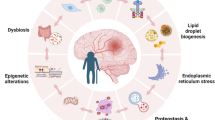
Abstract
Ageing is generally characterised by the declining ability to respond to stress, increasing homeostatic imbalance, and increased risk of ageing-associated diseases. Mechanistically, the lifelong accumulation of a wide range of molecular and cellular impairments leads to organismal senescence. The aging population poses a severe medical concern due to the burden it places on healthcare systems and the general public as well as the prevalence of diseases and impairments associated with old age. In this chapter, we discuss organ failure during ageing as well as ageing of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis and drugs that can regulate it. A much-debated subject is about ageing and regeneration. With age, there is a gradual decline in the regenerative properties of most tissues. The goal of regenerative medicine is to restore cells, tissues, and structures that are lost or damaged after disease, injury, or ageing. The question arises as to whether this is due to the intrinsic ageing of stem cells or, rather, to the impairment of stem-cell function in the aged tissue environment. The risk of having a stroke event doubles each decade after the age of 55. Therefore, it is of great interest to develop neurorestorative therapies for stroke which occurs mostly in elderly people. Initial enthusiasm for stimulating restorative processes in the ischaemic brain with cell-based therapies has meanwhile converted into a more balanced view, recognising impediments related to survival, migration, differentiation, and integration of therapeutic cells in the hostile aged brain environment. Therefore, a current lack of understanding of the fate of transplanted cells means that the safety of cell therapy in stroke patients is still unproven. Another issue associated with ischaemic stroke is that patients at risk for these sequels of stroke are not duly diagnosed and treated due to the lack of reliable biomarkers. However, recently neurovascular unit-derived exosomes in response to Stroke and released into serum are new plasma genetic and proteomic biomarkers associated with ischaemic stroke. The second valid option, which is also more economical, is to invest in prevention.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbatecola AM, Ferrucci L, Ceda G, Russo CR, Lauretani F, Bandinelli S et al (2005) Insulin resistance and muscle strength in older persons. J Gerontol 60:1278–1282. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/60.10.1278
Aguilera G (2011) HPA axis responsiveness to stress: implications for healthy aging. Exp Gerontol 46(2–3):90–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2010.08.023
Albers GW, Marks MP, Kemp S, Christensen S, Tsai JP, Ortega-Gutierrez S, McTaggart RA, Torbey MT, Kim-Tenser M, Leslie-Mazwi T et al (2018) Thrombectomy for stroke at 6 to 16 hours with selection by perfusion imaging. N Engl J Med 378:708–718. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1713973
Allsop D, Mayes J, Moore S, Masad A, Tabner BJ (2008) Metal-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species from amyloid proteins implicated in neurodegenerative disease. Biochem Soc Trans 36(6):1293–1298. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST0361293
Amaya-Montoya M, Perez-Londono A, Guatibonza-Garcia V, Vargas-Villanueva A, Mendivil CO (2020) Cellular senescence as a therapeutic target for age-related diseases: a review. Adv Ther 37:1407–1424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2020.101251
Baek SJ, Nam GE, Han KD, Choi SW, Jung SW, Bok AR et al (2014) Sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity and their association with dyslipidemia in Korean elderly men: the 2008–2010 Korea National health and nutrition examination survey. J Endocrinol Investig 37:247–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-013-0011-3
Barden N (1996) Modulation of glucocorticoid receptor gene expression by antidepressant drugs. Pharmacopsychiatry 29(1):12–22. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-979536
Berkhemer OA, Fransen PS, Beumer D, van den Berg LA, Lingsma HF, Yoo AJ, Schonewille WJ, Vos JA, Nederkoorn PJ, Wermer MJ et al (2015) A randomized trial of intraarterial treatment for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 372:11–20. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1411587
Bhalla A, Patel M, Birns J (2021) An update on hyper-acute management of ischaemic stroke. Clin Med 21:215–221. https://doi.org/10.7861/clinmed.2020-0998
