potentials. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 12(12):1477–1486
Kaparakis-Liaskos M, Ferrero RL (2015) Immune modulation by bacterial outer membrane vesicles. Nat Rev Immunol 15(6):375–387
Kariuki S et al (2015) Antimicrobial resistance and management of invasive Salmonella disease. Vaccine 33(Supplement 3):C21–C29
Kathawala RJ et al (2015) The modulation of ABC transporter-mediated multidrug resistance in cancer: a review of the past decade. Drug Resist Updates 18:1–17
Katz ML et al (2006) Where have all the antibiotic patents gone? Nat Biotechnol 24(12):1529–1531
Katzif S et al (2005) CspA regulates pigment production in Staphylococcus aureus through a SigB-dependent mechanism. J Bacteriol 187(23):8181–8184
Kaur G et al (2011) Nisin and class IIa bacteriocin resistance among listeria and other foodborne pathogens and spoilage bacteria. Microbial Drug Resist 17(2):197–205
Keo T et al (2011) Campylobacter capsule and lipooligosaccharide confer resistance to serum and cationic antimicrobials. Virulence 2(1):30–40
Kilelee E et al (2010) Lysyl-phosphatidylglycerol attenuates membrane perturbation rather than surface association of the cationic antimicrobial peptide 6 W-RP-1 in a model membrane system: implications for daptomycin resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 54(10):4476–4479
Kindrachuk J, Napper S (2008) Host and pathogen sensory systems as targets for therapeutic intervention, VDM Publishing
Kingry LC, Petersen JM (2014) Comparative review of Francisella tularensis and Francisella novicida. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 4:35
Klein JS, Lewinson O (2011) Bacterial ATP-driven transporters of transition metals: physiological roles, mechanisms of action, and roles in bacterial virulence. Metallomics 3(11):1098–1108
Kobayashi N, Nishino K, Yamaguchi A (2001) Novel macrolide-specific ABC-type efflux transporter in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 183(19):5639–5644
Kocianova S et al (2005) Key role of poly-γ-DL-glutamic acid in immune evasion and virulence of Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Clin Invest 115(3):688–694
Köck K, Brouwer KLR (2012) A perspective on efflux transport proteins in the liver. Clin Pharmacol Ther 92(5):599–612
Koo SP et al (1996) Staphylocidal action of thrombin-induced platelet microbicidal protein is not solely dependent on transmembrane potential. Infect Immun 64(3):1070–1074
Koprivnjak T, Peschel A (2011) Bacterial resistance mechanisms against host defense peptides. Cell Mol Life Sci 68(13):2243–2254
Kukkonen M, Korhonen TK (2004) The omptin family of enterobacterial surface proteases/adhesins: from housekeeping in Escherichia coli to systemic spread of Yersinia pestis. Int J Med Microbiol 294(1):7–14
Kumar A, Schweizer HP (2005) Bacterial resistance to antibiotics: active efflux and reduced uptake. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 57(10):1486–1513
Kumar S et al (2013) Bacterial antimicrobial efflux pumps of the MFS and MATE transporter families: a review. In: Pandali S (ed) Recent research developments in antimicrobial agents & chemotherapy. Research Signpost Inc., Kerala, India, pp 1–21
Kupferwasser LI et al (1999) Plasmid-mediated resistance to thrombin-induced platelet microbicidal protein in staphylococci: role of the qacA locus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 43(10):2395–2399
Kupferwasser LI et al (2002) In vitro susceptibility to thrombin-induced platelet microbicidal protein is associated with reduced disease progression and complication rates in experimental Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis: microbiological, histopathologic, and echocardiographic analyses. Circulation 105(6):746–752
Lai R et al (2002) An anionic antimicrobial peptide from toad Bombina maxima. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 295(4):796–799
LaRock CN, Nizet V (2015) Cationic antimicrobial peptide resistance mechanisms of streptococcal pathogens. Biochim Biophys Acta
Last NB, Schlamadinger DE, Miranker AD (2013) A common landscape for membrane-active peptides. Protein Sci 22(7):870–882
Lauth X et al (2009) M1 protein allows group a streptococcal survival in phagocyte extracellular traps through cathelicidin inhibition. J Innate Immun 1(3):202–214
Law CJ, Maloney PC, Wang D-N (2008) Ins and outs of major facilitator superfamily, antiporters. Annu Rev Microbiol 62:289–305
Lee CR et al (2013) Lipid a biosynthesis of multidrug-resistant pathogens—a novel drug target. Curr Pharm Des 19(36):6534–6550
Lemaitre B, Hoffmann J (2007) The host defense of Drosophila melanogaster. Annu Rev Immunol 25:697–743
Lewis K (2000) Translocases: a bacterial tunnel for drugs and proteins. Curr Biol 10(18):R678–R681
Lewis DA (2003) Chancroid: clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and management. Sex Transm Infect 79(1):68–71
Lewis VG, Ween MP, McDevitt CA (2012) The role of ATP-binding cassette transporters in bacterial pathogenicity. Protoplasma 249(4):919–942
Li X-Z, Nikaido H (2004) Efflux-mediated drug resistance in bacteria. Drugs 64(2):159–204
