Abstract
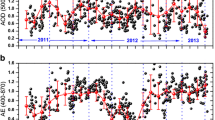
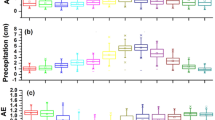
It is well established that aerosols affect the climate in a variety of ways. In order to understand these effects, we require an insight into the properties of aerosols. In this paper we present a study of aerosol properties such as aerosol optical depth (AOD), single scattering albedo (SSA) and aerosol radiative forcing (ARF) over mega city of Lahore (Pakistan). The data from Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) have been used for the period December 2009 to October 2011. The seasonal average values of AOD, asymmetry parameter (ASY) and volume size distribution in coarse mode were observed to be highest in summer. On the other hand, the average values of Angstrom exponent (AE) and imaginary part of refractive index (RI) were found to be maximum in winter. The average value of real part of RI was found to be higher in spring than in all other seasons. The SSA exhibited an increasing trend with wavelength in the range 440 nm–1020 nm in spring, summer and fall indicating the dominance of coarse particles (usually dust). However, a decreasing trend was found in winter in the range 675 nm–1020 nm pointing towards the dominance of biomass and urban/industrial aerosols. As far as aerosol radiative forcing (ARF) is concerned, we have found that during the spring season ARF was lowest at the surface of Earth and highest at top of the atmosphere (TOA). This indicates that the atmosphere was warmer in spring than in all the remaining seasons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam, K., M. J. Iqbal, T. Blaschke, S. Qureshi, and G. Khan, 2010: Monitoring spatiotemporal variations in aerosols and aerosol-cloud interactions over Pakistan using MODIS data. Adv. Space Res., 46, 1162–1176.
____, T. Trautmann, and T. Blaschke, 2011a: Aerosol optical properties and radiative forcing over mega city Karachi. Atmos. Res., 101, 773–782.
____, S. Qureshi, and T. Blaschke, 2011b: Monitoring spatio-temporal aerosol patterns over Pakistan based on MODIS, TOMS and MISR satellite data and a HYSPLIT model. Atmos. Environ., 45, 4641–4651.
____, T. Trautmann, T. Blaschke, and M. Hussain, 2012: Aerosol optical and radiative properties during summer and winter seasons over Lahore and Karachi. Atmos. Environ., 50, 234–245.
Biswas, K. F., B. M. Ghauri, and L. Husain, 2008: Gaseous and aerosol pollutants during fog and clear episodes in south Asian urban atmosphere. Atmos. Environ., 42, 7775–7785.
Bohren, C. F., and D. R. Huffman, 1983: Absorption and scattering of light by small particles. John Wiley, 550 pp.
Charlson, R. J., S. E. Schwartz, J. M. Hales, R. D. Cess, J. A. Coakley Jr., J. E. Hansen, and D. J. Hofmann, 1992: Climate forcing by anthropogenic aerosols. Science, 255, 423–430.
Coakley Jr., J. A., R. D. Cess, and F. B. Yurevich, 1983: The effect of tropospheric aerosols on the Earth’s radiation budget: a parameterization for climate model. J. Atmos. Sci., 40, 116–138.
Dey, S., S. N. Tripathi, R. P. Singh, and B. N. Holben, 2004: Influence of dust storms on the aerosol optical properties over the Indo-Gangetic basin, J. Geophys. Res., 109, D20211, doi:10.1029/2004JD004924.
Dubovik, O., and M. D. King, 2000: A flexible inversion algorithm for retrieval of aerosol optical properties from sun and sky radiance measurements. J. Geophys. Res., 105, 20,673–20,696.
____, B. N. Holben, T. F. Eck, A. Smirnov, Y. J. Kaufman, M. D. King, D. Tanre, and I. Slutsker, 2002: Climatology of atmospheric aerosol absorption and optical properties in key locations. J. Atmos. Sci., 59, 590–608.
____, _____, T. F. Eck, A. Smirnov, Y. J. Kaufman, M. D. King, D. Tanre, and I. Slutsker, 2002a: Variability of absorption and optical properties of key aerosol types observed in worldwide locations. J. Atmos. Sci., 59, 590–608.
____, and Coauthors, 2006: Application of spheroid models to account for aerosol particle nonsphericity in remote sensing of desert dust. J. Geophys. Res., 111, D11208, doi:10.1029/2005JD006619.
Eck, T. F., and Coauthors, 2001: Characterization of the optical properties of biomass burning aerosols in Zambia during the 1997 ZIBBEE field campaign. J. Geophys. Res. 106,(D4), 3425–3448.
