Abstract
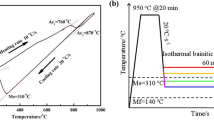
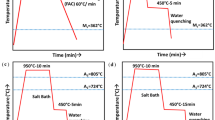
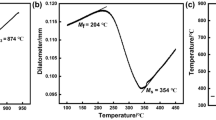
Changes in microstructure and mechanical properties of medium-carbon spring steel during austempering were investigated. After austempering for 1 h at 290 °C or 330 °C, the bainite transformation stabilized austenite, and microstructure consisting of bainitic ferrite and austenite could be obtained after final cooling; the retained austenite fraction was smaller in the alloy austempered at 290 °C because carbon redistribution between bainitic ferrite and austenite slowed as the temperature decreased, and thereby gave persistent driving force for the bainite transformation. The products of tensile strength and reduction of area in the austempered alloy were much larger in the austempered steel than in quenched and tempered alloy, mainly because of significant increase in reduction of area in austempered alloy.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.J. Matas, R.F. Hehemann, The structure of bainite in hypoeutectoid steels. Trans. Metall. Soc AIME 221(1), 179–185 (1961)
R.L. Houillier, G. Begin, A. Dube, Study of peculiarities of austenite during formation of bainite. Metall. Trans. 2(9), 2645–2653 (1971)
F.G. Caballero, H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, K.J.A. Mawella, D.G. Jones, P. Brown, Design of novel high strength bainitic steels: part 1. Mater. Sci. Technol. 17(5), 512–516 (2001)
F.G. Caballero, H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, K.J.A. Mawella, D.G. Jones, P. Brown, Design of novel high strength bainitic steels: part 2. Mater. Sci. Technol. 17(5), 517–522 (2001)
F. Perrad, C. Mendibide, N. Yoshihara, Y. Namimura and N. Ibaraki, High strength spring steels with improved ductility and corrosion resistance. International Conference on Steels in Cars and Trucks, pp. 106–113 (2008)
F. Perrad, F. Charvieux and J. Languillaume, A new spring steel with improved ductility dedicated for high strength parabolic leaf springs. 2nd International Conference Super-High Strength Steels, Peschiera del Garda (2010)
T. Fukuzumi, S. Komazaki, T. Misawa, Hydrogen embrittlement and corrosion fatigue caused by pitting corrosion of spring steels for automobile with improved pitting corrosion resistance by alloying elements and chemical passivation treatment. J. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 88(2), 81–87 (2002)
G.E. Hollox, R.A. Hobbs, J.M. Hampshire, Lower bainite bearings for adverse environments. Wear 68(2), 229–240 (1981)
F.C. Akbasoglu, D.V. Edmonds, Rolling contact fatigue and fatigue crack propagation in 1C-1.5 Cr bearing steel in the bainitic condition. Metall. Trans. A 21(3), 889–893 (1990)
N. Luzginova, L. Zhao, J. Sietsma, Evolution and thermal stability of retained austenite in SAE 52100 bainitic steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 448(1), 104–110 (2007)
J. Chakraborty, D. Bhattacharjee, I. Manna, Austempering of bearing steel for improved mechanical properties. Scr. Mater. 59(2), 247–250 (2008)
J. Chakraborty, D. Bhattacharjee, I. Manna, Development of ultrafine bainite + martensite duplex microstructure in SAE 52100 bearing steel by prior cold deformation. Scr. Mater. 61(6), 604–607 (2009)
W.F. Smith, Structure and Properties of Engineering Alloys (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1993), p. 75
J.L. Paez, F. Fuentes, A. Battegliese, Isothermal treatment of SAE92XX type high silicon steels. Rev. Metal. 32(1), 3–9 (1996)
J.A. Cruz Jr., T.F.M. Rodrigues, V.D.C. Viana, H. Abreu, D.B. Santos, Influence of temperature and time of austempering treatment on mechanical properties of SAE 9254 commercial steel. Steel Res. Int. 83(1), 22–31 (2012)
J.A. Cruz Jr., D.B. Santos, Effect of tempering temperature on isothermal decomposition product formed below Ms. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2(2), 93–99 (2013)
H.M. Rietveld, Line profiles of neutron powder-diffraction peaks for structure refinement. Acta Crystallogr. A 22(1), 151–152 (1967)
ASTM Standard E8/E8M (2004)
W.H. Bragg, W.L. Bragg, The reflection of X-rays by crystals. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Containing Papers of a Mathematical and Physical Character, vol. 88, 605, pp. 428–438 (1913)
S.H. Kim, D.H. Kim, K.C. Hwang, S.B. Lee, S.K. Lee, H.U. Hong, D.W. Suh, Heat treatment response of TiC-reinforced steel matrix composite. Met. Mater. Int. 22(5), 935–941 (2016)
N. Ridley, H. Stuart, L. Zwell, Lattice parameters of Fe-C austenites at room temperature. Trans. Met. Soc. AIME 245(8), 1834–1836 (1969)
C.S. Roberts, Effect of carbon on the volume fractions and lattice parameters of retained austenite and martensite. Trans. AIME 197(2), 203–204 (1953)
J.H. Jang, H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, D.W. Suh, Solubility of carbon in tetragonal ferrite in equilibrium with austenite. Scr. Mater. 68(3), 195–198 (2013)
B.C. De Cooman, K. Findley, Introduction to the Mechanical Behavior of Steel (AIST, Warrendale, 2016), pp. 209–215
C. Garcia-Mateo, F.G. Caballero, Ultra-high-strength bainitic steels. ISIJ 45(11), 1736–1740 (2005)
A. Fallahi, Microstructure-properties correlation of dual phase steels produced by controlled rolling process. Mater. Sci. Technol. 18(5), 451–454 (2002)
N. Fonstein, M. Kapustin, N. Pottore, I. Gupta, O. Yakubovsky, Factors that determine the level of the yield strength and the return of the yield-point elongation in low-alloy ferrite-martensite steels. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 104(3), 315–323 (2007)
G.E. Dieter, Mechanical Metallurgy (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1976), p. 343
N. Fonstein, Advanced High Strength Sheet Steels: Physical Metallurgy, Design, Processing, and Properties (Springer, Berlin, 2015), pp. 97–108
W. Sha, Steels: From Materials Science to Structural Engineering (Springer, Berlin, 2016), pp. 27–58
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, D.V. Edmonds, Bainite in silicon steels: new composition–property approach part 1. Met. Sci. 17(9), 411–419 (1983)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S.H., Kim, KH., Bae, CM. et al. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Austempered Medium-Carbon Spring Steel. Met. Mater. Int. 24, 693–701 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-018-0085-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-018-0085-8