Li X-Z, Nikaido H (2009) Efflux-mediated drug resistance in bacteria: an update. Drugs 69(12):1555–1623
Li M et al (2007a) The antimicrobial peptide-sensing system aps of Staphylococcus aureus. Mol Microbiol 66(5):1136–1147
Li M et al (2007b) Gram-positive three-component antimicrobial peptide-sensing system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(22):9469–9474
Li Y et al (2012) LPS remodeling is an evolved survival strategy for bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109(22):8716–8721
Lima IFN, Havt A, Lima AAM (2015) Update on molecular epidemiology of Shigella infection. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 31(1):30–37
Lin J, Huang S, Zhang Q (2002) Outer membrane proteins: key players for bacterial adaptation in host niches. Microbes Infect 4(3):325–331
Lin QY et al (2014a) Serratia marcescens arn, a PhoP-regulated locus necessary for polymyxin B resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58(9):5181–5190
Lin YT et al (2014b) MacABCsm, an ABC-type tripartite efflux pump of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia involved in drug resistance, oxidative and envelope stress tolerances and biofilm formation. J Antimicrob Chemother 69(12):3221–3226
Liu R et al (2011) There are abundant antimicrobial peptides in brains of two kinds of bombina toads. J Proteome Res 10(4):1806–1815
Llobet E et al (2011) Analysis of the networks controlling the antimicrobial-peptide-dependent induction of Klebsiella pneumoniae virulence factors. Infect Immun 79(9):3718–3732
Lohner K, Prenner EJ (1999) Differential scanning calorimetry and X-ray diffraction studies of the specificity of the interaction of antimicrobial peptides with membrane-mimetic systems. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) 1462(1–2):141–156
Lopez-Solanilla E, Garcia-Olmedo F, Rodriguez-Palenzuela P (1998) Inactivation of the sapA to sapF locus of Erwinia chrysanthemi reveals common features in plant and animal bacterial pathogenesis. Plant Cell 10(6):917–924
Lösel DM (1900) Lipids in the structure and function of fungal membranes. In: Kuhn P et al (ed) Biochemistry of cell walls and membranes in fungi. Springer, Berlin, pp 119–133
Loutet SA et al (2011) A two-tier model of polymyxin B resistance in Burkholderia cenocepacia. Environ Microbiol Rep 3(2):278–285
Luckenbach T, Fischer S, Sturm A (2014) Current advances on ABC drug transporters in fish. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 165:28–52
Lupp C, Hancock RW, Ruby E (2002) The Vibrio fischeri sapABCDF locus is required for normal growth, both in culture and in symbiosis. Arch Microbiol 179(1):57–65
Lycklama ANJA, Driessen AJ (2012) The bacterial sec-translocase: structure and mechanism. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 367(1592):1016–1028
Madej MG (2014) Function, structure, and evolution of the major facilitator superfamily: the LacY manifesto. Adv Biol 2014:20 Article ID 523591. doi: 10.1155/2014/523591
Maisetta G et al (2011) Gingipains produced by Porphyromonas gingivalis ATCC49417 degrade human-β-defensin 3 and affect peptide’s antibacterial activity in vitro. Peptides 32(5):1073–1077
Mandal SM et al (2014) Challenges and future prospects of antibiotic therapy: from peptides to phages utilization. Front Pharmacol 5
Manning AJ (2013) Outer membrane vesicles: a new paradigm of bacterial innate immunity. PhD thesis, Department of biochemistry, Duke University, Durham, USA
Manning AJ, Kuehn MJ (2011) Contribution of bacterial outer membrane vesicles to innate bacterial defense. Bmc Microbiol 11
Manning AJ, Kuehn MJ (2013) Functional advantages conferred by extracellular prokaryotic membrane vesicles. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 23(1–2):131–141
Marcos JF, Gandia M (2009) Antimicrobial peptides: to membranes and beyond. Expert Opin Drug Discov 4(6):659–671
Martinez JL et al (2009) Functional role of bacterial multidrug efflux pumps in microbial natural ecosystems. FEMS Microbiol Rev 33(2):430–449
Mason KM, Munson RS, Bakaletz LO (2005) A Mutation in the sap operon attenuates survival of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae in a Chinchilla Model of Otitis Media. Infect Immun 73(1):599–608
Mason KM et al (2006) The non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae Sap transporter provides a mechanism of antimicrobial peptide resistance and SapD-dependent potassium acquisition. Mol Microbiol 62(5):1357–1372
Mason KM et al (2011) Heme utilization by nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae is essential and dependent on sap transporter function. J Bacteriol 193(10):2527–2535
Masureel M et al (2014) Protonation drives the conformational switch in the multidrug transporter LmrP. Nat Chem Biol 10(2):149–155
Matsuo M et al (2011) Growth-phase dependence of susceptibility to antimicrobial peptides in Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiology-Sgm 157:1786–1797
Mattiuzzo M et al (2007) Role of the Escherichia coli SbmA in the antimicrobial activity of proline-rich peptides. Mol Microbiol 66(1):151–163
