Abstract
Background
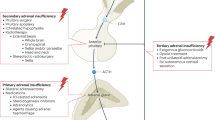
Adrenal insufficiency (AI) is a wellknown cause of potentially life-threatening disorders. Defects at each level of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis can impair adrenal function, leading to varying degrees of glucocorticoid (GC) deficiency. Iatrogenic AI induced by exogenous GCs is the most common cause of AI. The criteria for the diagnosis and management of iatrogenic AI, neonatal AI, and critical illness-related corticosteroid insufficiency (CIRCI) are not clear.
Data sources
We reviewed the recent original publications and classical data from the literature, as well as the clinical, diagnostic and management strategies of pediatric AI.
Results
Practical points in the diagnosis and management of AI with an emphasis on iatrogenic AI, neonatal AI, and CIRCI are provided. Given the lack of sensitive and practical biochemical tests for diagnosis of subtle AI, GC treatment has to be tailored to highly suggestive clinical symptoms and signs. Treatment of adrenal crisis is well standardized and patients almost invariably respond well to therapy. It is mainly the delay in treatment that is responsible for mortality in adrenal crisis.
Conclusions
Education of patients and health care professionals is mandatory for timely interventions for patients with adrenal crisis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arlt W, Allolio B. Adrenal insufficiency. Lancet 2003;361:1881–1893.
Bornstein SR. Predisposing factors for adrenal insufficiency. N Engl J Med 2009;360:2328–2339.
Neary N, Nieman L. Adrenal insufficiency: etiology, diagnosis and treatment. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 2010;17:217–223.
Stewart PM. The adrenal cortex. In: Kronenberg HM, Melmed, Polonsky KS, Larsen RP, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders;2008: 445–503.
Ibanez L, Dimartino-Nardi J, Potau N, Saenger P. Premature Adrenarche—Normal Variant or Forerunner of Adult Disease Endocrine Reviews 2000;21:671–696.
Cooper MS, Stewart P. M. Corticosteroid insufficiency in acutely ill patients. N Engl J Med 2003;348:727–734.
Brandon DD, Isabelle LM, Samuels MH, Kendall JW, Loriaux DL. Cortisol production rate measurement by stable isotope dilution using gas chromatography-negative ion chemical ionizationmass spectrometry. Steroids 1999;64:372–378.
Shulman DI, Palmert MR, Kemp SF, Lawson Wilkins Drug and Therapeutic Committee. Adrenal insufficiency: still a cause of morbidity and death in childhood. Pediatrics 2007;119:e484–e494.
Czock D, Keller F, Rasche FM, Haussler U. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of systemically administered glucocorticoids. Clin Pharmacokinet 2005;44:61–98.
Lamberts SW, Bruining HA, de Jong FH. Corticosteroid therapy in severe illness. N Engl J Med 1997;337:1285–1292.
Castro Md. Anti-inflammatory and anti-proliferative effects of glucocorticoids: concordance or discordance? Arq Bras Endocrinol Metab 2005;49:334–336. [In Portuguese]
Hillier SG. Diamonds are forever: the cortisone legacy. J Endocrinol 2007;195:1–6.
Ferraz-de-Souza, Achermann JC. Disorders of adrenal development Endocr Dev 2008;13:19–32.
Kempna P, Flück C. Adrenal gland development and defects. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008;2281:77–93.
Nerup J. Addison’s disease-clinical studies. A report of 108 cases. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1974;76:127–141.
Perry R, Kecha O, Paquette J, Huot C, Van Vliet G, Deal C. Primary adrenal insufficiency in children: twenty years experience at the Sainte-Justine Hospital, Montreal. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005;90:3243–3250.
Erichsen MM, Løvås K, Skinningsrud B, Wolff AB, Undlien DE, Svartberg J, et al. Clinical, immunological, and genetic features of autoimmune primary adrenal insufficiency: observations from a Norwegian registry. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2009;94:4882–4890.