Bloom FE (1979) Norepinephrinc mediated synaptic transmission and hypotheses of psychiatric disorders. Research in the psychobiology of human behavior. The Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, p 11 I. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00443
Brady LS, Whitfield HJ, Fox RJ, Gold PW, Herkenham M (1991) Long-term antidepressant administration alters corticotropin-releasing hormone, tyrosine hydroxylase and mineralocorticoid receptor gene expression in rat brain: therapeutic implications. J Clin Invest 87:831–837. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci115086
Brennan LA, Kantorow M (2009) Mitochondrial function and redox control in the ageing eye: role of MsrA and other repair systems in cataract and macular degenerations. Exp Eye Res 88:195–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2008.05.018
Brennan LA, McGreal-Estrada R, Logan CM, Cvekl A, Menko AS, Kantorow M (2018) BNIP3L/NIX is required for elimination of mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus during eye lens organelle-free zone formation. Exp Eye Res 174:173–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2018.06.003
Brewer GJ (2010) Epigenetic oxidative redox shift (EORS) theory of aging unifies the free radical and insulin signaling theories. Exp Gerontol 45:173–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2009.11.007
Broocks G, McDonough R, Bechstein M, Hanning U, Brekenfeld C, Flottmann F, Kniep H, Nawka MT, Deb-Chatterji M, Thomalla G, Sporns P, Yeo LL, Tan BY, Gopinathan A, Kastrup A, Politi M, Papanagiotou P, Kemmling A, Fiehler J, Meyer L, German Stroke Registry – Endovascular Treatment (GSR-ET) (2023) Benefit and risk of intravenous alteplase in patients with acute large vessel occlusion stroke and low ASPECTS. J Neurointerv Surg 15(1):8–13. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2021-017986
Buga AM, Vintilescu R, Pop OT, Popa-Wagner A (2011) Brain aging and regeneration after injuries: an organismal approach. Aging Dis 2(1):64–79
Burkewitz K, Zhang Y, Mair WB (2014) AMPK at the nexus of energetics and aging. Cell Metab 20:10–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2014.03.002
Campbell BC, Mitchell PJ, Kleinig TJ, Dewey HM, Churilov L, Yassi N, Yan B, Dowling RJ, Parsons MW, Oxley TJ et al (2015) Endovascular therapy for ischemic stroke with perfusion-imaging selection. N Engl J Med 372:1009–1018. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1414792
Chabriat H, Bassetti CL, Marx U, Audoli-Inthavong ML, Sors A, Lambert E, Wattez M, Hermann DM, RESTORE BRAIN study investigators (2020) Safety and efficacy of GABAA α5 antagonist S44819 in patients with ischaemic stroke: a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 19(3):226–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30004-1
Clarkson AN, Huang BS, Macisaac SE, Mody I, Carmichael ST (2010) Reducing excessive GABA-mediated tonic inhibition promotes functional recovery after stroke. Nature 468:305–309. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09511
Cullinan WE, Ziegler DR, Herman JP (2008) Functional role of local GABAergic influences on the HPA axis. Brain Struct Funct 213:63–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-008-0192-2
da Costaa JP, Vitorino R, Silvad GM, Vogeld C, Duartea AC, Rocha-Santos T (2016) A synopsis on aging – theories, mechanisms and future prospects. Ageing Res Rev 29:90–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2016.06.005
Dagonnier M, Donnan GA, Davis SM, Dewey HM, Howells DW (2021) Acute stroke biomarkers: are we there yet? Front Neurol 5(12):619721. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2021.619721
Dickerson SS, Kemeny ME (2004) Acute stressors and cortisol responses: a theoretical integration and synthesis of laboratory research. Psychol Bull 130(3):355–391. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.130.3.355
Doeppner TR, Bähr M, Hermann DM, Giebel B (2017) Concise review: extracellular vesicles overcoming limitations of cell therapies in ischemic stroke. Stem Cells Transl Med 6(11):2044–2052. https://doi.org/10.1002/sctm.17-0081
Dominguez LJ, Barbagallo M (2007) The cardiometabolic syndrome and sarcopenic obesity in older persons. J Cardiometab Syndr 2:183–189. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.15594564.2007.06673.x
Dong Y, Qu J, Zhang Z, Wang C, Dong Q (2020) Human urinary kallidinogenase in treating acute ischemic stroke patients: analyses of pooled data from a randomized double-blind placebocontrolled phase IIb and phase III clinical trial. Neurol Res 42:286–290. https://doi.org/10.1080/01616412.2020.1711648