Mattiuzzo M et al (2014) Proteolytic activity of Escherichia coli oligopeptidase B against proline-rich antimicrobial peptides. J Microbiol Biotechnol 24(2):160–167
May JJ et al (2005) Inhibition of the D-alanine:D-alanyl carrier protein ligase from Bacillus subtilis increases the bacterium’s susceptibility to antibiotics that target the cell wall. FEBS J 272(12):2993–3003
McBroom AJ, Kuehn MJ (2007) Release of outer membrane vesicles by Gram-negative bacteria is a novel envelope stress response. Mol Microbiol 63(2):545–558
McPhee JB et al (2009) Antibiotic resistance due to reduced uptake. In: Mayers D (ed) Antimicrobial drug resistance, Humana Press, pp 97–110
McPhee JB et al (2014) Host defense peptide resistance contributes to colonization and maximal intestinal pathology by crohn’s disease-associated adherent-invasive Escherichia coli. Infect Immun 82(8):3383–3393
Mehla J, Sood SK (2011) Substantiation in Enterococcus faecalis of dose-dependent resistance and cross-resistance to pore-forming antimicrobial peptides by use of a polydiacetylene-based colorimetric assay. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(3):786–793
Mehla J, Sood SK (2013) Connecting membrane fluidity and surface charge to pore-forming antimicrobial peptides resistance by an ANN-based predictive model. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(10):4377–4384
Menozzi FD et al (2002) Enhanced bacterial virulence through exploitation of host glycosaminoglycans. Mol Microbiol 43(6):1379–1386
Miller DS (2015) Regulation of ABC transporters blood-brain barrier: the good, the bad, and the ugly. Adv Cancer Res 125:43–70
Miller SI et al (1990) Characterization of defensin resistance phenotypes associated with mutations in the phoP virulence regulon of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun 58(11):3706–3710
Miller AK et al (2011) PhoQ mutations promote lipid A modification and polymyxin resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa found in colistin-treated cystic fibrosis patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 55(12):5761–5769
Mills SD, Dougherty TJ (2012) Cell-based screening in antibacterial discovery. In: Dougherty TJ, Pucci MJ (eds) Antibiotic discovery and development, vols 1 and 2. Springer, New York, pp 901–929
Misaka S, Muller F, Fromm MF (2013) Clinical relevance of drug efflux pumps in the gut. Curr Opin Pharmacol 13(6):847–852
Mishra A, Jha B (2013) Microbial exopolysaccharides. In: Rosenberg E et al (ed) The Prokaryotes. Springer, Berlin, pp 179–192
Mishra NN et al (2011) Carotenoid-related alteration of cell membrane fluidity impacts Staphylococcus aureus susceptibility to host defense peptides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 55(2):526–531
Mishra NN et al (2012) Differential adaptations of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus to serial in vitro passage in daptomycin: evolution of daptomycin resistance and role of membrane carotenoid content and fluidity. Int J Microbiol 2012:6
Mohamed Mustafa MS et al (2012) Assessment of substrate inhibition of bacterial oligopeptidase B. Biol Pharm Bull 35(11):2010–6
Mohammad H, Thangamani S, Seleem MN (2015) Antimicrobial peptides and peptidomimetics—potent therapeutic allies for staphylococcal infections. Curr Pharm Des 21(16):2073–2088
Morace G, Perdoni F, Borghi E (2014) Antifungal drug resistance in Candida species. J Global Antimicrob Resist 2(4):254–259
Morita Y et al (2000) NorM of vibrio parahaemolyticus is an Na+-driven multidrug efflux pump. J Bacteriol 182(23):6694–6697
Mount KLB et al (2010) Haemophilus ducreyi SapA contributes to cathelicidin resistance and virulence in humans. Infect Immun 78(3):1176–1184
Murakami S (2008) Multidrug efflux transporter, AcrB—the pumping mechanism. Curr Opin Struct Biol 18(4):459–465
Murphy EC, Frick IM (2013) Gram-positive anaerobic cocci—commensals and opportunistic pathogens. FEMS Microbiol Rev 37(4):520–553
Murphy EC et al (2014) Identification of molecular mechanisms used by Finegoldia magna to penetrate and colonize human skin. Mol Microbiol 94(2):403–417
Mysak J et al (2014) Porphyromonas gingivalis: major periodontopathic pathogen overview. J Immunol Res 2014:8
Muzamal U et al (2014) Diversity of two-component systems: insights into the signal transduction mechanism by the Staphylococcus aureus two-component system GraSR [version 1; referees: 2 approved with reservations], vol 3
Naito M et al (2010) Effects of sequential Campylobacter jejuni 81-176 lipooligosaccharide core truncations on biofilm formation, stress survival, and pathogenesis. J Bacteriol 192(8):2182–2192
Nakamura T et al (1988) Tachyplesin, a class of antimicrobial peptide from the hemocytes of the horseshoe crab (Tachypleus tridentatus). Isolation and chemical structure. J Biol Chem 263(32):16709–16713
Nakka S, Qi M, Zhao Y (2010) The Erwinia amylovora PhoPQ system is involved in resistance to antimicrobial peptide and suppresses gene expression of two novel type III secretion systems. Microbiol Res 165(8):665–673
