Abstract
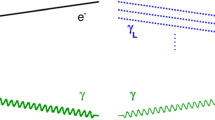
The ultra-high fields of high-power short-pulse lasers are expected to contribute to understanding fundamental properties of the quantum vacuum and quantum theory in very strong fields. For example, the neutral QED vacuum breaks down at the Schwinger field strength of 1.3×1018 V/m, where a virtual e+e- pair gains its rest mass energy over a Compton wavelength and materializes as a real pair. At such an ultra-high field strength, an electron experiences an acceleration of aS=2×1028g and hence fundamental phenomena such as the long predicted Unruh effect start to play a role. The Unruh effect implies that the accelerated electron experiences the vacuum as a thermal bath with the Unruh temperature. In its accelerated frame the electron scatters photons off the thermal bath, corresponding to the emission of an entangled pair of photons in the laboratory frame. While it remains an experimental challenge to reach the critical Schwinger field strength within the immediate future even in view of the enormous thrust in high-power laser developments in recent years, the near-future laser technology may allow to probe the signatures of the Unruh effect mentioned above. Using a laser-accelerated electron beam (γ∼300) and a counter-propagating laser beam acting as optical undulator should allow to create entangled Unruh photon pairs (i.e., signatures of the Unruh effect) with energies of the order of several hundred keV. An even substantially improved experimental scenario can be realized by using a brilliant 20 keV photon beam as X-ray undulator together with a low-energy (γ≈2) electron beam. In this case the separation of the Unruh photon pairs from background originating from linearly accelerated electrons (classical Larmor radiation) is significantly improved. Detection of the Unruh photons may be envisaged by Compton polarimetry in a 2D-segmented position-sensitive germanium detector.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Sauter, Z. Phys. 69, 742 (1931); F. Sauter, Z. Phys. 73, 547 (1931); W. Heisenberg, H. Euler, Z. Phys. 98, 714 (1936); V. Weisskopf, Kong. Dans. Vid. Selsk., Mat.-fys. Medd. XIV, 6 (1936); J. Schwinger, Phys. Rev. 82, 664 (1951)
R. Schützhold, H. Gies, G. Dunne, Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 130404 (2008)
W.G. Unruh, Phys. Rev. D 14, 870 (1976)
S.W. Hawking, Commun. Math. Phys. 43, 194 (1975)
R. Schützhold, G. Schaller, D. Habs, Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 121302 (2006)
R. Schützhold, G. Schaller, D. Habs, Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 091301 (2008)
W.G. Unruh, R.M. Wald, Phys. Rev. D 29, 1047 (1984)
A. Higuchi, G.E.A. Matsas, D. Sudarsky, Phys. Rev. D 45, R3308 (1992)
L.C.B. Crispino, A. Higuchi, G.E.A. Matsas, Rev. Mod. Phys. 80, 787 (2008)
R. Schützhold, C. Maia, Eur. Phys. J. D 55, 375 (2009)
J.S. Bell, J.M. Leinaas, Nucl. Phys. B 284, 488 (1987)
W.G. Unruh, Phys. Rep. 307, 163 (1998)
I. Freund, B.F. Levine, Phys. Rev. Lett. 23, 854 (1969)
P. Eisenberger, S.L. McCall, Phys. Rev. Lett. 26, 684 (1971)
Y. Yoda et al., J. Synchrotron Radiat. 5, 980 (1998)
B. Adams et al., J. Synchrotron Radiat. 7, 81 (2000)
P. Chen, T. Tajima, Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 256 (1999)
S.P.D. Mangles et al., Nature 431, 535 (2004)
C.G.R. Geddes et al., Nature 431, 538 (2004)
J. Faure et al., Nature 431, 541 (2004)
W.P. Leemans et al., Nature Phys. 2, 696 (2006)
S. Karsch et al., New J. Phys. 9, 415 (2007)
Zs. Major et al., accepted for publication in: The Review of Laser Engineering (Journal of the Laser Society of Japan) (2009)
S. Gordienko et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 103903 (2005)
P. Jacobs et al., Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 54, 443 (2005)
C.G.R. Geddes et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 215004 (2008)
S. Tashenov, Ph.D. thesis, Univ. Frankfurt, 2005, unpublished
A. Ferguson, Nucl. Instrum. Meth. 162, 565 (1979)
R. Kroeger et al., Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 436, 165 (1999)
T. Stöhlker et al., J. Phys. 58, 411 (2007)
J.D. Jackson, Classical Electrodynamics, 2nd edn. (Wiley, New York, 1975), p. 682
D. Habs et al., Appl. Phys. B 93, 349 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thirolf, P., Habs, D., Henig, A. et al. Signatures of the Unruh effect via high-power, short-pulse lasers. Eur. Phys. J. D 55, 379–389 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2009-00149-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2009-00149-x