Abstract
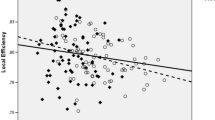
Several lines of evidence suggest that efficient information integration between brain regions is disrupted in schizophrenia. Abnormalities in white matter tracts that interconnect brain regions may be directly relevant to this pathophysiological process. As a complex mental disorder with high heritability, mapping abnormalities in patients and their first-degree relatives may help to disentangle the risk factors for schizophrenia. We established a weighted network model of white matter connections using diffusion tensor imaging in 25 nuclear families with schizophrenic probands (19 patients and 41 unaffected parents) and two unrelated groups of normal controls (24 controls matched with patients and 26 controls matched with relatives). The patient group showed lower global efficiency and local efficiency. The decreased regional efficiency was localized in hubs such as the bilateral frontal cortices, bilateral anterior cingulate cortices, and left precuneus. The global efficiency was negatively correlated with cognition scores derived from a 5-factor model of schizophrenic psychopathology. We also found that unaffected parents displayed decreased regional efficiency in the right temporal cortices, left supplementary motor area, left superior temporal pole, and left thalamus. The global efficiency tended to be lower in unaffected parents. Our data suggest that (1) the global efficiency loss in neuroanatomical networks may be associated with the cognitive disturbances in schizophrenia; and (2) genetic vulnerability to schizophrenia may influence the anatomical organization of an individual’s brain networks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bullmore E, Sporns O. Complex brain networks: graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems. Nat Rev Neurosci 2009, 10: 186–198.
Bassett DS, Bullmore ET. Human brain networks in health and disease. Curr Opin Neurol 2009, 22: 340–347.
Watts DJ, Strogatz SH. Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’ networks. Nature 1998, 393: 440–442.
Sporns O, Chialvo DR, Kaiser M, Hilgetag CC. Organization, development and function of complex brain networks. Trends Cogn Sci 2004, 8: 418–425.
Achard S, Bullmore E. Efficiency and cost of economical brain functional networks. PLoS Comput Biol 2007, 3: e17.
Liu Y, Liang M, Zhou Y, He Y, Hao Y, Song M, et al. Disrupted small-world networks in schizophrenia. Brain 2008, 131: 945–961.
Wang L, Metzak PD, Honer WG, Woodward TS. Impaired efficiency of functional networks underlying episodic memory-for-context in schizophrenia. J Neurosci 2010, 30: 13171–13179.
Bassett DS, Bullmore E, Verchinski BA, Mattay VS, Weinberger DR, Meyer-Lindenberg A. Hierarchical organization of human cortical networks in health and schizophrenia. J Neurosci 2008, 28: 9239–9248.
van den Heuvel MP, Mandl RC, Stam CJ, Kahn RS, Hulshoff Pol HE. Aberrant frontal and temporal complex network structure in schizophrenia: a graph theoretical analysis. J Neurosci 2010, 30: 15915–15926.
Zalesky A, Fornito A, Seal ML, Cocchi L, Westin CF, Bullmore ET, et al. Disrupted axonal fiber connectivity in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 2011, 69: 80–89.
Konrad A, Winterer G. Disturbed structural connectivity in schizophrenia primary factor in pathology or epiphenomenon? Schizophr Bull 2008, 34: 72–92.
Bullmore ET, Frangou S, Murray RM. The dysplastic net hypothesis: an integration of developmental and dysconnectivity theories of schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 1997, 28: 143–156.
Friston KJ, Frith CD. Schizophrenia: a disconnection syndrome? Clin Neurosci 1995, 3: 89–97.
Stephan KE, Baldeweg T, Friston KJ. Synaptic plasticity and dysconnection in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 2006, 59: 929–939.
Wang Q, Su TP, Zhou Y, Chou KH, Chen IY, Jiang T, et al. Anatomical insights into disrupted small-world networks in schizophrenia. Neuroimage 2012, 59: 1085–1093.
Viding E, Williamson DE, Hariri AR. Developmental imaging genetics: challenges and promises for translational research. Dev Psychopathol 2006, 18: 877–892.
Lawrie SM, McIntosh AM, Hall J, Owens DG, Johnstone EC. Brain structure and function changes during the development of schizophrenia: the evidence from studies of subjects at increased genetic risk. Schizophr Bull 2008, 34: 330–340.
Hoptman MJ, Nierenberg J, Bertisch HC, Catalano D, Ardekani BA, Branch CA, et al. A DTI study of white matter microstructure in individuals at high genetic risk for schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 2008, 106: 115–124.