Nawrocki KL, Crispell EK, McBride SM (2014) Antimicrobial peptide resistance mechanisms of Gram-positive bacteria. Antibiotics (Basel) 3(4):461–492
Needham BD, Trent MS (2013) Fortifying the barrier: the impact of lipid A remodelling on bacterial pathogenesis. Nat Rev Microbiol 11(7):467–481
Nelson DC, Garbe J, Collin M (2011) Cysteine proteinase SpeB from Streptococcus pyogenes—a potent modifier of immunologically important host and bacterial proteins. Biol Chem 392(12):1077–1088
Neumann A et al (2014a) Novel role of the antimicrobial peptide LL-37 in the protection of neutrophil extracellular traps against degradation by bacterial nucleases. J Innate Immun 6(6):860–868
Neumann A et al (2014b) The antimicrobial peptide LL-37 facilitates the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps. Biochem J 464:3–11
Nicolas P (2009) Multifunctional host defense peptides: intracellular-targeting antimicrobial peptides. FEBS J 276(22):6483–6496
Nikaido H, Pagès J-M (2012) Broad-specificity efflux pumps and their role in multidrug resistance of Gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 36(2):340–363
Nikaido H, Zgurskaya HI (2001) AcrAB and related multidrug efflux pumps of Escherichia coli. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 3(2):215–218
Nishie M, Nagao J, Sonomoto K (2012) Antibacterial peptides “bacteriocins”: an overview of their diverse characteristics and applications. Biocontrol Sci 17(1):1–16
Norsworthy AN, Visick KL (2013) Gimme shelter: how Vibrio fischeri successfully navigates an animal’s multiple environments. Front Microbiol 4
Nwodo UU, Green E, Okoh AI (2012) Bacterial exopolysaccharides: functionality and prospects. Int J Mol Sci 13(11):14002–14015
Nyberg P, Rasmussen M, Bjorck L (2004) alpha2-Macroglobulin-proteinase complexes protect Streptococcus pyogenes from killing by the antimicrobial peptide LL-37. J Biol Chem 279(51):52820–52823
Olaitan AO, Morand S, Rolain J-M (2014) Mechanisms of polymyxin resistance: acquired and intrinsic resistance in bacteria. Front Microbiol 5:643
Oliver JD (2015) The Biology of Vibrio vulnificus. Microbiol Spectr 3(3)
Olsen I, Amano A (2015) Outer membrane vesicles—offensive weapons or good Samaritans? 7
Opperman TJ, Nguyen S (2015) Recent advances toward a molecular mechanism of efflux pump inhibition. Front Microbiol 6
Ormeno-Orrillo E et al (2012) Genomic basis of broad host range and environmental adaptability of Rhizobium tropici CIAT 899 and Rhizobium sp PRF 81 which are used in inoculants for common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Bmc Genomics 13
Otto M (2006) Bacterial evasion of antimicrobial peptides by biofilm formation. In: Shafer W (ed) Antimicrobial peptides and human disease. Springer, Berlin, pp 251–258
Otto M (2009) Bacterial sensing of antimicrobial peptides. In: Collin M, Schuch R (ed) Bacterial sensing and signaling, pp 136–149
Padilla E et al (2010) Klebsiella pneumoniae AcrAB efflux pump contributes to antimicrobial resistance and virulence. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 54(1):177–183
Palmer T, Berks BC (2012) The twin-arginine translocation (Tat) protein export pathway. Nat Rev Microbiol 10(7):483–496
Park PW et al (2000) Syndecan-1 shedding is enhanced by LasA, a secreted virulence factor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Biol Chem 275(5):3057–3064
Park PW et al (2001) Exploitation of syndecan-1 shedding by Pseudomonas aeruginosa enhances virulence. Nature 411(6833):98–102
Parra-Lopez C, Baer MT, Groisman EA (1993) Molecular genetic analysis of a locus required for resistance to antimicrobial peptides in Salmonella typhimurium. The EMBO Journal 12(11):4053–4062
Parra-Lopez C et al (1994) A Salmonella protein that is required for resistance to antimicrobial peptides and transport of potassium. The EMBO J 13(17):3964–3972
Paulsen IT (2003) Multidrug efflux pumps and resistance: regulation and evolution. Curr Opin Microbiol 6(5):446–451
Pelz A et al (2005) Structure and biosynthesis of staphyloxanthin from Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem 280(37):32493–32498
Pence MA et al (2010) Streptococcal inhibitor of complement promotes innate immune resistance phenotypes of invasive M1T1 group A Streptococcus. J Innate Immun 2(6):587–595
Perron GG, Zasloff M, Bell G (2006) Experimental evolution of resistance to an antimicrobial peptide. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 273(1583):251–256
Peschel A, Sahl H-G (2006) The co-evolution of host cationic antimicrobial peptides and microbial resistance. Nat Rev Micro 4(7):529–536
Phoenix DA, Dennison SR, Harris F (2013a) Antimicrobial peptides: their history, evolution, and functional promiscuity. In Antimicrobial Peptides, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, pp 1–37
Phoenix DA, Dennison SR, Harris F (2013b) Cationic antimicrobial peptides, in antimicrobial peptides. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, pp 39–81
Phoenix DA, Dennison SR, Harris F (2013c) Anionic antimicrobial peptides, in antimicrobial peptides. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, pp 83–113
