Abstract
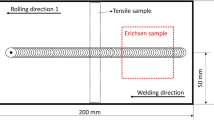
Based on the imperative social demand for lighter vehicles, lightweight materials such as aluminum alloys are expected to replace conventional steels in many automotive applications. In automotive parts manufacturing, most of the components produced in conventional stamping operations are geometrically complex as the blanks are subjected to both stretching and drawing deformations. However, aluminum alloys have intrinsic drawbacks, such as the inferior formability of these materials, although the effects of the weight reduction in terms of performance are highly promising. In an effort to improve the formability of aluminum alloy sheets, the surface friction stir process is proposed in this study. This process locally modifies the surface of automotive aluminum alloy sheets via stirring and advancing on the surface of the sheet, similar to the Friction Stir Welding (FSW) process that utilizes a probe without a pin. When the surface of the sheet is modified locally by stirring, dynamic recrystallization due to the severe shear deformation along with heat resulting from the friction occur due to changes in the micro-structure and mechanical properties in the stirred zone, while the dislocation density and grain size refinement are curtailed. In this work, the drawability performance of AA5052-H32 sheets (thickness 1.5 mm) that were welded using the surface friction stir process was experimentally and numerically investigated in cylindrical cup drawing tests. When applied to AA5052-H32 automotive sheets, the surface friction stir process improved the drawability of the entire aluminum alloy sheet. For numerical simulations, the non-quadratic anisotropic yield function Yld2000-2d was employed along with isotropic hardening, while the formability was evaluated by utilizing theoretical forming limit diagrams (FLD) based on Hill's bifurcation and M-K theories.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. W. Thomas, E. D. Nicholas, J. C. Needham, M. G. Murch, P. Templesmith, and C. J. Dawes, GB Patent Applications No. 9125978.8 (1991), US Patent No. 5460317 (1995).
W. S. Miller, L. Zhuang, J. Bottema, A. J. Wittebrood, P. De Smet, A. Haszler, and A. Vieregge, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 280, 37 (2000).
Y. S. Sato, Y. Sugiura, Y. Shoji, S. H. Park, H, Kokawa, and K. Ikeda, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 369, 138 (2004).
M. Jansson, L. Nilsson, and K. Simonsson, Int. J. Plasticity 21, 1041 (2005).
R. Smerd, S. Winkler, C. Salisbury, M. Worswick, D. Lloyd, and M. Finn, Int. J. Impact Eng. 32, 541 (2005).
C. G. Lee, S. Park, K. Chung, H. N. Han, and S. J. Kim, Proc. of the Twentieth Conf. on Mechanical Behaviors of Materials (eds. D. I. Kwon, Y. J, Kim, D. H. Shin, and S. I. Hong), p. 116–123, Korean Institute of Metals and Materials, Busan, Korea (2006).
M. Jain, J. Allin, and M. J. Bull, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 256, 69 (1998).
C. G. Lee, S. J. Kim, H. N. Han, K. Chung, and S. Park, Korea Patent No. 10-0680183-0000 (2007).
S. H. Kang, H. S. Chung, H. N. Han, K. H. Oh, C. G. Lee, and S. J. Kim, Scri. Mater. 57, 17 (2007).
F. Barlat, J. C. Brem, J. W. Yoon, K. Chung, R. E. Dick, S. H. Choi, F. Pourboghrat, E. Chu, and D. J. Lege, Int. J. Plasticity 19, 1297 (2003).
R. Hill, J. Mech. Phys. Solid 1, 19 (1952).
Z. Marciniak, and K. Kuczynski, Int. J. Mech. Sci. 9, 609 (1967).
ABAQUS User's manual (version 6.5), Hibbit, Karlsson & Sorensen Inc., USA (2005).
K. Chung, and O. Richmond, Int. J. Plasticity 9, 907 (1993).
J. W. Yoon, D. Y. Yang, and K. Chung, Int. J. Plasticity 16, 595 (2000).
C. Kaye, and T. Laby, Table of Physical and Chemical Constants, p. 29, Longman, New York (1986).
D. Kim, M. G. Lee, C. Kim, M. L. Wenner, R. H. Wagoner, F. Barlat, K. Chung, J. R. Youn, and T. J. Kang, Met. Mater.-Int. 9, 561 (2003).
J. Kim, W. Lee, D. Kim, J. Kong, C. Kim, M. L. Wenner, and K. Chung, Met. Mater.-Int. 12, 293 (2006).
W. F. Hosford, J. Appl. Mech. Trans. ASME 39, 607 (1972).
R. K. Verma, and S. Chandra, J. Mat. Proc. Tech. 172, 218 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, S., Lee, C.G., Han, H.N. et al. Improvement of the drawability based on the surface friction stir process of AA5052-H32 automotive sheets. Met. Mater. Int. 14, 47–57 (2008). https://doi.org/10.3365/met.mat.2008.02.047
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3365/met.mat.2008.02.047