Abstract
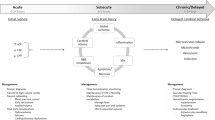
The first 72 h after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is a critical period for the patient. Most of the deaths in the SAH patient population occur during this time, and a number of key events activate and trigger mechanisms that not only contribute to early brain injury but evolve over time and participate in the delayed complications. This review highlights the contribution of key events to the early brain injury and to overall outcome after SAH.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Le Roux PD, Winn HR (1998) Management of the ruptured aneurysm. Neurosurg Clin N Am 9:525–540
Macdonald RL, Weir BK (1991) A review of hemoglobin and the pathogenesis of cerebral vasospasm. Stroke 22:971–982
Simeone FA, Ryan KG, Cotter JR (1968) Prolonged experimental cerebral vasospasm. J Neurosurg 29:357–366
Dupont S, Rabinstein AA (2013) Extent of acute hydrocephalus after subarachnoid hemorrhage as a risk factor for poor functional outcome. Neurol Res 35:107–110
Vermeulen M, van Gijn J (1990) The diagnosis of subarachnoid haemorrhage. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 53:365–372
Ishiguro M, Murakami K, Link T, Zvarova K, Tranmer BI, Morielli AD, Wellman GC (2008) Acute and chronic effects of oxyhemoglobin on voltage-dependent ion channels in cerebral arteries. Acta Neurochir Suppl 104:99–102
Sehba FA, Friedrich V (2013) Cerebral microvasculature is an early target of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir Suppl 115:199–205
Kajikawa H, Ohta T, Yoshikawa Y, Funatsu N, Yamamoto M, Someda K (1979) Cerebral vasospasm and hemoglobins – clinical and experimental studies. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 19:61–71
Meguro T, Chen B, Lancon J, Zhang JH (2001) Oxyhemoglobin induces caspase-mediated cell death in cerebral endothelial cells. J Neurochem 77:1128–1135
Rollins S, Perkins E, Mandybur G, Zhang JH (2002) Oxyhemoglobin produces necrosis, not apoptosis, in astrocytes. Brain Res 945:41–49
Sehba FA, Schwartz AY, Chereshnev I, Bederson JB (2000) Acute decrease in cerebral nitric oxide levels after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 20:604–611
Ishiguro M, Morielli AD, Zvarova K, Tranmer BI, Penar PL, Wellman GC (2006) Oxyhemoglobin-induced suppression of voltage-dependent K+ channels in cerebral arteries by enhanced tyrosine kinase activity. Circ Res 99:1252–1260
Ohlstein EH, Storer BL (1992) Oxyhemoglobin stimulation of endothelin production in cultured endothelial cells. J Neurosurg 77:274–278
Maines MD (1997) The heme oxygenase system: a regulator of second messenger gases. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 37:517–554
Ozawa H, Nishida A, Mito T, Takashima S (1994) Immunohistochemical study of ferritin-positive cells in the cerebellar cortex with subarachnoidal hemorrhage in neonates. Brain Res 651:345–348
Ono S, Zhang ZD, Marton LS, Yamini B, Windmeyer E, Johns L, Kowalczuk A, Lin G, Macdonald RL (2000) Heme oxygenase-1 and ferritin are increased in cerebral arteries after subarachnoid hemorrhage in monkeys. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 20:1066–1076
Petzold A, Worthington V, Appleby I, Kerr ME, Kitchen N, Smith M (2011) Cerebrospinal fluid ferritin level, a sensitive diagnostic test in late-presenting subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 20:489–493
Lee JY, Keep RF, He Y, Sagher O, Hua Y, Xi G (2010) Hemoglobin and iron handling in brain after subarachnoid hemorrhage and the effect of deferoxamine on early brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30:1793–1803
Kranc KR, Pyne GJ, Tao L, Claridge TD, Harris DA, Cadoux-Hudson TA, Turnbull JJ, Schofield CJ, Clark JF (2000) Oxidative degradation of bilirubin produces vasoactive compounds. Eur J Biochem 267:7094–7101
Pyne-Geithman GJ, Morgan CJ, Wagner K, Dulaney EM, Carrozzella J, Kanter DS, Zuccarello M, Clark JF (2005) Bilirubin production and oxidation in CSF of patients with cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25:1070–1077
Brinker T, Seifert V, Dietz H (1992) Cerebral blood flow and intracranial pressure during experimental subarachnoid haemorrhage. Acta Neurochir 115:47–52
Lee VH, Oh JK, Mulvagh SL, Wijdicks EF (2006) Mechanisms in neurogenic stress cardiomyopathy after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurocrit Care 5:243–249