Phoenix DA, Dennison SR, Harris F (2013d) Models for the membrane interactions of antimicrobial peptides, in antimicrobial peptides. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, pp 145–180
Phoenix DA, Dennison SR, Harris F (2013e) Graphical techniques to visualize the amphiphilic structures of antimicrobial peptides. In: Antimicrobial peptides. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, pp 115–144
Phoenix DA, Harris F, Dennison SR (2014) Novel antimicrobial agents and strategies. Wiley, Weinheim
Phoenix DA et al (2015) The increasing role of phosphatidylethanolamine as a lipid receptor in the action of host defence peptides. Prog Lipid Res 59:26–37
Piddock LJV (2006a) Multidrug-resistance efflux pumps? not just for resistance. Nat Rev Micro 4(8):629–636
Piddock LJV (2006b) Clinically relevant chromosomally encoded multidrug resistance efflux pumps in bacteria. Clin Microbiol Rev 19(2):382–402
Poelarends GJ, Mazurkiewicz P, Konings WN (2002) Multidrug transporters and antibiotic resistance in Lactococcus lactis. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Bioenerg 1555(1–3):1–7
Poole K (2000) Efflux-mediated resistance to fluoroquinolones in Gram-positive bacteria and the mycobacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44(10):2595–2599
Poole K (2008) Bacterial multidrug efflux pumps serve other functions. Microbe 3(4):179–185
Poole K (2012) Bacterial stress responses as determinants of antimicrobial resistance. J Antimicrob Chemother. doi:10.1093/jac/dks196
Port GC et al (2014) Streptococcus pyogenes polymyxin B-resistant mutants display enhanced exPortal integrity. J Bacteriol 196(14):2563–2577
Pranting M et al (2008) Mechanism and fitness costs of PR-39 resistance in salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium LT2. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 52(8):2734–2741
Prasad R, Rawal MK (2014) Efflux pump proteins in ant fungal resistance. Front Pharmacol 5:202. doi:10.3389/fphar.2014.00202
Pringle P (2013) Experiment eleven: deceit and betrayal in the discovery of the cure for tuberculosis. Bloomsbury Publishing PLC, London
Proft T, Baker EN (2009) Pili in gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria—structure, assembly and their role in disease. Cell Mol Life Sci 66(4):613–635
Putman M, van Veen HW, Konings WN (2000) Molecular properties of bacterial multidrug transporters. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 64(4):672–692
Radecka I, Martin C, Hill D (2014) The problem of microbial drug resistance, in novel antimicrobial agents and strategies. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, pp 1–16
Radestock S, Forrest LR (2011) The alternating-access mechanism of MFS transporters arises from inverted-topology repeats. J Mol Biol 407(5):698–715
Rasmussen M, Bjorck L (2002) Proteolysis and its regulation at the surface of Streptococcus pyogenes. Mol Microbiol 43(3):537–544
Ratledge C, Wilkinson SG (1988) Microbial lipids. Academic Press, London
Reddy VS et al (2012) The major facilitator superfamily (MFS) revisited. FEBS J 279(11):2022–2035
Reverchon S, Nasser W (2013) Dickeya ecology, environment sensing and regulation of virulence programme. Environ Microbiol Rep 5(5):622–636
Rieg S et al (2009) Resistance against antimicrobial peptides is independent of Escherichia coli AcrAB, Pseudomonas aeruginosa MexAB and Staphylococcus aureus NorA efflux pumps. Int J Antimicrob Agents 33(2):174–176
Rodas PI, Contreras I, Mora GC (2010) Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi has a 4.1 kb genetic island inserted within the sapABCDF operon that causes loss of resistance to the antimicrobial peptide protamine. J Antimicrob Chemother 65(8):1624–1630
Romalde JL et al (2014) New Vibrio species associated to molluscan microbiota: a review. Front Microbiol 4:413. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2013.00413
Rosch JW, Caparon MG (2005) The ExPortal: an organelle dedicated to the biogenesis of secreted proteins in Streptococcus pyogenes. Mol Microbiol 58(4):959–968
Rosch JW, Hsu FF, Caparon MG (2007) Anionic lipids enriched at the ExPortal of Streptococcus pyogenes. J Bacteriol 189(3):801–806
Roy H (2009) Tuning the properties of the bacterial membrane with aminoacylated phosphatidylglycerol. IUBMB Life 61(10):940–953
Rubin EJ et al (2015) PmrD is required for modifications to Escherichia coli endotoxin that promote antimicrobial resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 59(4):2051–2061
Sahin O et al (2015) Campylobacter in poultry: ecology and potential interventions. Avian Dis 59(2):185–200
Saidijam M et al (2006) Microbial drug efflux proteins of the major facilitator superfamily. Curr Drug Targets 7(7):793–811
Saier Jr MH (1998) Molecular phylogeny as a basis for the classification of transport proteins from bacteria, archaea and eukarya. In: Poole RK (ed) Advances in microbial physiology, Academic Press, pp 81–136
Santa Maria JP et al (2014) Compound-gene interaction mapping reveals distinct roles for Staphylococcus aureus teichoic acids. In: Proceedings of the national academy of sciences 111(34):12510–12515