Betterle C, Morlin L. Autoimmune Addison’s disease. Endocr Dev 2011;20:161–172.
Mitchel AL, Pearce SH. Autoimmune Addison disease: pathophysioology and genetic complexity. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2012;8:306–316.
Lalli E, Sassone-Corsi P. DAX-1 and the adrenal cortex. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes 1999;6:185–190.
Presotto F, Fornasini F, Betterle C, Federspil G, Rossato M. Acute adrenal failure as the heralding symptom of primary anti-phospholipid syndrome: report of a case and review of the literetaure. Eur J Endocrinol 2005;153:507–514.
Ramon I, Mathian A, Bachelot A, Hervier B, Haroche J, Boutin-Le Thi Huong D, et al. Primary adrenal insufficiency due to bilateral adrenal hemorrhage-adrenal infarction in the antiphospholipid syndrome: long-term outcome of 16 patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2013;98:3179–3189.
Huseybe E, Lovas K. Pathogenesis of primary adrenal insufficiency. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2009;23: 147–157.
Tsigos C, Arai K, Hung W, Crousos GP. Hereditary isolated glucocorticoid deficiency is associated with abnormalities of the adrenocorticotropin receptor gene. J Clin Invest 1993;92:2458–2461.
Clark A, Weber A. Molecular insights into inherited ACTH resistance syndromes. Trends Endocrinol Metab 1994;5:209–214.
Handschug K, Sperling S, Yoon SJ, Henning S, Clark AJ, Huebner A. Triple A syndrome is caused by mutations in AAAS, a new WD-repeat protein gene. Hum Mol Genet 2001;10:283–290.
Grant DB, Barnes ND, Dumic M, Ginalska-Malinowska M, Milla PJ, von Petrykowski W. Neurological and adrenal dysfunction in the adrenal insufficiency/alacrima (3A) syndrome. Arch Dis Child 1993;68:779–782.
Meimaridou E, Kowalczyk J, Guasti L, Hughes CR, Wagner F, Frommolt P, et al. Mutations in NNT encoding nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase cause familial glucocorticoid deficiency Nat Genet 2012;44:740–742.
Prasad R, Chan LF, Hughes CR, Kaski JP, Kowalczyk JC, Savage MO, et al. Thioredoxin Reductase 2 (TXNRD2) mutation associated with familial glucocorticoid deficiency (FGD). J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2014;99:E1556–1563.
Meimaridou E, Hughes CR, Kowalczyk J, Guasti L, Chapple JP, King PJ, et al. Familial glucocorticoid deficiency: New genes and mechanisms. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2013;371:195–200.
Vilain E, Le Merrer M, Lecointre C, Desangles F, Kay MA, Maroteaux P, et al. IMAGe, a new clinical association of intrauterine growth retardation, metaphyseal dysplasia, adrenal hypoplasia congenita, and genital anomalies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999;84:4335–4340.
Hamajima N, Johmura Y, Suzuki S, Nakanishi M, Saitoh S. Increased protein stability of CDKN1C causes a gain-of-function phenotype in patients with IMAGe syndrome. PLoS One 2013;8:e75137.
Orme LM, Bond JD, Humphrey MS, Zacharin MR, Downie PA, Jamsen KM, et al. Megestrol acetate in pediatric oncology patients may lead to severe, symptomatic adrenal suppression. Cancer 2003;98:397–405.
Pizarro CF, Troster EJ, Damiani D, Carcillo JA. Absolute and relative adrenal insufficiency in children with septic shock. Crit Care Med 2005;33:855–859.
Fleseriu M, Loriaux DL. "Relative" adrenal insufficiency in critical illness. Endocr Pract 2009;15:632–640.
Hsieh S, White PC. Presentation of primary adrenal insufficiency in childhood. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2011;96:E925–928.
Laureti S, Vecchi L, Santeusanio F, Falorni A. Is the prevalence of Addison’s disease underestimated? J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999;84:1762.
