Abstract
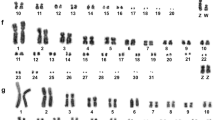
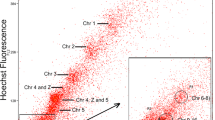
Chickens and the great flightless emu belong to two distantly related orders of birds in the carinate and ratite subclasses that diverged at least 80 million years ago. In the first ZOO-FISH study between bird species, we hybridized single chromosome paints from the chicken (Gallus domesticus) onto the emu chromosomes. We found that the nine macrochromosomes show remarkable homology between the two species, indicating strong conservation of karyotype through evolution. One chicken macrochromosome (4) was represented by a macro- and a microchromosome in the emu, suggesting that microchromosomes and macrochromosomes are interconvertible. The chicken Z chromosome paint hybridized to the emu Z and most of the W, confirming that ratite sex chromosomes are largely homologous; the centromeric region of the W which hybridized weakly may represent the location of the sex determining gene(s).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ansari HA, Takagi N, Sasaki M (1988) Morphological differentiation of sex chromosomes in three species of ratite birds. Cytogenet Cell Genet 47: 185-188.
de Boer LEM (1980) Do the chromosomes of the kiwi provide evidence for a monophyletic origin of the ratites? Nature 287: 84-85.
Ferguson-Smith MA, Yang F, O'Brien PCM (1998) Comparative mapping using chromosome sorting and painting. ILAR J 39: (2&3) 68-76.
Fillion V (1998) The chicken as a model to study microchromosomes in birds: a review. Genet Sel Evol 30: 209-219.
Fridolfsson AK, Cheng H, Copeland NG et al. (1998) Evolution of the avian sex chromosomes from an ancestral pair of autosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 8147-8152.
Frönicke L, Muller-Navia J, Romanakis K, Scherthan H (1997) Chromosomal homeologies between human, harbor seal (Phoca vitulina) and the putative ancestral carnivore karyotype revealed by Zoo-FISH. Chromosoma 106: 108-113.
Glas R, De Leo AA, Delbridge ML et al. (1999) Chromosome painting in marsupials: Genome conservation in the kangaroo family. Chromosome Res 7: 161-176.
Graves JAM (1995) The origin and function of the mammalian Y chromosome and Y-borne genes — an evolving understanding. Bioessays 17: 311-320.
Griffin DK, Haberman F, O'Brien PCM et al. (1999) Defining the avian genome using chromosome painting probes isolated by flow cytometry and microdissection. Chromosome Res (submitted).
Härlid A, Janke A, Arnason U (1998) The complete motochondrial genome of Rhea americana and early avian divergences. J Mol Evol 46: 669-679.
Ladjadi K, Tixier-Boichard M, Cribiu EO (1993) High resolution chromosome preparations for G-and R-banding in Gallus domesticus. J Hered 86: 136-139.
Ogawa A, Murata K, Mizuno S (1998) The location of Z-and W-linked marker genes and sequence on the homomorphic sex chromosomes of the ostrich and the emu. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 4415-4418.
Ohno S (1967) Sex Chromosomes and Sex Determination. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Pigozzi MI, Solari AJ (1997) Extreme axial equalization and wide distribution of recombination nodules in the primitive ZW pair of Rhea americana (Aves, Ratitae). Chromosome Res 5: 421-428.
Raudsepp T, Frönicke L, Scherthan H, Gustavsson I, Chowdhary BP (1996) Zoo-FISH delineates conserved chromosomal segments in horse and man. Chromosome Res 4: 218-225.
Rettenberger G, Klett CH, Zeehner U et al. (1995) Zoo-FISH analysis: cat and human karyotypes closely resemble the putative ancestral mammalian karyotype. Chromosome Res 3: 479-486.
Rodoinov AV (1997) Evolution of avian chromosome and linkage groups. Russian J Genet 33: 605-617.
Scherthan H, Cremer T, Arnason U, Weier H, Lima-de-Faria A, Frönicke L (1994) Comparative chromosome painting discloses homologous segments in distantly related mammals. Nature Genet 6: 342-347.
Schmid M, Enderle E, Schindler D, Schempp W (1995) Chromosome banding and replication patterns in bird karyotypes. Cytogenet Cell Genet 5: 139-146.
Sibley CG, Ahlquist JE. (1990) Phylogeny and Classification of Birds. New Haven, Connecticut: Yale University Press.
Solari AJ (1993) Sex Chromosomes and Sex Determination in Vertebrates. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, pp. 43-73.
Solinas-Toldo S, Lengauer C, Fries R (1995) Comparative genome map of human and cattle. Genomics 27: 489-496.
Stapel SO, Leunissen JAM, Versteeg M, Wattel J, Jong WW de (1984) Ratites as oldest offshoot of avian stem — evidence from α-crystallin A sequences. Nature 311: 257-259.
Stevens L (1997) Sex chromosomes and sex determining mechanisms in birds. Sci Prog 80(3): 197-216.
Telenius H, Pelmear A, Tunnacliffe A et al. (1992) Cytogenetic analysis by chromosome painting using DOP-PCR amplified flow-sorted chromosomes. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 4: 257-263.
Thorne M, Sheldon BL (1993) Triploid intersex and chimeric chickens: Useful models for studies of avian sex determination. In: Reed KC, Graves JAM, eds. Sex Chromosomes and Sex Determining Genes. Chur, Switzerland: Harwood Academic, pp 201-208.
Toder R, O'Neill RJW, Weinberg J, O'Brien PCM, Voullaire L, Graves JAM (1997) Comparative chromosome painting between two marsupials: origins of an XX/XY1 Y2 sex chromosome system. Mammalian Genome 8: 418-422.
Yang F, O'Brien PCM, Wienberg J, Neitzel H, Lin CC, Ferguson-Smith MA (1997) Chromosomsal evolution of the chinese muntjac (Muntiacus reevesi). Chromosoma 106: 37-43.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shetty, S., Griffin, D.K. & Graves, J.A.M. Comparative Painting Reveals Strong Chromosome Homology Over 80 Million Years of Bird Evolution. Chromosome Res 7, 289–295 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009278914829
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009278914829