Schaffer W (2006) Antimicrobial peptides and human disease. Springer, Berlin
Schmid J, Sieber V, Rehm B (2015) Bacterial exopolysaccharides: biosynthesis pathways and engineering strategies. Front Microbiol 6:496. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2015.00496
Schmidt NW, Wong GCL (2013) Antimicrobial peptides and induced membrane curvature: geometry, coordination chemistry, and molecular engineering. Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci 17(4):151–163
Schmidtchen A, Frick IM, Bjorck L (2001) Dermatan sulphate is released by proteinases of common pathogenic bacteria and inactivates antibacterial alpha-defensin. Mol Microbiol 39(3):708–713
Schmidtchen A et al (2002) Proteinases of common pathogenic bacteria degrade and inactivate the antibacterial peptide LL-37. Mol Microbiol 46(1):157–168
Selsted ME et al (1983) Primary structures of MCP-1 and MCP-2, natural peptide antibiotics of rabbit lung macrophages. J Biol Chem 258(23):4485–4489
Selsted ME, Szklarek D, Lehrer RI (1984) Purification and antibacterial activity of antimicrobial peptides of rabbit granulocytes. Infect Immun 45(1):150–154
Selsted ME et al (1985) Primary structures of 6 antimicrobial peptides of rabbit peritoneal neutrophils. J Biol Chem 260(8):4579–4584
Shafer WM et al (1998) Modulation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae susceptibility to vertebrate antibacterial peptides due to a member of the resistance/nodulation/division efflux pump family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(4):1829–1833
Shelton, C.L., et al., Sap Transporter Mediated Import and Subsequent Degradation of Antimicrobial Peptides in Haemophilus. Plos Pathogens, 2011. 7(11)
Shen CJ et al (2010) Proteomic identification of membrane proteins regulating antimicrobial peptide resistance in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Appl Microbiol 108(4):1398–1407
Shireen T et al (2013) Differential adaptive responses of Staphylococcus aureus to in vitro selection with different antimicrobial peptides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57(10):5134–5137
Silhavy TJ, Kahne D, Walker S (2010) The bacterial cell envelope. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2(5), a000414:1-16
Slotboom DJ (2014) Structural and mechanistic insights into prokaryotic energy-coupling factor transporters. Nat Rev Microbiol 12(2):79–87
Smyth D et al (2014) DrsG from Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis inhibits the antimicrobial peptide LL-37. Infect Immun 82(6):2337–2344
Sohlenkamp C et al (2007) The lipid lysyl-phosphatidylglycerol Is present in membranes of Rhizobium tropici CIAT899 and confers increased resistance to polymyxin B under acidic growth conditions. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 20(11):1421–1430
Solheim M et al (2007) Transcriptional responses of Enterococcus faecalis V583 to bovine bile and sodium dodecyl sulfate. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(18):5767–5774
Soto SM (2013) Role of efflux pumps in the antibiotic resistance of bacteria embedded in a biofilm. Virulence 4(3):223–229
Sperandio B et al (2008) Virulent Shigella flexneri subverts the host innate immune response through manipulation of antimicrobial peptide gene expression. J Exp Med 205(5):1121–1132
Splith K, Neundorf I (2011) Antimicrobial peptides with cell-penetrating peptide properties and vice versa. Eur Biophys J 40(4):387–397
Spoel SH, Dong X (2012) How do plants achieve immunity? Defence without specialized immune cells. Nat Rev Immunol 12(2):89–100
Stefani S et al (2015) Insights and clinical perspectives of daptomycin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: a review of the available evidence. Int J Antimicrob Agents 46:278–289
Steiner H et al (1981) Sequence and specificity of 2 anti-bacterial proteins involved in insect immunity. Nature 292(5820):246–248
Straley SC, Perry RD (1995) Environmental modulation of gene-expression and pathogenesis in Yersinia. Trends Microbiol 3(8):310–317
Strempel N et al (2013) Human host defense peptide LL-37 stimulates virulence factor production and adaptive resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS ONE 8(12):12
Stumpe S et al (1998) Identification of OmpT as the protease that hydrolyzes the antimicrobial peptide protamine before it enters growing cells of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 180(15):4002–4006
Subashchandrabose S et al (2013) Genome-wide detection of fitness genes in uropathogenic Escherichia coli during systemic infection. PLoS Pathog 9(12):15
Sun J, Deng Z, Yan A (2014) Bacterial multidrug efflux pumps: mechanisms, physiology and pharmacological exploitations. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 453(2):254–267
Szeltner Z, Polgar L (2008) Structure, function and biological relevance of prolyl oligopeptidase. Curr Protein Pept Sci 9(1):96–107
Tanaka Y et al (2013) Structural basis for the drug extrusion mechanism by a MATE multidrug transporter. Nature 496(7444):247–251