Brouwers PJ, Wijdicks EF, Hasan D, Vermeulen M, Wever EF, Frericks H, van Gijn J (1989) Serial electrocardiographic recording in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 20:1162–1167
Eisalo A, Perasalo J, Halonen PI (1972) Electrocardiographic abnormalities and some laboratory findings in patients with subarachnoid haemorrhage. Br Heart J 34:217–226
Frontera JA, Parra A, Shimbo D, Fernandez A, Schmidt JM, Peter P, Claassen J, Wartenberg KE, Rincon F, Badjatia N, Naidech A, Connolly ES, Mayer SA (2008) Cardiac arrhythmias after subarachnoid hemorrhage: risk factors and impact on outcome. Cerebrovasc Dis 26:71–78
Sakr YL, Lim N, Amaral AC, Ghosn I, Carvalho FB, Renard M, Vincent JL (2004) Relation of ECG changes to neurological outcome in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Int J Cardiol 96:369–373
van der Kleij FG, Henselmans JM, van de Loosdrecht AA (1999) Cardiac arrhythmia as initial presentation of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neth J Med 55:242–246
Norris JW, Hachinski VC, Myers MG, Callow J, Wong T, Moore RW (1979) Serum cardiac enzymes in stroke. Stroke 10:548–553
Fabinyi G, Hunt D, McKinley L (1977) Myocardial creatine kinase isoenzyme in serum after subarachnoid haemorrhage. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 40:818–820
Zhu BL, Ishikawa T, Michiue T, Li DR, Zhao D, Bessho Y, Kamikodai Y, Tsuda K, Okazaki S, Maeda H (2007) Postmortem cardiac troponin I and creatine kinase MB levels in the blood and pericardial fluid as markers of myocardial damage in medicolegal autopsy. Leg Med (Tokyo) 9:241–250
Kolin A, Norris JW (1984) Myocardial damage from acute cerebral lesions. Stroke 15:990–993
Sato K, Masuda T, Izumi T (1999) Subarachnoid hemorrhage and myocardial damage clinical and experimental studies. Jpn Heart J 40:683–701
Masuda T, Sato K, Yamamoto S, Matsuyama N, Shimohama T, Matsunaga A, Obuchi S, Shiba Y, Shimizu S, Izumi T (2002) Sympathetic nervous activity and myocardial damage immediately after subarachnoid hemorrhage in a unique animal model. Stroke 33:1671–1676
Muroi C, Keller M, Pangalu A, Fortunati M, Yonekawa Y, Keller E (2008) Neurogenic pulmonary edema in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol 20:188–192
McLaughlin N, Bojanowski MW, Girard F, Denault A (2005) Pulmonary edema and cardiac dysfunction following subarachnoid hemorrhage. Can J Neurol Sci 32:178–185
Walder B, Brundler MA, Totsch M, Elia N, Morel DR (2002) Influence of the type and rate of subarachnoid fluid infusion on lethal neurogenic pulmonary edema in rats. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol 14:194–203
Sehba FA, Pluta RM, Zhang JH (2011) Metamorphosis of subarachnoid hemorrhage research: from delayed vasospasm to early brain injury. Mol Neurobiol 43:27–40
Sehba FA, Hou J, Pluta RM, Zhang JH (2012) The importance of early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Prog Neurobiol 97:14–37
Fein JM (1976) Brain energetics and circulatory control after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 45:498–507
Fein JM (1978) Brain energetics and cerebral death. Ann N Y Acad Sci 315:97–104
Gewirtz RJ, Dhillon HS, Goes SE, DeAtley SM, Scheff SW (1999) Lactate and free fatty acids after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Brain Res 840:84–91
Sarrafzadeh AS, Sakowitz OW, Kiening KL, Benndorf G, Lanksch WR, Unterberg AW (2002) Bedside microdialysis: a tool to monitor cerebral metabolism in subarachnoid hemorrhage patients? Crit Care Med 30:1062–1070
Dreier JP, Drenckhahn C, Woitzik J, Major S, Offenhauser N, Weber-Carstens S, Wolf S, Strong AJ, Vajkoczy P, Hartings JA (2013) Spreading ischemia after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir Suppl 115:125–129
Kohno K, Sakaki S, Ohue S, Kumon Y, Matsuoka K (1991) Intracellular calcium levels in canine basilar artery smooth muscle following experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage: an electron microscopic cytochemical study. Acta Neuropathol 81:664–669
Wang J, Ohta S, Sakaki S, Araki N, Matsuda S, Sakanaka M (1994) Changes in Ca(++)-ATPase activity in smooth-muscle cell membranes of the canine basilar artery with experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 80:269–275
Hubschmann OR (1987) The role of calcium in parenchymal cell injury in subarachnoid haemorrhage. Neurol Res 9:265–269
