Abstract.
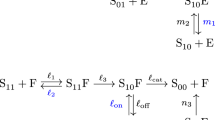
We studied the spatio-temporal dynamics of a cell signal cascade with negative feedback that quantitatively emulates the regulative process that occurs in the Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase/Extracellular Regulated Kinase (MAPK/ERK) pathway. The model consists of a set of six coupled reaction-diffusion equations that describes the dynamics of the six-module pathway. In the basic module the active form of the protein transmits the signal to the next pathway’s module. As suggested by experiments, the model considers that the fifth module’s kinase down-regulates the first and third modules. The feedback parameter is defined as, \( \mu^{r}_{j}\) = k kin 5/k kin j, (j = 1, 3). We analysed the pathway’s dynamics for \( \mu^{r}_{j}\) = 0.10 , 1.0, and 10 in the kinetic regimes: i) saturation of both kinases and phosphatases, ii) saturation of the phosphatases and iii) saturation of the kinases. For a regulated pathway the Total Activated Protein Profiles (TAPPs) as a function of time develop a maximum during the transient stage in the three kinetic regimes. These maxima become higher and their positions shift to longer times downstream. This scenario also applies to the TAPP’s regulatory kinase that sums up its inhibitory action to that of the phosphatases leading to a maximum. Nevertheless, when \( \mu^{r}_{j}\) = 1.0 , the TAPPs develop two maxima, with the second maximum being almost imperceptible. These results are in qualitative agreement with experimental data obtained from NIH 3T3 mouse fibroblasts. In addition, analyses of the stationary states as a function of position indicate that in the kinetic regime i) which is of physiological interest, signal transduction occurs with a relatively large propagation length for the three values of the regulative parameter. However, for \( \mu^{r}_{j}\) = 0.10 , the sixth module concentration profile is transmitted with approximately 45% of its full value. The results obtained for \( \mu^{r}_{j}\) = 10 , indicate that the first five concentration profiles are small with a short propagation length; nonetheless, the last concentration profile, c6, attains more than 90% of its full value with a relatively large propagation length as an indication of signal transduction. Signal transduction also occurred favourably in the kinetic regimes ii) and iii), but the signal was longer-ranged in the regime ii).
Graphical abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. Voltmat, J. Pouysseguir, Biol. Cell 93, 71 (2001)
M.J. Robinson, M.H. Cobb, Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 9, 180 (1997)
L. Chang, M. Karin, Nature 410, 37 (2001)
E. Nishida, Y. Gotoh, Trends Biochem. Sci. 18, 128 (1993)
K. Kondoh, E. Nishida, Biochim. et Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 1773, 1227 (2007)
F.A. Brightman, D.A. Fell, FEBS Lett. 482, 169 (2000)
S. Yamada, S. Shiono, A. Joo, A. Yoshimura, FEBS Lett. 534, 190 (2003)
B.N. Kholodenko, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7, 165 (2006)
C. Dong, S.B. Waters, K.H. Holt, J.E. Pessin, J. Biol. Chem. 271, 6328 (1996)
R. Fritsche-Guenther, F. Witzel, A. Sieber, R. Herr, N. Schmidt, S. Braun, T. Brummer, C. Sers, N. Blüthgen, Mol. Syst. Biol. 7, 489 (2011)
M.M. McKay, D.K. Morrison, Oncogene 26, 3113 (2007)
S.Y. Shin, O. Rath, S.M. Choo, F. Fee, B. McFerrran, W. Kolch, K.H. Cho, J. Cell. Sci. 122, 425 (2009)
