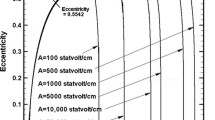
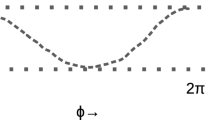
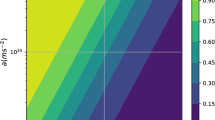
Abstract
The present study examines the behavior of a classical charged point particle orbiting an infinitely massive and oppositely charged nucleus, while acted upon by circularly polarized electromagnetic plane waves. This system is intended to represent a classical model of a hydrogen atom interacting with radiation. Despite the simplicity of the system, very nonlinear behavior result, making a numerical study of the system nearly essential. The results should be of interest to researchers studying the classical behavior of Rydberg-like atoms. The numerical results naturally suggest a number of experiments that could be done involving the novel control of chemical reactions and of excited atomic states. Moreover, and perhaps more immediately, the present article has close ties and implications regarding the behavior of the classical hydrogen atomic model within the domain of the theory called stochastic electrodynamics.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Clark, W., and Greene, C. H. (1999). Adventures of a rydberg electron in an anisotropic world. Rev. Mod. Phys. 71, 821–833.
Braun, P. A. (1993). Discrete semiclassical methods in the theory of rydberg atoms in external fields. Rev. Mod. Phys. 65, 115–161.
Griffiths, J. A., and Farrelly, D. (1992). Ionization of rydberg atoms by circularly and elliptically polarized microwave fields. Phys. Rev. A 45(5), R2678–R2681.
Grochmalicki, J., Lewenstein, M., and Rzazewski, K. (1991). Stabilization of atoms in superintense laser fields: Is it real? Phys. Rev. Lett. 66(8), 1038–1041.
Wesdorp, C., Robicheaux, F., and Noordam, L. D. (2001). Displacing rydberg electrons: The mono-cycle nature of half-cycle pulses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87(8), 083001.
Yoshida, S., Reinhold, C. O., Kristofel, P., and Burgdorfer, J. (2000). Exponential and nonexponential localization of the one-dimensional periodically kicked rydberg atom. Phys. Rev. A 62, 023408.
Rockwell, G. N., Hoffman, V. F., Clausen, Th., and Blumel, R. (2002). Realistic three-dimensional computations of microwave-ionization curves of hydrogen rydberg atoms. Phys. Rev. A 65, 025401.
Koch, P. M., and van Leeuwen, K. A. H. (1995). The importance of resonances in microwave “ionization” of excited hydrogen atoms. Phys. Rep. 255, 289–403.
Leopold, J. G., and Percival, I. C. (1978). Microwave ionization and excitation of Rydberg atoms. Phys. Rev. Lett. 41(14), 944–947.
Noel, M. W., Griffith, W. M., and Gallagher, T. F. (2000). Classical subharmonic resonances in microwave ionization of lithium Rydberg atoms. Phys. Rev. A 62, 063401.
Gallagher, T. F., Hill, R. M., and Edelstein, S. A. (1978). Method and apparatus for field ionization for isotope separation. US Patent No. 4,070,580; see: www.uspto.gov, pp. 1–7.
Bir, R., and Schermann, J. P. (1982). Method of isotope separation. US Patent No. 4,360,501; see: www.uspto.gov, pp. 1–6.
Oomori, T., Ono, K., and Fujita, S. (1990). Ion current generator system for thin film formation, ion implantation, etching and sputtering. US Patent No. 4,893,019; see: www.uspto.gov, pp. 1–43.
Oomori, T., and Ono, K. (1992). Ion source. US Patent No. 5,115,135; see: www.uspto. gov, pp. 1–75.
Noordam, L. D., and Lankhuijzen, M. D. (2000). Apparatus for detecting a photon pulse. US Patent No. 6,049,079; see: www.uspto.gov, pp. 1–9.
Cole, D. C. (1993). Reviewing and Extending Some Recent Work on Stochastic Electrodynamics, pp. 501–532, World Scientific, Singapore.
de la Pena, L., and Cetto, A. M. (1996). The Quantum Dice-An Introduction to Stochastic Electrodynamics. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Kluwer Dordrecht.
Boyer, T. H. (1975). Random electrodynamics: The theory of classical electrodynamics with classical electromagnetic zero-point radiation. Phys. Rev. D 11(4), 790–808.
Boyer, T. H. (1985). The classical vacuum. Sci. American 253, 70–78.
Cole, D. C. (1990). Derivation of the classical electromagnetic zero-point radiation spectrum via a classical thermodynamic operation involving van der waals forces. Phys. Rev. A 42, 1847–1862.
Marshall, T. W. (1963). Random electrodynamics. Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 276, 475–491.
Marshall, T. W. (1965). Statistical electrodynamics. Proc. Camb. Phil. Soc. 61, 537–546.
Boyer, T. H. (1969). Derivation of the blackbody radiation spectrum without quantum assumptions. Phys. Rev. 182, 1374–1383.
