Abstract
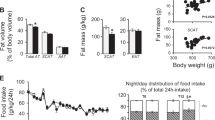
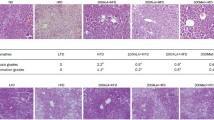
The effect of activation of liver X receptor by N-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-N-[4-[2,2,2-trifluoro-1-hydroxy-1(trifluoromethyl)ethyl]phenyl] benzenesulfonamide (T0901317) on high fat diet (HFD)-induced obesity and insulin resistance was examined in C57BL/6 mice. When on HFD continuously for 10 weeks, C57BL/6 mice became obese with an average body weight of 42 g, insulin resistant, and glucose intolerant. Twice weekly intraperitoneal injections of T0901317 at 50 mg/kg in animals on the same diet completely blocked obesity development, obesity-associated insulin resistance, and glucose intolerance. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis showed that T0901317-treated animals had significantly higher mRNA levels of genes involved in energy metabolism, including Ucp-1, Pgc1a, Pgc1b, Cpt1a, Cpt1b, Acadm, Acadl, Aox, and Ehhadh. Transcription activation of Cyp7a1, Srebp-1c, Fas, Scd-1, and Acc-1 genes was also seen in T0901317-treated animals. T0901317 treatment induced reversible aggregation of lipids in the liver. These results suggest that liver X receptor could be a potential target for prevention of obesity and obesity-associated insulin resistance.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yanovski SZ, Yanovski JA. Obesity prevalence in the United States—up, down, or sideways? N Engl J Med. 2011;364(11):987–9.
Wang Y, Beydoun MA. The obesity epidemic in the United States—gender, age, socioeconomic, racial/ethnic, and geographic characteristics: a systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Epidemiol Rev. 2007;29:6–28.
Suzuki K, Simpson KA, Minnion JS, Shillito JC, Bloom SR. The role of gut hormones and the hypothalamus in appetite regulation. Endocr J. 2010;57(5):359–72.
Zimmet P, Alberti KGMM, Shaw J. Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature. 2001;414(6865):782–7.
Kaiyala KJ, Schwartz MW. Toward a more complete (and less controversial) understanding of energy expenditure and its role in obesity pathogenesis. Diabetes. 2011;60(1):17–23.
Grun F, Blumberg B. Perturbed nuclear receptor signaling by environmental obesogens as emerging factors in the obesity crisis. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2007;8(2):161–71.
Chiang JY. Nuclear receptor regulation of lipid metabolism: potential therapeutics for dyslipidemia, diabetes, and chronic heart and liver diseases. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2005;6(10):994–1001.
Liu YY, Brent GA. Thyroid hormone crosstalk with nuclear receptor signaling in metabolic regulation. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2010;21(3):166–73.
Chen Z, Vigueira PA, Chambers KT, Hall AM, Mitra MS, Qi N, et al. Insulin resistance and metabolic derangements in obese mice are ameliorated by a novel peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-sparing thiazolidinedione. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(28):23537–48.
Miyazaki S, Taniguchi H, Moritoh Y, Tashiro F, Yamamoto T, Yamato E, et al. Nuclear hormone retinoid X receptor (RXR) negatively regulates the glucose-stimulated insulin secretion of pancreatic ss-cells. Diabetes. 2010;59(11):2854–61.
Faulds MH, Zhao C, Dahlman-Wright K. Molecular biology and functional genomics of liver X receptors (LXR) in relationship to metabolic diseases. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2010;10(6):692–7.
Edwards PA, Kast HR, Anisfeld AM. BAREing it all: the adoption of LXR and FXR and their roles in lipid homeostasis. J Lipid Res. 2002;43(1):2–12.
Liu Y, Yan C, Wang Y, Nakagawa Y, Nerio N, Anghel A, et al. Liver X receptor agonist T0901317 inhibition of glucocorticoid receptor expression in hepatocytes may contribute to the amelioration of diabetic syndrome in db/db mice. Endocrinology. 2006;147(11):5061–8.
Cao GQ, Liang Y, Broderick CL, Oldham BA, Beyer TP, Schmidt RJ, et al. Antidiabetic action of a liver X receptor agonist mediated by inhibition of hepatic gluconeogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(2):1131–6.
Babaya N, Fujisawa T, Nojima K, Itoi-Babaya M, Yamaji K, Yamada K, et al. Direct evidence for susceptibility genes for type 2 diabetes on mouse chromosomes 11 and 14. Diabetologia. 2010;53(7):1362–71.