Y. Kamioka, S. Yasuda, Y. Fujita, K. Aoki, M. Matsuda, J. Biol. Chem. 285, 33540 (2010)
B.N. Kholodenko, O.V. Demin, G. Moehren, J.B. Hoek, J. Biol. Chem. 274, 30169 (1999)
A.R. Asthagiri, D.A. Lauffenburger, Biotechnol. Prog. 17, 227 (2001)
B. Schoeberl, C. Eichler-Jonsson, E.D. Gilles, G. Muller, Nat. Biotechnol. 20, 370 (2002)
G. Moehren, N. Markevich, O. Demin, A. Kiyatkin, I. Goryanin, J.B. Hoek, B.N. Kholodenko, Biochemistry 41, 306 (2002)
S.Y. Shvartsman, C.B. Muratov, D.A. Lauffenburger, Development 129, 2577 (2002)
H.S. Wiley, S.Y. Shvartsman, D.A. Lauffenburger, Trends Cell. Biol. 13, 43 (2003)
B.N. Kholodenko, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7, 165 (2010)
J.J. Tyson, K.C. Chen, B. Novak, Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 15, 221 (2003)
E.R. Stadtman, P.B. Chock, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 2761 (1977)
A. Goldbeter, D.E. Koshlan, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 6840 (1981)
S. Hooshangi, S. Thiberge, R. Weiss, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102, 3581 (2005)
J.E. Jr. Ferrell, Trends Biochem. Sci. 78, 288 (1997)
C.Y.F. Huang, J.E. Ferrell Jr., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93, 10078 (1996)
J.E. Ferrell Jr., Trends Biochem. Sci. 21, 460 (1996)
B.N. Kholodenko, Eur. J. Biochem. 267, 1583 (2000)
N.I. Markevich, J.B. Hoek, B.N. Kholodenko, J. Cell Biol. 164, 353 (2004)
X. Wang, N. Hao, H.G. Dohlman, T.C. Elston, Biophys. J. 90, 1961 (2006)
M. Behar, N. Hao, H.G. Dohlman, T.C. Elston, Biophys. J. 93, 806 (2007)
Z. Han, T.M. Vondriska, L. Yang, W.R. MacLellan, J.N. Weiss, Z. Qu, J. Theor. Biol. 246, 755 (2007)
R. Heinrich, B.G. Neel, T.A. Rapoport, Mol. Cell 9, 957 (2002)
M. Chaves, E.D. Sontag, R.J. Dinerstein, J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 15311 (2004)
E. Sontag, M. Chaves, Automatica 42, 1987 (2006)
Y. Morishita, T.J. Kobayashi, K. Aihara, Biophys. J. 91, 2072 (2006)
Z. Qu, T.M. Vondriska, Phys. Biol. 6, 1 (2009)
J. Muñoz-García, Z. Neufeld, B.N. Kholodenko, PLOS Comput. Biol. 5, e1000330 (2009)
Y. Hwang, P. Kumar, A.I. Barakat, J. Math. Biol. 69, 213 (2014)
C.I. Maeder, M.A. Hink, A. Kinkhabwala, R. Mayr, P.I. Bastiaens et al., Nat. Cell Biol. 9, 1319 (2007)
C.G. Brown, B.N. Kholodenko, FEBS Lett. 457, 452 (1999)
P. Kaláb, K. Weis, R. Heald, Science 295, 2452 (2002)
P. Niethammer, P. Bastiaens, E. Karsenti, Science 303, 1862 (2004)
M. Caudron, G. Bunt, P. Bastiaens, E. Karsenti, Science 309, 1373 (2005)
P. Kaláb, A. Pralle, E.Y. Isacoff, R. Heald, K. Weis, Nature 440, 697 (2006)
D.L. Nelson, M.M. Cox, Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry, sixth edition (W.H. Freeman and Company, 2012)
A. Fujioka, K. Terai, R.E. Itoh, K. Aoki, T. Nakamura, S. Kuroda, E. Nishida, M. Matsuda, J. Biol. Chem. 281, 8917 (2006)
S. Ahmed, K.G. Grant, L.E. Edwards, A. Rahman, M. Cirit, M.B. Goshe, J.M. Haugh, Mol. Syst. Biol. 10, 718 (2014)
O.E. Sturm, R. Orton, J. Grindlay, M. Birtwistle, V. Vyshemirsky, D. Gilbert, M. Calder, A. Pitt, B. Kholodenko, W. Kolch, Sci. Signal. 3, ra90 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maya-Bernal, J., Ramírez-Santiago, G. Spatio-temporal dynamics of a cell signal pathway with negative feedbacks: the MAPK/ERK pathway. Eur. Phys. J. E 39, 28 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2016-16028-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2016-16028-3