Driga MP, Catalin B, Olaru DG, Slowik A, Plesnila N, Hermann DM, Popa-Wagner A (2021) The need for new biomarkers to assist with stroke prevention and prediction of post-stroke therapy based on plasma-derived extracellular vesicles. Biomedicine 9(9):1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091226
Dunnett SB (2013) Neural tissue transplantation, repair, and rehabilitation. Handb Clin Neurol. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-52901-5.00004-6
Dzięgielewska-Gęsiak S, Stołtny D, Brożek A, Muc-Wierzgoń M, Wysocka E (2020) Are insulin-resistance and oxidative stress cause or consequence of aging. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 245(14):1260–1267. https://doi.org/10.1177/1535370220929621
Edwards MG, Anderson RM, Yuan M, Kendziorski CM, Weindruch R, Prolla TA (2007) Gene expression profiling of aging reveals activation of a p53-mediated transcriptional program. BMC Genomics 8:80. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-8-80
Enomoto M, Endo A, Yatsushige H, Fushimi K, Otomo Y (2019) Clinical effects of early edaravone use in acute ischemic stroke patients treated by endovascular reperfusion therapy. Stroke 50:652–658. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.023815
Ernst A, Alkass K, Bernard S, Salehpour M, Perl S, Tisdale J, Possnert G, Druid H, Frisén J (2014) Neurogenesis in the striatum of the adult human brain. Cell 156:1072–1083. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.01.044
Fang M (2018) Trends in the prevalence of diabetes among US adults: 1999-2016. Am J Prev Med 55:497–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cdtm.2020.11.003
Ferrari E, Cravello L, Muzzoni B, Casarotti D, Paltro M, Solerte SB, Fioravanti M, Cuzzoni G, Pontiggia B, Magri F (2001) Age-related changes of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis: pathophysiological correlates. Eur J Endocrinol 144:319–329. https://doi.org/10.1530/eje.0.1440319
Franceschi C, Garagnani P, Parini P, Giuliani C, Santoro A (2018) Inflammaging: a new immune-metabolic viewpoint for age-related diseases. Nat Rev Endocrinol 14:576–590. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-018-0059-4
Gage FH (1998) Stem cells of the central nervous system. Curr Opin Neurobiol 8(5):671–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0959-4388(98)80098-6
Goyal M, Demchuk AM, Menon BK, Eesa M, Rempel JL, Thornton J, Roy D, Jovin TG, Willinsky RA, Sapkota BL et al (2015) Randomized assessment of rapid endovascular treatment of ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 372:1019–1030. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1414905
Goyal M, Menon BK, van Zwam WH, Dippel DW, Mitchell PJ, Demchuk AM, Dávalos A, Majoie CB, van der Lugt A, de Miquel MA et al (2016) Endovascular thrombectomy after large-vessel ischaemic stroke: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from five randomised trials. Lancet 387:1723–1731. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00163-X
Gupta D (2014) Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and aging. Comprehensive Physiol 4. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphy.c130049
Herman JP, Cullinan WE (1997) Neurocircuitry of stress: central control of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical axis. Trends Neurosci 20:78–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-2236(96)10069-2
Hermann DM, Chopp M (2012) Promoting brain remodelling and plasticity for stroke recovery: therapeutic promise and potential pitfalls of clinical translation. Lancet Neurol 11:369–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(12)70039-X
Hermann DM, Buga AM, Popa-Wagner A (2015) Neurovascular remodeling in the aged ischemic brain. J Neural Transm 122(Suppl 1):S25–S33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-013-1148-0
Hermann DM, Popa-Wagner A, Peruzzotti-Jametti L, Gunzer M (2022a) Editorial: hot topics in cellular neuropathology. Front Cell Neurosci 16:895861. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2022.895861
Hermann DM, Xin W, Bähr M, Giebel B, Doeppner TR (2022b) Emerging roles of extracellular vesicle-associated non-coding RNAs in hypoxia: insights from cancer, myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke. Theranostics 12(13):5776–5802. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.73931
Heydendael W, Jacobson L (2008) Differential effects of imipramine and phenelzine on corticosteroid receptor gene expression in mouse brain: potential relevance to antidepressant response. Brain Res 1238:93–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2008.08.018