Yuksel B. Adrenal Insufficiency. The Journal of Current Pediatrics 2007;6:26–30.
Ten S, New M, Maclaren N. Clinical Review: Addison disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001;86:2909–2920.
Lovas K, Huseybe ES. Addison’s disease. Lancet 2005;365: 2058–2061.
Charmandari E, Nicolaides N, Chrousos GP. Adrenal insufficiency. The Lancet 2014;383:2152–2167.
Aron DC. Diagnostic implications of adrenal physiology and clinical epidemiology for evaluation of glucocorticoid excess and deficiency. In: DeGroot LJ, Jameson JL, eds. Endocrinology, 4th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders, 2001: 1655–1670.
Forest MG. Adrenal function tests. In: Ranke MB, eds. Diagnostics of Endocrine Function in Children and Adolescents, 3rd ed. Basel: Karger, 2003: 372–426.
Bethin KE, Muglia LJ. Adrenal insufficiency. In: Radovick S, MacGillivray MH, eds. Pediatric Endocrinology. Totowa: Humana Press, 2003: 203–247.
Kazlauskaite R, Evans AT, Villabona CV, Abdu TA, Ambrosi B, Atkinson AB, et al. Consortium for Evaluation of Corticotropin Test in Hypothalamic-Pituitary Adrenal Insufficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008;93:4245–4253.
Kazlauskaite R, Maghnie M. Pitfalls in the Diagnosis of Central Adrenal Insufficiency in Children. Endocr Dev 2010;17:96–107.
Fischli S, Jenni S, Allemann S, Zwahlen M, Diem P, Christ ER, et al. Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate in the assessment of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008;93:539–942.
Bethin KE, Muglia LJ. Adrenal insufficiency. In: Radovick S, MacGillivray MH, eds. Pediatric Endocrinology. Totowa: Human Press, 2003: 203–247.
Nieman LK, Oldfield EH, Wesley R, Chrousos GP, Loriaux DL, Cutler GBJ. A simplified morning ovine corticotropinreleasing hormone stimulation test for the differential diagnosis of adrenocorticotropin dependent Cushing’s syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1993;77:1308–1312.
Lytras N, Grossman A, Perry L, Tomlin S, Wass JA, Coy DH, et al. Corticotropin-releasing factor: Responses in normal subjects and patients with disorders of the hypothalamus and pituitary. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1984;20:71–84.
Miller WL, Flück CE. Adrenal cortex and its disorders. In: Mark Sperling, ed. Pediatric Endocrinology, 4th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders, 2014: 471–532.
Polgreen LE, Sarafoglou K, Petryk A. Adrenal Insufficiency. In: Kyriakie Sarafoglou, Georg Hoffmann, Karl Roth, eds. Pediatric Endocrinology and Inborn Errors of Metabolism, 1st ed. USA: McGraw-Hills, 2009: 419–437.
Mormede P, Foury A, Barat P, Corcuff JB, Terenina E, Marissal-Arvy N, et al. Molecular genetics of hypothalamicpituitary-adrenal axis activity and function. Ann N YAcad Sci. 2011;1220:127–136.
Derijk RH. Single nucleotide polymorphisms related to HPA axis reactivity. Neuroimmunomodulationn 2009;16:340–352.
Bhattacjharyya A, Kaushal K, Tymms DJ, Davis JR. Steroid withdrawal syndrome after successful treatment of Cushing’s syndrome: a reminder. Eur J Endocrinol 2005;153:207–210.
Margolin L, Cope DK, Bakst-Sisser R, Greenspan J. The steroid withdrawal syndrome. A review of the implications, etiology and treatments. J Pain Symptom Manage 2007;33:224–228.
Amatruda TT, Hollingsworth DR, D’Esopo ND, Upton GV, Bondy PK. A study of the mechanism of the steroid withdrawal syndrome. Evidence for integrity og the hypothalamic pituitary adrenal system. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1960;20:339–354.
