Abstract
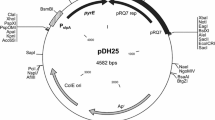
Lactococcus lactis has become the best studied species of the lactic acid bacteria (LAB) clade and an ideal cell factory for heterogenous proteins. We have constructed an antibiotic-free expression vector, pMG-thyA, using thymidine synthase gene thyA as the selection marker. The thyA gene was cloned from the food industry strain Streptococcus thermophilus St-JY and was used to replace the erythromycin resistance genes on L. lactis expression vector pMG36e in order to construct pMG-thyA. The construction of the new vector and thyA-null host L. lactis MG1363-TT yielded an antibiotic-free expression system. The α-amylase gene (amy) was cloned onto the multiple cloning site of the vector pMG-thyA as a reporter gene, yielding the recombinant plasmid pMGthyA-amy. This plasmid was electroporated into L. lactis MG1363-TT, and the recombinant strain grown on SA plates containing 0.5 % (w/v) soluble starch formed distinct bacterial colonies and clear zones (halo) around the colonies following the addition of iodine solution. These research findings lay the foundation for food-grade expression in L. lactis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bolotin A, Wincker P, Mauger S, Jaillon O, Malarme K, Weissenbach J, Ehrlich SD, Sorokin A (2001) The complete genome sequence of the lactic acid bacterium Lactococcus lactis ssp. lacts IL1403. Genome Res 11:731–753
de Vos WM (1999) Safe and sustainable systems for food-grade fermentations by genetically modified lactic acid bacteria. Int Dairy J 9:3–10
Geriletu XR, Jia H, Terkawi MA, Xuan X, Zhang H (2011) Immunogenicity of orally administrated recombinant Lactobacillus casei Zhang expressing Cryptosporidium parvum surface adhesion protein P23 in mice. Curr Microbiol 62:1573–1580
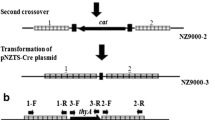
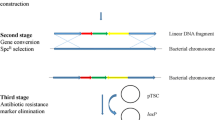
Gu X, Li C, Cai Y, Dong H, Xu W, Tian H, Yang J (2012) Construction of Lactococcus lactis thyA-null using the Red recombination system. Ann Microbiol 63:951–956
Holo H, Nes IF (1989) High-frequency transformation, by electroporation, of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris grown with glycine in osmotically stabilized media. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:3119–3123
Jensen PR, Hammer K (1993) Minimal requirements for exponential growth of Lactococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:4363–4366
Jeong DW, Kim JH, Kim KH (2004) Screening and characterization of secretion signals from Lactococcus lactis ssp. cremoris LM0230. J Microbiol Biotechnol 14:1052–1056
Le Loir Y, Azevedo V, Oliveira SC, Freitas DA, Miyoshi A, Bermúdez-Humarán LG, Nouaille S, Ribeiro LA, Leclercq S, Gabriel JE, Guimaraes VD, Oliveira MN, Charlier C, Gautier M, Langella P (2005) Protein secretion in Lactococcus lactis: an efficient way to increase the overall heterologous protein production. Microb Cell Fact 4:2
Leroy F, de Vuyst L (2004) Lactic acid bacteria as functional starter cultures for the food fermentation industry. Trends Food Sci Technol 15:267–278
Liu CQ, Su P, Khunajakr N, Deng YM, Sumual S, Kim WS, Tandianus JE, Dunn NW (2005) Development of food-grade cloning and expression vectors for Lactococcus lactis. J Appl Microbiol 98:127–135
Noreen N, Hooi WY, Baradaran A, Rosfarizan M, Sieo CC, Rosli MI, Yusoff K, Raha AR (2011) Lactococcus lactis M4, a potential host for the expression of heterologous proteins. Microb Cell Fact 10:28
Okada T, Homma J, Sonohara H (1962) Improved method for obtaining thymineless mutants of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol 84:602–603
OSsullivan DJ, Klaenhammer TR (1993) Rapid mini-prep isolation of high-quality plasmid DNA from Lactococcus and Lactobacillus spp. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:2730–2733
Peterbauer C, Maischberger T, Haltrich D (2011) Food-grade gene expression in lactic acid bacteria. Biotechnol J 6:1147–1161
Ross P, O’Gara F, Condon S (1990a) Cloning and characterization of the thymidylate synthase gene from Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:2156–2163
Ross P, O’Gara F, Condon S (1990b) Thymidylate synthase gene from Lactococcus lactis as a genetic marker: an alternative to antibiotic resistancegenes. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:2164–2169
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Sasaki Y, Ito Y, Sasaki T (2004) ThyA as a selection marker in construction of food-grade host-vector and integration systems for Streptococcus thermophilus. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:1858–1864
Schleifer KH, Kraus J, Dvorak C, Kilpper-Bälz R, Collins MD, Fischer W (1985) Transfer of Streptococcus lactis and related streptococci to the genus Lactococcus gen. nov. Syst Appl Microbiol 6:183–195
Shareck J, Choi Y, Lee B, Miguez CB (2004) Cloning vectors based on cryptic plasmids isolated from lactic acid bacteria: their characteristics and potential applications in biotechnology. Crit Rev Biotechnol 24:155–208
Sohail M (1998) A simple and rapid method for preparing genomic DNA from Gram-positive bacteria. Mol Biotechnol 10:191–193
Sridhar VR, Smeianov VV, Steele JL (2006) Construction and evaluation of food-grade vectors for Lactococcus lactis using aspartate aminotransferase and alpha-galactosidase as selectable markers. J Appl Microbiol 101:161–171
Toomey N, Monaghan A, Fanning S, Bolton D (2009) Transfer of antibiotic resistance marker genes between lactic acid bacteria in model rumen and plantenvironments. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:3146–3152
van Asseldonk M, Rutten G, Oteman M, Siezen RJ, de Vos WM, Simons G (1990) Cloning of usp45, a gene encoding a secreted protein from Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis MG1363. Gene 95:155–160
van de Guchte M, van der Vossen JM, Kok J, Venema G (1989) Construction of a lactococcal expression vector: expression of hen egg white lysozyme in Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:224–228
van de Guchte M, Kok J, Venema G (1992) Gene expression in Lactococcus lactis. FEMS Microbiol Rev 8:73–92
Vidal L, Pinsach J, Striedner G, Caminal G, Ferrer P (2008) Development of an antibiotic-free plasmid selection system based on glycine auxotrophy for recombinant protein overproduction in Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol 134:127–136
Wang C, Zhang CW, Liu HC, Yu Q, Pei XF (2008) Non-fusion and fusion expression of beta-galactosidase from Lactobacillus bulgaricus in Lactococcus lactis. Biomed Environ Sci 21:389–397
Wegmann U, O’Connell-Motherway M, Zomer A, Buist G, Shearman C, Canchaya C, Ventura M, Goesmann A, Gasson MJ, Kuipers OP, van Sinderen D, Kok J (2007) Complete genome sequence of the prototype lactic acid bacterium Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris MG1363. J Bacteriol 189:3256–3270
Yang EJ, Chang HC (2011) Construction and evaluation of shuttle vector, pGYC4α, based on pYC2 from Lactobacillus sakei. Biotechnol Lett 33:599–605
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Chinese High Technology Program (863) (2006AA10Z317) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31301520).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Chen Li and Hui Dong contributed equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Dong, H., Lu, H. et al. Development of an antibiotic-free plasmid selection system based on thymine auxotrophy in Lactococcus lactis . Ann Microbiol 65, 1049–1055 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-014-0950-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-014-0950-8