Hill MD, Goyal M, Menon BK, Nogueira RG, McTaggart RA et al (2020) Efficacy and safety of nerinetide for the treatment of acute ischaemic stroke (ESCAPENA1): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 395:878–887. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30258-0
Holm MM, Kaiser J, Schwab ME (2018) Extracellular vesicles: multimodal envoys in neural maintenance and repair. Trends Neurosci 41:360–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2018.03.006
Ida H, Boylan SA, Weigel AL, Hjelmeland LM (2003) Age-related changes in the transcriptional profile of mouse RPE/choroid. Physiol Genomics 15(3):258–262. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiolgenomics.00126.2003
Jin K, Wang X, Xie L, Mao XO, Zhu W, Wang Y et al (2006) Evidence for stroke-induced neurogenesis in the human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(35):13198–13200. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0603512103
Johnson K, Appel LJ, Brands M, Howard BV, Lefevre M, Lustig RH, Steffen L, Wylie-Rosett J (2009) Dietary sugars intake and cardiovascular health. Circulation 120:1011–1120. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.192627
Jovin TG, Chamorro A, Cobo E, de Miquel MA, Molina CA, Rovira A, San Román L, Serena J, Abilleira S, Ribó M et al (2015) Thrombectomy within 8 hours after symptom onset in ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 372:2296–2306. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1503780
Kalogeras KT, Calogero AE, Kuribayiashi T, Khan I, Gallucci WT, Kling MA et al (1990) In vitro and in vivo effects of the triazolobenzodiazepine alprazolam on hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal function: pharmacological and clinical implications. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 70(5):1462–1471. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem-70-5-1462
Kanfi Y, Naiman S, Amir G, Peshti V, Zinman G, Nahum L, Bar-Joseph Z, Cohen HY (2012) The sirtuin SIRT6 regulates lifespan in male mice. Nature 483:218–221. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10815
Kanninen KM, Bister N, Koistinaho J, Malm T (2016) Exosomes as new diagnostic tools in CNS diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1862:403–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2015.09.020
Khadra D, Itani L, Chebaro Y, Obeid M, Jaber M, Ghanem R et al (2019) Association between sarcopenic obesity and higher risk of type 2 diabetes in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. World. J Diabetes 10:311–323. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573403X16666200214104122
Khan RMM, Chua ZJY, Tan JC, Yang Y, Liao Z, Zhao Y (2019) From pre-diabetes to diabetes: diagnosis, treatments and translational research. Medicina (Kaunas) 55:546. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55090546
Kobayashi M, Suhara T, Baba Y, Kawasaki NK, Higa JK, Matsui T (2018) Pathological roles of iron in cardiovascular disease. Curr Drug Targets 19:1068–1076. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389450119666180605112235
Kremastinos DT, Farmakis D (2011) Iron overload cardiomyopathy in clinical practice. Circulation 124:2253–2263. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.050773
Kumar S, Vijayan M, Bhatti JS, Reddy PH (2017) MicroRNAs as peripheral biomarkers in ageing and age-related diseases. Mol Biol Ageing:47–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.pmbts.2016.12.013
Lai M, McCormick JA, Chapman KE, Kelly PA, Seckl JR, Yau JL (2003) Differential regulation of corticosteroid receptors by monoamine neurotransmitters and antidepressant drugs in primary hippocampal culture. Neuroscience 118(4):975–984. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0306-4522(03)00038-1
Lai X, Schmitz U, Gupta SK, Bhattacharya A, Kunz M, Wolkenhauer O, Vera J (2012) Computational analysis of target hub gene repression regulated by multiple and cooperative miRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 40(18):8818–8834. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks657
Langhorne P, Coupar F, Pollock A (2009) Motor recovery after stroke: a systematic review. Lancet Neurol 8(8):741–754. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70150-4
Lee MS, Kim YH, Park WS, Park OK, Kwon SH, Hong KS et al (2016) Temporal variability of glucocorticoid receptor activity is functionally important for the therapeutic action of fluoxetine in the hippocampus. Mol Psychiatry 21(2):252–260. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2014.137
Lee J, You JH, Shin D, Roh JL (2020) Inhibition of glutaredoxin 5 predisposes cisplatin-resistant head and neck cancer cells to ferroptosis. Theranostics 10:7775–7786. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.46903