____, and Coauthors, 2010: Climatological aspects of the optical properties of fine/coarse mode aerosol mixtures. J. Geophys. Res., 115, D19205, doi:10.1029/2010JD014002.
García, O. E., and Coauthors, 2008: Validation of AERONET estimates of atmospheric solar fluxes and aerosol radiative forcing by ground-based broadband measurements. J. Geophys. Res., 113, D21207, doi:10.1029/2008JD010211.
Ge, J. M., J. Su, T. P. Ackerman, Q. Fu, J. P. Huang, and J. S. Shi, 2010: Dust aerosol optical properties retrieval and radiative forcing over northwestern China during the 2008 China-U.S. joint field experiment. J. Geophys. Res., 115, D00k12, doi:10.1029/2009JD013263.
Holben, B. N., and Coauthors, 1998: AERONET-A federated instrument network and data archive for aerosol characterization. Remote Sens. Environ., 66, 1–16.
____, and Coauthors, 2001: An emerging ground-based aerosol climatology: Aerosol Optical Depth from AERONET. J. Geophys. Res., 106, 12067–12097.
____, T. F. Eck, I. Slutsker, A. Smirnov, A. Sinyuk, J. Schafer, D. Giles, O. Dubovik, 2006: AERONET’s Version 2.0 quality assurance criteria. Remote Sensing of the Atmosphere and Clouds, Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng., 6408, 64080Q, doi:10.1117/12.706524.
Hoppel, W. A., J. W. Fitzgerald, and R. E. Larson, 1985: Aerosol size distributions in air masses advecting off the east coast of the United States. J. Geophys. Res., 90,(D1), 2365–2379.
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), 1995: Climate change 1994: Radiative forcing of climate. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1-231 pp.
____, 2001. Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom, New York, NY, USA, 881 pp.
Kaskaoutis D. G., and H. D. Kambezidis, 2006: Investigation on the wavelength dependence of the aerosol optical depth in the Athens area. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 132, 2217–2234.
Kaufman, Y. J., A. Gitelson, A. Karnieli, E. Ganor, R. S. Fraser, T. Nakajima, S. Matoo, and B. N. Holben, 1994: Size distribution and scattering phase function of aerosol particles retrieved from sky brightness measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett., 99, 10 341–10 356.
____, C. Tanre, L. A. Remer, E. F. Vermote, A. Chu, and B. N. Holben, 1997: Operational remote sensing of tropospheric aerosol over land from EOS moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer. J. Geophys. Res., 102, 17051–17067.
Koepke, P., M. Hess, I. Schult, and E. P. Shettle, 1997: Global aerosol data set. MPI Meteorologie Humburg Rep., 243, 44 pp.
King, M. D., Y. J. Kaufman, D. Tanre, and T. Nakijima, 1999: Remote sensing of tropospheric aerosols from space: Past, present, and future. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 80, 2229–2259.
Levin, Z., J. H. Joseph, and Y. Mekler, 1980: Properties of Sharav (Khamsin) dust-Comparison of optical and direct sampling data. J. Atmos. Sci., 37, 182–191.
Li, Z., K. H. O. Lee, Y. Wang, J. Xin, and W. M. Hao, 2010: First observation-based estimates of cloud-free aeroso radiative forcing across China. J. Geophys. Res., 115, D00K18, doi:10.1029/2009JD013306.
Liu, J., Y. Zheng, Z. Li, and R. Wu, 2008: Ground-based remote sensing of aerosol optical properties in one city in Northwest China. Atmos. Res., 89, 194–205.
Lohmann, U., and J. Feichter, 2005: Global indirect aerosol effects: a review. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 5, 715–737.
Miller, R. L., and I. Tegen, 1999: Radiative forcing of a tropical direct circulation by soil dust aerosols. J. Atmos. Sci., 56, 2403–2433.
Nakajima, T., G. Tonna, R. Rao, P. Boi, Y. Kaufman, and B. Holben, 1996: Use of sky brightness measurements from ground for remote sensing of particulate polydispersions. Appl. Opt., 35, 2672–2686.
Otterman, J., R. S. Fraser, and O. P. Bahethi, 1982: Characterization of tropospheric desert aerosols at solar wavelengths by multispectral radiometry from Landsat. J. Geophys. Res., 87, 1270–1278.
Prasad, A. K., and R. P. Singh, 2009: Validation of MODIS Terra, AIRS, NCEP/DOE AMIP-II Reanalysis-2, and AERONET Sun photometer derived integrated precipitable water vapor using ground-based GPS receivers over India. J. Geophys. Res., 114, D05107, doi:10.1029/2008JD011230.