Boyer, T. H. (1969). Classical statistical thermodynamics and electromagnetic zero-point radiation. Phys. Rev. 186, 1304–1318.
Cole, D. C., and Rueda, A. (1996). The quantum dice: An introduction to stochastic electrodynamics. Found. Phys. 26, 1559–1562.
Cole, D. C. (1992). Reinvestigation of the thermodynamics of blackbody radiation via classical physics. Phys. Rev. A 45, 8471–8489.
Cole, D. C. (2000). Thermodynamics of blackbody radiation via classical physics for arbitrarily shaped cavities with perfectly conducting walls. Found. Phys. 30(11), 1849–1867.
Franca, H. M., and Marshall, T. W. (1988). Excited states in stochastic electrodynamics. Phys. Rev. A 38(7), 3258–3263.
Boyer, T. H. (1980). Thermal effects of acceleration through random classical radiation. Phys. Rev. D 21(8), 2137–2148.
Boyer, T. H. (1984). Thermal effects of acceleration for a classical dipole oscillator in classical electromagnetic zero-point radiation. Phys. Rev. D 29(6), 1089–1095.
Cole, D. C. (1985). Properties of a classical charged harmonic oscillator accelerated through classical electromagnetic zero-point radiation. Phys. Rev. D 31(8), 1972–1981.
Cole, D. C. (1987). Thermal effects of acceleration for a spatially extended electromagnetic system in classical electromagnetic zero-point radiation: Transversely positioned classical oscillators. Phys. Rev. D 35, 562–583.
Boyer, T. H. (1975). General connection between random electrodynamics and quantum electrodynamics for free electromagnetic fields and for dipole oscillator systems. Phys. Rev. D 11(4), 809–830.
Boyer, T. H. (1976). Equilibrium of random classical electromagnetic radiation in the presence of a nonrelativistic nonlinear electric dipole oscillator. Phys. Rev. D 13(10), 2832–2845.
Boyer, T. H. (1978). Statistical equilibrium of nonrelativistic multiply periodic classical systems and random classical electromagnetic radiation. Phys. Rev. A 18, 1228–1237.
Blanco, R., Pesquera, L., and Santos, E. (1983). Equilibrium between radiation and matter for classical relativistic multiperiodic systems. derivation of Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution from Rayleigh-Jeans spectrum. Phys. Rev. D (Particles and Fields) 27(6), 1254–87.
Blanco, R., Pesquera, L., and Santos, E. (1984). Equilibrium between radiation and matter for classical relativistic multiperiodic systems. ii. study of radiative equilibrium with Rayleigh-Jeans radiation. Phys. Rev. D (Particles and Fields) 29(10), 2240–54.
Marshall, T. W., and Claverie, P. (1980). Stochastic electrodynamics of nonlinear systems. I. Particle in a central field of force. J. Math. Phys. 21(7), 1819–25.
Claverie, P., Pesquera, L., and Soto, F. (1980). Existence of a constant stationary solution for the hydrogen atom problem in stochastic electrodynamics. Phys. Lett. A 80(2/3), 113–16.
Denis, A., Pesquera, L., and Claverie, P. (1981). Linear response of stochastic multiperiodic systems in stationary states with application to stochastic electrodynamics. Physica A 109(1/2), 178–92.
Claverie, P., and Soto, F. (1982). Nonrecurrence of the stochastic process for the hydrogen atom problem in stochastic electrodynamics. J. Math. Phys. 23(5), 753–9.
Cole, D. C. (1990). Entropy and other thermodynamic properties of classical electromagnetic thermal radiation. Phys. Rev. A 42, 7006–7024.
Boyer, T. H (1989). Scaling symmetry and thermodynamic equilibrium for classical electromagnetic radiation. Found. Phys. 19, 1371–1383.
Cole, D. C. (1990). Classical electrodynamic systems interacting with classical electromagnetic random radiation. Found. Phys. 20, 225–240.
Dirac, P. A. M. (1938). Classical theory of radiating electrons. Proc. R. Soc. London Ser. A 167, 148–169.
Teitelboim, C. (1970). Splitting of the maxwell tensor: Radiation reaction without advanced fields. Phys. Rev. D 1(6), 1572–1582.
Teitelboim, C., Villarroel, D., and van Weert, Ch. G. (1980). Classical electrodynamics of retarded fields and point particles. Riv. del Nuovo Cimento 3(9), 1–64.
Rohrlich, F. (1965). Classical Charged Particles, Addison-Wesley, MA.
Hockney, R. W., and Eastwood, J. W. (1988). Computer Simulation Using Particles. McGraw-Hill, New York.
Press, W. H., Teukolsky, S. A., Vetterling, W. T., and Flannery, B. P. (1992). Numerical Recipes in C: The Art of Scientific Computing, Cambridge University Press, New York, 2nd edn.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cole, D.C., Zou, Y. Simulation Study of Aspects of the Classical Hydrogen Atom Interacting with Electromagnetic Radiation: Circular Orbits. Journal of Scientific Computing 20, 43–68 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025846412872
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025846412872