Sakaki S, Ohue S, Kohno K, Takeda S (1989) Impairment of vascular reactivity and changes in intracellular calcium and calmodulin levels of smooth muscle cells in canine basilar arteries after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 25:753–761
Bederson JB, Levy AL, Ding WH, Kahn R, DiPerna CA, Jenkins AL 3rd, Vallabhajosyula P (1998) Acute vasoconstriction after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 42:352–360
Sehba FA, Ding WH, Chereshnev I, Bederson JB (1999) Effects of S-nitrosoglutathione on acute vasoconstriction and glutamate release after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 30:1955–1961
Yatsushige H, Calvert JW, Cahill J, Zhang JH (2006) Limited role of inducible nitric oxide synthase in blood-brain barrier function after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurotrauma 23:1874–1882
Durmaz R, Ozkara E, Kanbak G, Arslan O, Dokumacioğlu A, Kartkaya K, Atasoy M (2008) Nitric oxide level and adenosine deaminase activity in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Turk Neurosurg 18:157–164
Jung CS, Oldfield EH, Harvey-White J, Espey MG, Zimmermann M, Seifert V, Pluta RM (2007) Association of an endogenous inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase with cerebral vasospasm in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 107:945–950
Wang X, Zhu C, Zhang G, Lu Y (1995) Changes of endothelin during cerebral vasospasm after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. Chin Med J (Engl) 108:586–590
Kramer A, Fletcher J (2009) Do endothelin-receptor antagonists prevent delayed neurological deficits and poor outcomes after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage?: a meta-analysis. Stroke 40:3403–3406
Etminan N, Vergouwen MD, Ilodigwe D, Macdonald RL (2011) Effect of pharmaceutical treatment on vasospasm, delayed cerebral ischemia, and clinical outcome in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 31:1443–1451
Mathiesen T, Edner G, Ulfarsson E, Andersson B (1997) Cerebrospinal fluid interleukin-1 receptor antagonist and tumor necrosis factor-alpha following subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 87:215–220
Dumont AS, Dumont RJ, Chow MM, Lin CL, Calisaneller T, Ley KF, Kassell NF, Lee KS (2003) Cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage: putative role of inflammation. Neurosurgery 53:123–133; discussion 133–135
Kaynar MY, Tanriverdi T, Kafadar AM, Kacira T, Uzun H, Aydin S, Gumustas K, Dirican A, Kuday C (2004) Detection of soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 in both cerebrospinal fluid and serum of patients after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 101:1030–1036
Gaetani P, Marzatico F, Rodriguez Y, Baena R, Pacchiarini L, Vigano T, Grignani G, Crivellari MT, Benzi G (1990) Arachidonic acid metabolism and pathophysiologic aspects of subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Stroke 21:328–332
Lin CL, Hsu YT, Lin TK, Morrow JD, Hsu JC, Hsu YH, Hsieh TC, Tsay PK, Yen HC (2006) Increased levels of F2-isoprostanes following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage in humans. Free Radic Biol Med 40:1466–1473
Kamezaki T, Yanaka K, Nagase S, Fujita K, Kato N, Nose T (2002) Increased levels of lipid peroxides as predictive of symptomatic vasospasm and poor outcome after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 97:1302–1305
Hsieh YP, Lin CL, Shiue AL, Yin H, Morrow JD, Hsu JC, Hsieh TC, Wei HJ, Yen HC (2009) Correlation of F4-neuroprostanes levels in cerebrospinal fluid with outcome of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage in humans. Free Radic Biol Med 47:814–824
Conflict of Interest Statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Sehba, F.A., Friedrich, V. (2015). Early Events After Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. In: Fandino, J., Marbacher, S., Fathi, AR., Muroi, C., Keller, E. (eds) Neurovascular Events After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Acta Neurochirurgica Supplement, vol 120. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-04981-6_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-04981-6_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-04980-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-04981-6
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)