Leite CF, Almeida TR, Lopes CS, Dias da Silva VJ (2015) Multipotent stem cells of the heart-do they have therapeutic promise? Front Physiol 8(6):123. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2015.00123
Lener T, Gimona M, Aigner L et al (2015) Applying extracellular vesicles based therapeutics in clinical trials - an ISEV position paper. J Extracell Vesicles 4:30087. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v4.30087
Lewis JS, Lee JA, Underwood JC, Harris AL, Lewis CE (1999) Macrophage responses to hypoxia: relevance to disease mechanisms. J Leukoc Biol 66(6):889–900. https://doi.org/10.1002/jlb.66.6.889
Luo J, Mills K, le Cessie S, Noordam R, van Heemst D (2020) Ageing, age-related diseases and oxidative stress: what to do next? Ageing Res Rev 57:100982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2019.100982
Lyden P, Pryor KE, Coffey CS, Cudkowicz M, Conwit R et al (2020) Final results of the RHAPSODY trial: a multi-center, phase 2 trial using a continual reassessment method to determine the safety and tolerability of 3K3A-APC, a recombinant variant of human activated protein C, in combination with tissue plasminogen activator, mechanical thrombectomy or both in moderate to severe acute ischemic stroke. Ann Neurol 85:125–136. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.25383
Macas J, Nern C, Plate KH, Momma S (2006) Increased generation of neuronal progenitors after ischemic injury in the aged adult human forebrain. J Neurosci 26(50):13114–13119. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4667-06.2006
Manwani B, Liu F, Xu Y, Persky R, Li J, McCullough L (2011) Functional recovery in aging mice after experimental stroke. Brain Behav Immun 25:1689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2011.06.015
Martí-Fàbregas J, Romaguera-Ros M, Gómez-Pinedo U, Martínez-Ramírez S, Jiménez-Xarrié E, Marín R, Martí-Vilalta JL, García-Verdugo JM (2010) Proliferation in the human ipsilateral subventricular zone after ischemic stroke. Neurology 74:357–365. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181cbccec
Matulewicz N, Karczewska-Kupczewska M (2016) Insulin resistance and chronic inflammation. Postepy Hig Med Dosw 70:1245–1258. https://doi.org/10.5604/17322693.1226662
McCarthy LH, Bigal ME, Katz M et al (2008) Chronic pain and obesity in elderly people: results from the Einstein aging study. J Am Geriatr Soc 57:115–119. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-5415.2008.02089.x
Mcternan PG, Kusminski CM, Kumar S (2006) Recent advances in the relationship between obesity, inflammation, insulin resistance. Eur Cytokine Netw 17:4–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphy.c170040
Menjot de Champfleur N, Saver JL, Goyal M, Jahan R, Diener HC, Bonafe A, Levy EI, Pereira VM, Cognard C, Yavagal DR, Albers GW (2017) Efficacy of stent-retriever thrombectomy in magnetic resonance imaging versus computed tomographic perfusion-selected patients in SWIFT PRIME trial (solitaire FR with the intention for thrombectomy as primary endovascular treatment for acute ischemic stroke). Stroke 48(6):1560–1566. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.016669
Michelson D, Galliven E, Hill L, Demitrack M, Chrousos G, Gold P (1997) Chronic imipramine is associated with diminished hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis responsivity in healthy humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82(8):2601–2606. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.82.8.4172
Miller GE, Cohen S, Janicki-Deverts D (2007) Psychological stress and disease. JAMA 298(14):1685–1687. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.298.14.1685
Minger SL, Ekonomou A, Carta EM, Chinoy A, Perry RH, Ballard CG (2007) Endogenous neurogenesis in the human brain following cerebral infarction. Regen Med 2(1):69–74. https://doi.org/10.2217/17460751.2.1.69
Morizane A, Li JY, Brundin P (2008) From bench to bed: the potential of stem cells for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Cell Tissue Res 331(1):323–336. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-007-0541-0
Nemeroff CB (1992) New vistas in neuropeptide research: focus on corticotropin-releasing factor. Neuro Psychopharmacol 6:787–794. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00443
Ngolab J, Trinh I, Rockenstein E, Mante M, Florio J, Trejo M, Masliah D, Adame A, Masliah E, Rissman RA (2017) Brainderived exosomes from dementia with Lewy bodies propagate α-synuclein pathology. Acta Neuropathol Commun 5:46. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-017-0445-5