Saracco P, Bertorello N, Faarinasso L, Einaudi S, Barisone E, Altare F, et al. Steroid withdrawal syndrome during steroid tapering in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a controlled study comparing prednisone versus dexamethasone in induction phase. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2005;27:141–144.
Stuart FA, Segal TY, Keady S. Adverse psychological effects of corticosteroids in children and adolescents. Arch Dis Child 2005;90:500–506.
Deshmukh CT. Minimizing side effects of systemic corticosteroids in children. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2007;73:218–221.
Alves C, Robazzi TCV, Mendonça M. Withdrawal from glucocorticosteroid therapy: clinical practice recommendations J Pediatr (Rio J) 2008;84:192–202.
Gordijn MS, Gemke RJ, van Dalen EC, Rotteveel J, Kaspers GJ. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression after treatment with glucocorticoid therapy for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;5:CD008727.
Zöllner EW, Lombard CJ, Galaf U, Hough SF, Irussen EM, Weinberg E. Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis Suppression in Asthmatic School Children. Pediatrics 2012;130:e1512–e1519.
Zöllner EW. Hypothalamic-pituitary axis suppression in asthmatic children on inhaled corticosteroids: part 1. Which test should be used? Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2007;18:401–409.
Krasner AS. Glucocorticoid-induced adrenal insufficiency. JAMA 1999;282:671–676.
Mieure KD, Smith KM, Winstead PS. Supplemental glucocorticoid therapy. Orthopedics 2007;30:116–119.
Kuperman H, Damiani D, Chrousos GP, Dichtchekenian V, Manna TD, Filho VO, et al. Evaluation of the hypothalamicpituitary-adrenal axis in children with leukemia before and after 6 weeks of high-dose glucocorticoid therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001;86:2993–2996.
Schlaghecke R, Kornely E, Santen RT, Ridderskamp P. The effect long-term glucocorticoid therapy on pituitary-adrenal responses to exogenous corticotrophin-releasing hormone. N Engl J Med 1992;326:226–230.
Karlsson R, Kallio J, Irjala K, Ekblad S, Toppari J, Kero P. Adrenocorticotropic and corticotrophin-releasing hormone tests in preterm infants. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85:4592–4595.
Fernandez EF, Watterberg KL. Relative adrenal insufficiency in the preterm and term infant. J Perinatol 2009;29:44–49.
Sari FN, Dizdar EA, Oguz SS, Andiran N, Erdeve O, Uras N, et al. Baseline and stimulated cortisol levels in preterm infants: is there any clinical relevance? Horm Res Paediatr 2012;77:12–18.
Hochwald O, Holsti L, Osiovich H. The use of an early ACTH test to identify hypoadrenalism-related hypotension in low birth weight infants. J Perinatol 2012;32:412–417.
Venkatesh B, Cohen J. The utility of the corticotropin test to diagnose adrenal insufficiency. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2015;83:289–297.
Hebbar KB, Petrillo T, Fortenberry JD. Adrenal insufficiency and response to corticosteroids in hypotensive critically ill children with cancer. J Crit Care 2012;27:480–487.
Menon K, Ward RE, Lawson ML, Gaboury I, Hutchison JS, Hebert PC. A prospective multicenter study of adrenal function in critically ill children. Am J Resir Crit Care Med 2010; 182:246–251.
Samransamruajkit R, Jitchaiwat S, Deerojanawong J, Sritippayawan S, Praphal N. Adrenal insufficiency in early phase of pediatric acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Crit Care 2007;22:314–318.
Annane D, Sébille V, Charpentier C, Bollaert PE, François B, Korach JM, et al. Effect of treatment with low doses of hydrocortisone and fludrocortisone on mortality in patients with septic shock. JAMA 2002;288:862–871.
Rady MY, Johnson DJ, Patel B, Larson J, Helmers R. Cortisol levels and corticosteroid administration fail to predict mortality in critical illness: the confounding effects of organ dysfunction and sex. Arch Surg 2005;140:661–668.