Taylor CM, Roberts IS (2005) Capsular polysaccharides and their role in virulence. In: Russell W, Herwald H (ed) Contributions to microbiology, pp 55–66
Teixeira V, Feio MJ, Bastos M (2012) Role of lipids in the interaction of antimicrobial peptides with membranes. Prog Lipid Res 51(2):149–177
Telford JL et al (2006) Pili in Gram-positive pathogens. Nat Rev Micro 4(7):509–519
Thanavala Y, Lugade AA (2011) Role of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae in otitis media and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. In: Harabuchi Y, Hayashi T, Katada A (eds) Recent advances in tonsils and mucosal barriers of the upper airways, pp 170–175
Thomassin J-L et al (2012a) OmpT outer membrane proteases of enterohemorrhagic and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli contribute differently to the degradation of human LL-37. Infect Immun 80(2):483–492
Thomassin J-L et al (2012b) Enterohemorrhagic and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli evolved different strategies to resist antimicrobial peptides. Gut Microbes 3(6):556–561
Tomaras AP et al (2014) LpxC Inhibitors as New Antibacterial Agents and Tools for Studying Regulation of Lipid A Biosynthesis in Gram-Negative Pathogens. mBio 5(5):e01551-14
Tremolieres F (2010) When the antibiotic miracle turns into a nightmare. MS Med Sci 26(11):925–929
Tzeng Y-L et al (2005) Cationic antimicrobial peptide resistance in Neisseria meningitidis. J Bacteriol 187(15):5387–5396
Ulett GC et al (2013) Uropathogenic Escherichia coli virulence and innate immune responses during urinary tract infection. Curr Opin Microbiol 16(1):100–107
Ullrich M (2009) Bacterial polysaccharides: current innovations and future trends, Caister Academic Press
Ulvatne H et al (2002) Proteases in Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus confer reduced susceptibility to lactoferricin B. J Antimicrob Chemother 50(4):461–467
Van Bambeke F et al (2003) Antibiotic efflux pumps in prokaryotic cells: occurrence, impact on resistance and strategies for the future of antimicrobial therapy. J Antimicrob Chemother 51(5):1055–1065
van Meer G, de Kroon AIPM (2011) Lipid map of the mammalian cell. J Cell Sci 124(1):5–8
van Meer G, Voelker DR, Feigenson GW (2008) Membrane lipids: where they are and how they behave. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9(2):112–124
Vanhove AS et al (2015) Outer membrane vesicles are vehicles for the delivery of Vibrio tasmaniensis virulence factors to oyster immune cells. Environ Microbiol 17(4):1152–1165
Vasil ML, Darwin AJ (2012) Regulation of bacterial virulence, ASM Press
Vega LA, Caparon MG (2012) Cationic antimicrobial peptides disrupt the Streptococcus pyogenes ExPortal. Mol Microbiol 85(6):1119–1132
Vega LA, Port GC, Caparon MG (2013) An association between peptidoglycan synthesis and organization of the Streptococcus pyogenes ExPortal. Mbio 4(5):9
Vilcinskas A (2013) Evolutionary plasticity of insect immunity. J Insect Physiol 59(2):123–129
Vilhena C, Bettencourt A (2012) Daptomycin: a review of properties, clinical use, drug delivery and resistance. Mini Rev Med Chem 12(3):202–209
Viti C et al (2014) Molecular mechanisms of Cr(VI) resistance in bacteria and fungi. FEMS Microbiol Rev 38(4):633–659
von Koeckritz-Blickwede M et al (2012) Novel role of the antimicrobial peptide LL37 in the formation and stabilization of neutrophil extracellular traps. Faseb J 26
Vuong C et al (2004a) A crucial role for exopolysaccharide modification in bacterial biofilm formation, immune evasion, and virulence. J Biol Chem 279(52):54881–54886
Vuong C et al (2004b) Polysaccharide intercellular adhesin (PIA) protects Staphylococcus epidermidis against major components of the human innate immune system. Cell Microbiol 6(3):269–275
Wang G (2008) Structures of human host defense cathelicidin LL-37 and its smallest antimicrobial peptide KR-12 in lipid micelles. J Biol Chem 283(47):32637–32643
Wang G, Li X, Wang Z (2009) APD2: the updated antimicrobial peptide database and its application in peptide design. Nucleic Acids Res 37:D933–D937
Wang G, Li X, Zasloff M (2010a) A database view of naturally occurring antimicrobial peptides: nomenclature, classification and amino acid sequence analysis. In: Wang G (ed) Antimicrobial peptides: discovery, design and novel therapeutic strategies, pp 1–21
Wang G et al (2010b) Identification of novel human immunodeficiency virus type 1-inhibitory peptides based on the antimicrobial peptide database. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 54(3):1343–1346
Wang RZ et al (2015) The pathogenesis, detection, and prevention of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Frontiers in Microbiology 6(13):144
Warner DM, Shafer WM, Jerse AE (2008) Clinically relevant mutations that cause derepression of the Neisseria gonorrhoeae MtrC-MtrD-MtrE efflux pump system confer different levels of antimicrobial resistance and in vivo fitness. Mol Microbiol 70(2):462–478
Wassenaar TM et al (2015) Review and phylogenetic analysis of qac genes that reduce susceptibility to quaternary ammonium compounds in Staphylococcus species. Eur J Microbiol Immunol 5(1):44–61