Ni J, Qu J, Yao M, Zhang Z, Zhong X et al (2017) Re-evaluate the efficacy and safety of human urinary kallidinogenase (RESK): protocol for an open-label, single-arm, multicenter phase IV trial for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke in Chinese patients. Transl Stroke Res 8:341–346. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-017-0527-5
Nikisch G (2009) Involvement and role of antidepressant drugs of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and glucocorticoid receptor function. Neuro Endocrinol Lett 30(1):11–16
Nogueira RG, Jadhav AP, Haussen DC, Bonafe A, Budzik RF, Bhuva P, Yavagal DR, Ribo M, Cognard C, Hanel RA et al (2018) Thrombectomy 6 to 24 hours after stroke with a mismatch between deficit and infarct. N Engl J Med 378:11–21. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa170644
Nomura T, Ikeda Y, Nakao S, Ito K, Ishida K, Suehiro T et al (2007) Muscle strength is a marker of insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes: a pilot study. Endocr J 54:791–796. https://doi.org/10.1507/endocrj.K07-055
Norden DM, Fenn AM, Dugan A, Godbout JP (2014) TGFβ produced by IL-10 redirected astrocytes attenuates microglial activation. Glia 62:881–895. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.22647
Palma-Tortosa S, García-Culebras A, Moraga A, Hurtado O, Perez-Ruiz A, Durán-Laforet V, Parra J, Cuartero MI, Pradillo JM, Moro MA et al (2017) Specific features of SVZ neurogenesis after cortical ischemia: a longitudinal study. Sci Rep 7:16343. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-16109-7
Paul S, Candelario-Jalil E (2021) Emerging neuroprotective strategies for the treatment of ischemic stroke: an overview of clinical and preclinical studies. Exp Neurol 335:113518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113518
Pepin MC, Beaulieu S, Barden N (1989) Antidepressants regulate glucocorticoid receptor messenger RNA concentrations in primary neuronal cultures. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 6(1):77–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/0169-328X(89)90031-4
Pescador N, Perez-Barba M, Ibarra JM, Corbaton A, Martinez-Larrad MT, Serrano-Rios M (2013) Serum circulating microRNA profiling for identification of potential type 2 diabetes and obesity biomarkers. PLoS One 8(10):e77251. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0077251
Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, Adeoye OM, Bambakidis NC, Becker K, Biller J, Brown M, Demaerschalk BM, Hoh B et al (2019) Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 50:e344–e418. https://doi.org/10.1161/STR.0000000000000211
Ramirez K, Niraula A, Sheridan JF (2016) GABAergic modulation with classical benzodiazepines prevent stress-induced neuro-immune dysregulation and behavioral alterations. Brain Behav Immun 51:154–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2015.08.011
Rea IM, Gibson DS, McGilligan V, McNerlan SE, Alexander HD, Ross OA (2018) Age and age-related diseases: role of inflammation triggers and cytokines. Front Immunol 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.00586
Riera E, Dillin A (2015) Tipping the metabolic scales towards increased longevity in mammals. Nat Cell Biol 17:196–203. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb3107
Roberts E (1976) Disinhibition as an organizing principle in the nervous system: the role of the GABA system. GABA in nervous system function. Raven, New York, pp 515–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1874-6055(99)80014-0
Robins SJ, Lyass A, Zachariah JP, Massaro JM, Vasan RS (2011) Insulin resistance and the relation of a dyslipidemia to coronary heart disease: the Framingham heart study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 31:1208–1214. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.219055
Rosell A, Lo EH (2008) Multiphasic roles for matrix metalloproteinases after stroke. Curr Opin Pharmacol 8:82–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coph.2007.12.001
Rosnick CB, Snall BJ, McEvoy CL, Borenstein AR, Mortimer JA (2007) Negative life events and cognitive performance in a population of older adults. J Aging Health 19(4):612–629. https://doi.org/10.1177/0898264307300975
Sardar Sinha M, Ansell-Schultz A, Civitelli L, Hildesjö C, Larsson M, Lannfelt L, Ingelsson M, Hallbeck M (2018) Alzheimer’s disease pathology propagation by exosomes containing toxic amyloid-beta oligomers. Acta Neuropathol 136:41–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-018-1868-1