Hirata A, Maeda N, Hiuge A, Hibuse T, Fujita K, Okada T, et al. Blockade of mineralocorticoid receptor reverses adipocyte dysfunction and insulin resistance in obese mice. Cardiovasc Res. 2009;84(1):164–72.
Choe SS, Choi AH, Lee JW, Kim KH, Chung JJ, Park J, et al. Chronic activation of liver X receptor induces beta-cell apoptosis through hyperactivation of lipogenesis—liver X receptor-mediated lipotoxicity in pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetes. 2007;56(6):1534–43.
Porter RK. A new look at UCP 1. BBA-Bioenergetics. 2006;1757(5–6):446–8.
Kajimura S, Seale P, Kubota K, Lunsford E, Frangioni JV, Gygi SP, et al. Initiation of myoblast to brown fat switch by a PRDM16-C/EBP-beta transcriptional complex. Nature. 2009;460(7259):1154–8.
Cheng Y, Meng QS, Wang CX, Li HK, Huang ZY, Chen SH, et al. Leucine deprivation decreases fat mass by stimulation of lipolysis in white adipose tissue and upregulation of uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1) in brown adipose tissue. Diabetes. 2010;59(1):17–25.
Ventura-Clapier R, Garnier A, Veksler V. Transcriptional control of mitochondrial biogenesis: the central role of PGC-1alpha. Cardiovasc Res. 2008;79(2):208–17.
Liang H, Ward WF. PGC-1alpha: a key regulator of energy metabolism. Adv Physiol Educ. 2006;30(4):145–51.
Carmiel-Haggai M, Cederbaum AI, Nieto N. A high-fat diet leads to the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in obese rats. FASEB J. 2005;19(1):136–8.
Cha JY, Repa JJ. The liver X receptor (LXR) and hepatic lipogenesis. The carbohydrate-response element-binding protein is a target gene of LXR. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(1):743–51.
Gerin I, Dolinsky VW, Shackman JG, Kennedy RT, Chiang SH, Burant CF, et al. LXRbeta is required for adipocyte growth, glucose homeostasis, and beta cell function. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(24):23024–31.
Laffitte BA, Chao LC, Li J, Walczak R, Hummasti S, Joseph SB, et al. Activation of liver X receptor improves glucose tolerance through coordinate regulation of glucose metabolism in liver and adipose tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(9):5419–24.
Dalen KT, Ulven SM, Bamberg K, Gustafsson JA, Nebb HI. Expression of the insulin-responsive glucose transporter GLUT4 in adipocytes is dependent on liver X receptor alpha. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(48):48283–91.
Steffensen KR, Gustafsson JA. Putative metabolic effects of the liver X receptor (LXR). Diabetes. 2004;53 Suppl 1:S36–42.
Hu T, Foxworthy P, Siesky A, Ficorilli JV, Gao H, Li S, et al. Hepatic peroxisomal fatty acid beta-oxidation is regulated by liver X receptor alpha. Endocrinology. 2005;146(12):5380–7.
Harris RBS, Apolzan JW. Changes in glucose tolerance and leptin responsiveness of rats offered a choice of lard, sucrose, and chow. Am J Physiol Regul Integr. 2012;302(11):R1327–39.
Nolan MA, Sikorski MA, McKnight GS. The role of uncoupling protein 1 in the metabolism and adiposity of RII beta-protein kinase A-deficient mice. Mol Endocrinol. 2004;18(9):2302–11.
Chisholm JW, Hong J, Mills SA, Lawn RM. The LXR ligand T0901317 induces severe lipogenesis in the db/db diabetic mouse. J Lipid Res. 2003;44(11):2039–48.
Joseph SB, Laffitte BA, Patel PH, Watson MA, Matsukuma KE, Walczak R, et al. Direct and indirect mechanisms for regulation of fatty acid synthase gene expression by liver X receptors. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(13):11019–25.
Acknowledgments
We thank Ms. Ryan Fugett for proofreading this manuscript. The study was supported in part by grants from NIH (RO1EB007357 and RO1HL098295).
Conflict of Interest
The authors claim no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 18 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, M., Liu, D. The Liver X Receptor Agonist T0901317 Protects Mice from High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin Resistance. AAPS J 15, 258–266 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-012-9429-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-012-9429-3