Ramanathan, V., P. J. Crutzen, J. T. Kiehl, and D. Rosenfeld, 2001a: Aerosol, climate, and hydrological cycle. Science, 294, 2119–2124.
Rosenfeld, D., and I. M. Lensky, 1998: Satellite-based insights into precipitation formation processes in continental and maritime convective clouds. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 79, 2457–2476.
Satheesh, S. K., and K. K. Moorthy, 2005: Radiative effects of natural aerosols: A review. Atmos. Environ., 39, 2089–2110, doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2004.12.029.
Schmid B., and Coauthors, 2001: Comparison of columnar water-vapor measurements from solar transmittance methods. Appl. Opt., 40, doi: 10.1364/AO.40.001886.
Sharma, A. R., S. K. Kharol, K. V. S. Badarinath, and D. Singh, 2010: Impact of agriculture crop residue burning on atmospheric aerosol loading — a study over Punjab State, India. Ann. Geophys., 28, 367–379, doi:10.5194/angeo-28-367-2010.
Shettle, E. P., and R. W. Fenn, 1979: Models of aerosols lower troposphere and the effect of humidity variations on their optical properties. AFCxRL Tech. Rep. 79 0214. Air Force Cambridge Research Laboratory, Hanscom Air Force Base, MA, 100 pp.
Singh, S., K. Soni, T. Bano, R. S. Tanwar, S. Nath, and B. C. Arya, 2010: Clear-sky direct aerosol radiative forcing variations over mega-city Delhi. Ann. Geophys., 28, 1157–1166, doi:10.5194/angeo-28-1157-2010.
Singh, R. P., S. Dey, S. N. Tripathi, V. Tare, and B. N. Holben, 2004: Variability of aerosol parameters over Kanpur city, northern India. J. Geophys. Res., 109, D23206, doi:10.1029/2004JD004966.
Smirnov, A., B. N. Holben, T. F. Eck, O. Dubovik, and I. Slutsker, 2000: Cloud screening and quality control algorithms for the AERONET data base. Remote Sens. Environ., 73, 337–349.
____, _____, A. Lyapustin, I. Slutsker, and T. F. Eck, 2004: AERONET processing algorithms refinement, paper presented at AERONET Workshop, El Arenosillo, Spain, 10–14 May.
Sokolik, I. N., and O. B. Toon, 1999: Incorporation of mineralogical composition into models of the radiative properties of mineral aerosol from UV to IR wavelengths. J. Geophys. Res., 104, 9423–9444.
____, A. Andronove, and T. C. Johnson, 1993: Complex refractive index of atmospheric dust aerosols. Atmos. Environ, 27A, 2495–2502.
Soni, K., S. Singh, T. Bano, R. Tanwar, S. Nath, and B. Arya, 2010: Variations in single scattering albedo and Angstrom absorption exponent during different seasons at Delhi, India. Atmos. Environ., 44, 4355–4363.
Twomey, S., 1977: The influence of pollution on the shortwave albedo of clouds. J. Atmos. Sci., 34, 1149–1152.
Wang, S., L. Fang, X. Gu, T. Yu, and J. Gao, 2011: Comparison of aerosol optical properties from Beijing and Kanpur. Atmos. Environ., 39, 7406–7414.
WMO, 1983: Radiation commission of IAMAP meeting of experts on aerosols and their climatic effects, World Meteorological Organization Rep, WCP55, 28 pp.
Yu, X., B. Zhu, Y. Yin, S. Fan, and A. Chen, 2011: Seasonal variation of columnar aerosol optical properties in Yangtze River Delta in China. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 28, 1326–1335.
____, _____, and M. Zhang, 2009: Seasonal variability of aerosol optical properties over Beijing. Atmos. Environ., 43, 4095–4101.
____, T. Cheng, J. Chen, and Y. Liu, 2006: A comparison of dust properties between China continent and Korea, Japan in east Asia. Atmos. Environ, 40, 5787–5797.
Zege, E. P., A. P. Ivanov, and I. L. Katzev, 1991: Image transfer through a scattering medium, Springer, Berlin, New York, 349 pp.
Zhao, T. X. P., I. Laszlo, P. Minnis, and L. Remer, 2005: Comparison and analysis of two aerosol retrievals over the ocean in the Terra/Clouds and the Earth’s Radiant Energy System-Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer single scanner footprint data: 1. Global evaluation. J. Geophys. Res., 110, D21208, doi:10.1029/2005JD005851.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, M., Tariq, S., Mahmood, K. et al. A study of aerosol properties over Lahore (Pakistan) by using AERONET data. Asia-Pacific J Atmos Sci 50, 153–162 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-014-0004-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-014-0004-y