Abstract
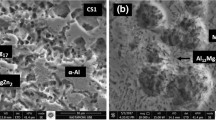
The effect of a minor change in alloy composition on the microstructure and corrosion properties of melt spun Mg98.3−xZnxY1.7 ribbons with x=9–12 is studied by X-ray diffractometry, differential scanning calorimetry, transmission electron microscopy and a dynamic polarization test. The ribbon specimens with x=9–10 revealed an in-situ composite microstructure consisting of icosahedral quasicrystalline phase (I-phase) particles distributed in an α-Mg matrix. The ribbon specimens with x=11 and 12 contained a minor MgZn2 phase together with an α-Mg phase and I-phase. With increasing Zn content, the corrosion potential increased because of a mixed potential effect, but the formation of a MgZn2 phase deteriorated the corrosion property through preferential attack, causing an irregular boundary between the corrosion product and the substrate. These results indicate that it is important to control alloy chemistry not to form the MgZn2 phase in developing an I-phase strengthened Mg-Zn-Y alloy for structural applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. J. Polmear. Mater Sci. Tech. 10, 1 (1994).
T. Homma, N. Kunito, and S. Kamado, Scripta Mater. 61, 644 (2009).
S.W. Xu, K. Oh-ishi, S. Kamado, F. Uchida, T. Homma, and K. Hono, Scripta Mater. 65, 269 (2011).
C. Janot, Quasicrystals, Clarendon Press, Oxford (1994).
F. S. Pierce, S. J. Poon, and Q. Guo, Science 261, 737 (1993).
Z. P. Luo, S. Q. Zhang, Y. L. Tang, and D. S. Zhao. Scripta Metall Mater. 28, 1513 (1993).
A.-P. Tsai, Y. Murakami, and A. Niikura, Phil. Mag. A 80, 1043 (2000).
S. Yi, E. S. Park, J. B. Ok, W. T. Kim, and D. H. Kim, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 300, 312 (2001).
E. S. Park, S. Yi, J. B. Ok, D. H. Bae, W. T. Kim Kim, and D. H. Kim, Proceedings MRS Fall Meeting, Boston, MA (2001).
D. H. Bae, S. H. Kim, D. H. Kim, and W. T. Kim, Acta Materialia 50, 2343 (2002).
D. H. Kim, J. Y. Lee, H. K. Lim, W. T. Kim, and D. H. Kim, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 487, 481 (2008).
J. Y. Lee, D. H. Kim, H. K. Lim, W. T. Kim, and D. H. Kim, Mater. Lett. 59, 3801 (2005).
Z. M. Zhang, C. J. Xu, and X. F. Guo, Acta Metall. Sin. 21, 30 (2008).
D. H. Kim, Y. K. Kim, W. T. Kim, and D. H. Kim, Korean J. Met. Mater. 49, 145 (2011).
H. Okouchi, Y. Seki, T. Sekigawa, H. HIRA, and Y. Kawamura, Mater. Sci. Forum 638–642, 1476 (2010).
G. Shao, V. Varsani, and Z. Fan. Calphad, 30, 28 (2006).
N. Birbilis and R. G. Buchheit, J. Electrochem. Soc. 152, B140 (2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nam, S.W., Kim, W.T., Kim, D.H. et al. Microstructure and corrosion behavior of rapidly solidified Mg-Zn-Y alloys. Met. Mater. Int. 19, 205–209 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-013-2010-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-013-2010-5