Levy-Schraga Y, Pinhas-Hamiel O. Critical Illness-Related Corticosteroid Insufficiency in Children Horm Res Paediatr 2013;80:309–317.
Hamrahian AH, Oseni TS, Arafah BM. Measurements of serum free cortisol in critically ill patients. N Engl J Med 2004 350:1629–1638.
Cohen J, Smith ML, Deans RV, Pretorius CJ, Ungerer JP, Tan T, et al. Serial changes in plasma total cortisol, plasma free cortisol, and tissue cortisol activity in patients with septic shock: an observational study. Shock 2012;37:28–33.
Widmer IE, Puder JJ, König C, Pargger H, Zerkowski HR, Girard J, et al. Cortisol response in relation to the severity of stress and illness. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005;90:4579–4586.
Christ-Crain M, Jutla S, Widmer I, Couppis O, König C, Pargger H, et al. Measurement of serum free cortisol shows discordant responsivity to stress and dynamic evaluation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007;92:1729–1735.
den Brinker M, Joosten KF, Liem O, de Jong FH, Hop WC, Hazelzet JA, et al. Adrenal insufficiency in meningococcal sepsis: bioavailable cortisol levels and impact of interleukin-6 levels and intubation with etomidate on adrenal function and mortality. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005;90:5110–5117.
Pretorius CJ, Galligan JP, McWhinney BC, Briscoe SE, Ungerer JP. Free cortisol method comparison: ultrafiltation, equilibrium dialysis, tracer dilution, tandem mass spectrometry and calculated free cortisol. Clin Chim Acta 2011;412:1043–1047.
Venkatesh B, Mortimer RH, Couchman B, Hall J. Evaluation of random plasma cortisol and the low dose corticotropin test as indicators of adrenal secretory capacity in critically ill patients: a prospective study. Anaesth Intensive Care 2005;33:201–209.
Balbão VM, Costa MM, Castro M, Carlotti AP. Evaluation of adrenal function in critically ill children. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2014;81:559–565.
Donohoue PA. Adrenal disorders. In: Kappy MS, Allen DB, Geffner ME, Eds. Pediatric Endocrinology. New York: McGraw Hill Medical, 2010: 132–190.
Hahner S, Hemmelmann N, Quinkler M, Beuschlein F, Spinnler C, Allolio B. Time lines in the management of adrenal crisistargets, limits and reality. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2015;82:497–502.
Speiser PW, Azziz R, Baskin LS, Ghizzoni L, Hensle TW, Merke DP, et al. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010; 95:4133–4160.
Bryan SM, Honour JW, Hindmarsh PC. Management of altered hydrocortisone pharmacokinetics in a boy with congenital adrenal hyperplasia using a continuous subcutaneous hydrocortisone infusion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2009;94:3477–3480.
Johannsson G, Bergthorsdottir R, Nilsson AG, Lennernas H, Hedner T, Skrtic S. Improving glucocorticoid replacement therapy using a novel modified-release hydrocortisone tablet: a pharmacokinetic study. Eur J Endocrinol 2009;161:119–130.
Newell-Price J, Whiteman M, Rostami-Hodjegan A, Darzy K, Shalet S, Tucker GT, et al. Modified-release hydrocortisone for circadian therapy: a proof-of-principle study in dexamethasonesuppressed normal volunteers. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2008;68:130–135.
Alkatib AA, Cosma M, Elamin MB, Erickson D, Swiglo BA, Erwin PJ, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials of DHEA treatment effects on quality of life in women with adrenal insufficiency J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2009;94:3676–3681.
Lang K, Burger-Stritt S, Hahner S. Is DHEA replacement beneficial in chronic adrenal failure? Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2015;29:25–32.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uçar, A., Baş, F. & Saka, N. Diagnosis and management of pediatric adrenal insufficiency. World J Pediatr 12, 261–274 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-016-0018-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-016-0018-x