Saver JL, Goyal M, Bonafe A, Diener HC, Levy EI, Pereira VM, Albers GW, Cognard C, Cohen DJ, Hacke W et al (2015) Stent-retriever thrombectomy after intravenous t-PA vs. t-PA alone in stroke. N Engl J Med 372:2285–2295. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1415061
Savitz SI, Yavagal D, Rappard G, Likosky W, Rutledge N, Graffagnino C, Alderazi Y, Elder JA, Chen PR, Budzik RF Jr, Tarrel R, Huang DY, Hinson JM Jr (2019) A phase 2 randomized, sham-controlled trial of internal carotid artery infusion of autologous bone marrow-derivedALD-401 cells in patients with recent stable ischemic stroke (RECOVER-Stroke). Circulation 139(2):192–205. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.030659
Shoelson SE, Herrero L, Naaz A (2007) Obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Gastroenterology 132:2169–2180. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2007.03.059
Simard S, Shail P, MacGregor J, El Sayed M, Duman RS, Vaccarino FM et al (2018) Fibroblast growth factor 2 is necessary for the antidepressant effects of fluoxetine. PLoS One 13(10):e0204980. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0204980
Stoll EA (2014) Advances toward regenerative medicine in the central nervous system: challenges in making stem cell therapy a viable clinical strategy. Mol Cell Ther 2:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/2052-8426-2-12
Strazzullo P, D’Elia L, Cairella G, Garbagnati F, Cappuccio F, Scalfi L (2010) Excess body weight and incidence of stroke meta-analysis of prospective studies with 2 million participants. Stroke 41:e418. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.576967
Swaab DF, Fliers E, Partiman TS (1985) The suprachiasmatic nucleus of the human brain in relation to sex, age and senile dementia. Brain Res 342:37–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(85)91350-2
Tafet GE, Nemeroff CB (2020) Pharmacological treatment of anxiety disorders: the role of the HPA axis. Front Psych 11:443. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00443
Tomimatsu K, Narita M (2015) Translating the effects of mTOR on secretory senescence. Nat Cell Biol 17:1230–1232. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb3244
Trayhurn P, Wang B, Wood IS (2008) Hypoxia in adipose tissue: a basis for the dysregulation of tissue function in obesity? Brit J Nutr 100(2):227–235. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114508971282
Uchino BN, Campo RA, Vaughn A, Maija R, Smith TW (2001) The assessment of positivity and negativity in social networks: the reliability and validity of the social relationships index. J Commun Psychol 37(4):471–486. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcop.20308
Valli A, Harris AL, Kessler BM (2015) Hypoxia metabolism in ageing. Aging 7(7):465–466
Wang M, Tan Y, Shi Y, Wang X, Liao Z, Wei P (2020) Diabetes and sarcopenic obesity: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatments. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 11:568. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2020.00568
Xu J, Knutson MD, Carter CS, Leeuwenburgh C (2008) Iron accumulation with age, oxidative stress and functional decline. PLoS One 3:e2865. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0002865
Yan LL, Daviglus ML, Liu K et al (2006) Midlife body mass index and hospitalization and mortality in older age. JAMA 295:190–198. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.2318
Zagrean AM, Hermann DM, Opris I, Zagrean L, Popa-Wagner A (2018) Multicellular crosstalk between exosomes and the neurovascular unit after cerebral ischemia. Therapeutic implications. Front Neurosci 12:811. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2018.00811
Zhang J, Meng L, Qin W, Liu N, Shi FD, Yu C (2014) Structural damage and functional reorganization in ipsilesional m1 in well-recovered patients with subcortical stroke. Stroke 45:788–793. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.003425
Zhou R-P, Chen Y, Wei X, Yu B, Xiong Z-G, Lu C, Hu W (2020) Novel insights into ferroptosis: implications for age-related diseases. Theranostics 10(26):11976–11997. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.50663
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Surugiu, R. et al. (2023). Clinical Ageing. In: Harris, J.R., Korolchuk, V.I. (eds) Biochemistry and Cell Biology of Ageing: Part IV, Clinical Science. Subcellular Biochemistry, vol 103. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-26576-1_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-26576-1_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-26575-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-26576-1
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)