Abstract
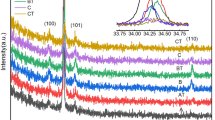
We report the laser-power dependence of a poly-silicon thin film fabricated using a 355-nm nanosecond laser annealing. The temperature distribution in the annealed thin film was investigated using thermal simulations as the laser power was varied to obtain the optimum laser conditions for crystalizing an amorphous silicon film. Based on the simulation results, laser annealing experiments were conducted for a 100-nm-thick amorphous silicon film deposited on a SiO2/Si wafer by using a Q-switched 355-nm nanosecond diode-pumped solid-state laser. The characteristics of the annealed silicon film were investigated using Raman spectroscopy and atomic force microscopy, which showed that both the crystal quality and the roughness of the annealed film increased as the laser was power increased. The experimentally obtained optimum laser power condition was found to be consistent with the simulation results. The demonstrated 355-nm nanosecond laser annealing is expected to provide a versatile solution for low-temperature poly-silicon processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Matsuo, A. Heya and H. Hamada, ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 8, 239 (2019).
M. Stewart, R. S. Howell, L. Pires and M. K. Hatalis, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 48, 845 (2001).
K. C. Phillips, H. H. Gandhi, E. Mazur and S. K. Sundaram, Adv. Opt. Photonics 7, 684 (2015).
M. J. Kang et al., J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 27, 34 (2019).
Y. H. Jung et al., Thin Solid Films 681, 93 (2019).
I. Theodorakos et al., J. Appl. Phys. 115, 043108 (2014).
K. Huet et al., Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 62, 92 (2017).
C. Fenouillet-Beranger et al., 2014 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (San Francisco, CA, 2014), p. 27.5.
K. Huet et al., Appl. Surf. Sci. 505, 144470 (2020).
T. Sameshima and S. Usui, J. Appl. Phys. 70, 1281 (1991).
R. Delmdahl and R. Patzel, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 47, 034004 (2014).
D. H. Choi, H. S. Kim, S. Y. Oh and C. H. Lee, Curr. Appl. Phys. 16, 876 (2016).
K. Jang, Y. Kim, J. Park and J. Yi, Materials 12, 1739 (2019).
C. H. Chou et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 103, 053515 (2013).
C. Wen et al., Mater. Res. Bull. 93, 238 (2017).
W. Beyer et al., J. Appl. Phys. 124, 153103 (2018).
T. Noguchi et al., Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 49, 03CA10 (2010).
S. Jin et al., IEEE Electron Device Lett. 37, 291 (2016).
Y. Choi and H. Y. Ryu, J. Korean Phys. Soc. 72, 939 (2018).
Y. H. Jung et al., Thin Sold Films 681, 93 (2019).
I. A. Palani, N. J. Vasa and M. Singaperumal, Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 11, 107 (2008).
F. Meyer et al., Appl. Phys. A 124, 254 (2018).
I. Theodorakos et al., J. Appl. Phys. 115, 043108 (2014).
M. Caninenberg et al., Opt. Laser Technol. 74, 132 (2015).
E. P. Donovan, F. Spaepen and D. Turnbull, Appl. Phys. Let. 42, 698 (1983).
Y. Liao, J. Y. Degorce and M. Meunier, Appl. Phys. A 82, 679 (2006).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Nano Material Technology Development Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (NRF- 2015M3A7B7045470), the Industrial Strategic Technology Developments Program (10052804) Funded by the Ministry of Knowledge Economy, Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology (MKE/KEIT), and Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology (KIAT) grant funded by the Korea Government (MOTIE) (P0008458, PBL Oriented Semiconductor Equipment Engineer Recruits (POSEER), 2020 The Competency Development Program for Industry Specialist).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pyo, J., Ryu, H.Y., Park, J. et al. Laser-Power Dependence of Poly-Silicon Crystallization Using 355-nm Nanosecond Laser Annealing. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 76, 1116–1120 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.76.1116
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.76.1116