Weatherspoon-Griffin N et al (2014) The CpxR/CpxA two-component regulatory system up-regulates the multidrug resistance cascade to facilitate Escherichia coli resistance to a model antimicrobial peptide. J Biol Chem 289(47):32571–32582
Weidenmaier C, Kristian SA, Peschel A (2003) Bacterial resistance to antimicrobial host defenses–an emerging target for novel antiinfective strategies? Curr Drug Targets 4(8):643–649
Wick MJ (2011) Innate immune control of salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium: mechanisms contributing to combating systemic salmonella infection. J Innate Immun 3(6):543–549
Wilkens S (2015) Structure and mechanism of ABC transporters. F1000prime reports 7:14–14
Wilmes M et al (2011) Antibiotic activities of host defense peptides: more to it than lipid bilayer perturbation. Nat Prod Rep 28(8):1350–1358
Winter M, Lawrence C (2011) Asperger syndrome—What teachers need to Know, 2nd edn. Jessica Kingsley Publishers
Wolf M, Moser B (2012) Antimicrobial activities of chemokines: not just a side-effect? Front Immunol 3:213
Wong SSY, Yuen K-Y (2012) Streptococcus pyogenes and re-emergence of scarlet fever as a public health problem. Emerg Microbes Infect 1:e2
Wong AR et al (2011) Enteropathogenic and enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli: even more subversive elements. Mol Microbiol 80(6):1420–1438
Wong K et al (2014) Towards understanding promiscuity in multidrug efflux pumps. Trends Biochem Sci 39(1):8–16
World Health Organization (2014) Antimicrobial resistance: global report on surveillance. Switzerland, Geneva
Wu H et al (2015) Strategies for combating bacterial biofilm infections. J Oral Sci 7(1):1–7
Yamaguchi A, Nakashima R, Sakurai K (2015) Structural basis of RND-type multidrug exporters. Front Microbiol 6:327. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2015.00327
Yan N (2013) Structural advances for the major facilitator superfamily (MFS) transporters. Trends Biochem Sci 38(3):151–159
Yan N (2015) Structural biology of the major facilitator superfamily transporters. Annu Rev Biophys 44(44):257–283
Yang S-J et al (2012) The Staphylococcus aureus two-component regulatory system, GraRS, senses and confers resistance to selected cationic antimicrobial peptides. Infect Immun 80(1):74–81
Yang S-C et al (2014) Antibacterial activities of bacteriocins: application in foods and pharmaceuticals. Front Microbiol 5:241
Yeaman MR, Yount NY (2003) Mechanisms of antimicrobial peptide action and resistance. Pharmacol Rev 55(1):27–55
Yeaman MR et al (1998) Platelet microbicidal proteins and neutrophil defensin disrupt the Staphylococcus aureus cytoplasmic membrane by distinct mechanisms of action. J Clin Investig 101(1):178–187
Yin Y et al (2006) Structure of the multidrug transporter EmrD from Escherichia coli. Science 312(5774):741–744
Yother J (2011) Capsules of Streptococcus pneumoniae and other bacteria: paradigms for polysaccharide biosynthesis and regulation. Annu Rev Microbiol 65(65):563–581
Yu EW et al (2013) Microbial efflux pumps: current research. Caister Academic Press
Yu Z et al (2015) Antibacterial mechanisms of polymyxin and bacterial resistance. Biomed Res Int 2015:11
Zaffiri L, Gardner J, Toledo-Pereyra LH (2012) History of antibiotics. From salvarsan to cephalosporins. J Invest Surg 25(2):67–77
Zähner D et al (2010) Human antimicrobial peptide LL-37 induces MefE/Mel-mediated macrolide resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 54(8):3516–3519
Zamfir A et al (2003) Structural investigation of chondroitin/dermatan sulfate oligosaccharides from human skin fibroblast decorin. Glycobiology 13(11):733–742
Zasloff M (1987) Magainins, a class of antimicrobial peptides from xenopus skin—isolation, characterization of 2 active forms, and partial cdna sequence of a precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84(15):5449–5453
Zasloff M (2002) Antimicrobial peptides of multicellular organisms. Nature 415(6870):389–395
Zgurskaya HI (2009) Multicomponent drug efflux complexes: architecture and mechanism of assembly. Future microbiology 4:919–932
Zgurskaya HI et al (2015) Mechanism of coupling drug transport reactions located in two different membranes. Front Microbiol 6:100. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2015.00100
Zhang YK et al (2015) Multidrug Resistance Proteins (MRPs) and cancer therapy. AAPS J 17(4):802–812
Zhou H et al (2014) Mechanisms of nisin resistance in Gram-positive bacteria. Ann Microbiol 64(2):413–420
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Phoenix, D.A., Dennison, S.R., Harris, F. (2016). Bacterial Resistance to Host Defence Peptides. In: Epand, R. (eds) Host Defense Peptides and Their Potential as Therapeutic Agents. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-32949-9_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-32949-9_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-32947-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-32949-9
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)