Camchong J, Lim KO, Sponheim SR, Macdonald AW. Frontal white matter integrity as an endophenotype for schizophrenia: diffusion tensor imaging in monozygotic twins and patients’ nonpsychotic relatives. Front Hum Neurosci 2009, 3: 35.
Hao Y, Yan Q, Liu H, Xu L, Xue Z, Song X, et al. Schizophrenia patients and their healthy siblings share disruption of white matter integrity in the left prefrontal cortex and the hippocampus but not the anterior cingulate cortex. Schizophr Res 2009, 114: 128–135.
Knochel C, Oertel-Knochel V, Schonmeyer R, Rotarska-Jagiela A, van de Ven V, Prvulovic D, et al. Interhemispheric hypoconnectivity in schizophrenia: fiber integrity and volume differences of the corpus callosum in patients and unaffected relatives. Neuroimage 2012, 59: 926–934.
Knochel C, O’Dwyer L, Alves G, Reinke B, Magerkurth J, Rotarska-Jagiela A, et al. Association between white matter fiber integrity and subclinical psychotic symptoms in schizophrenia patients and unaffected relatives. Schizophr Res 2012, 140: 129–135.
Collin G, Kahn RS, de Reus MA, Cahn W, van den Heuvel MP. Impaired rich club connectivity in unaffected siblings of schizophrenia patients. Schizophr Bull 2014, 40: 438–448.
Latora V, Marchiori M. Efficient behavior of small-world networks. Phys Rev Lett 2001, 87: 198701.
Schmitt JE, Lenroot RK, Wallace GL, Ordaz S, Taylor KN, Kabani N, et al. Identification of genetically mediated cortical networks: a multivariate study of pediatric twins and siblings. Cereb Cortex 2008, 18: 1737–1747.
Smit DJ, Stam CJ, Posthuma D, Boomsma DI, de Geus EJ. Heritability of “small-world” networks in the brain: a graph theoretical analysis of resting-state EEG functional connectivity. Hum Brain Mapp 2008, 29: 1368–1378.
Oldfield RC. The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 1971, 9: 97–113.
World Health Organization. The ICD-10 classification of mental and behavioural disorders: diagnostic criteria for research. Geneva: World Health Organization, 1993.
Woods SW. Chlorpromazine equivalent doses for the newer atypical antipsychotics. J Clin Psychiatry 2003, 64: 663–667.
Bai YM, Ting Chen T, Chen JY, Chang WH, Wu B, Hung CH, et al. Equivalent switching dose from oral risperidone to risperidone long-acting injection: a 48-week randomized, prospective, single-blind pharmacokinetic study. J Clin Psychiatry 2007, 68: 1218–1225.
Lehman AF, Steinwachs DM. Translating research into practice: the Schizophrenia Patient Outcomes Research Team (PORT) treatment recommendations. Schizophr Bull 1998, 24: 1–10.
Kay SR, Fiszbein A, Opler LA. The positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 1987, 13: 261–276.
Lindenmayer JP, Bernstein-Hyman R, Grochowski S. A new five factor model of schizophrenia. Psychiatr Q 1994, 65: 299–322.
Li YH, Liu Y, Li J, Qin W, Li KC, Yu CS, et al. Brain anatomical network and intelligence. PLoS Comput Biol 2009, 5: e1000395
Tzourio-Mazoyer N, Landeau B, Papathanassiou D, Crivello F, Etard O, Delcroix N, et al. Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. Neuroimage 2002, 15: 273–289.
Gong GL, He Y, Concha L, Lebel C, Gross DW, Evans AC, et al. Mapping anatomical connectivity patterns of human cerebral cortex using in vivo diffusion tensor imaging tractography. Cereb Cortex 2009, 19: 524–536.
Mori S, Crain BJ, Chacko VP, van Zijl PC. Three-dimensional tracking of axonal projections in the brain by magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol 1999, 45: 265–269.
Thottakara P, Lazar M, Johnson SC, Alexander AL. Application of Brodmann’s area templates for ROI selection in white matter tractography studies. Neuroimage 2006, 29: 868–878.
Gong G, Rosa-Neto P, Carbonell F, Chen ZJ, He Y, Evans AC. Age- and gender-related differences in the cortical anatomical network. J Neurosci 2009, 29: 15684–15693.
Yu Q, Sui J, Rachakonda S, He H, Pearlson G, Calhoun VD. Altered small-world brain networks in temporal lobe in patients with schizophrenia performing an auditory oddball task. Front Syst Neurosci 2011, 5: 7.
Li X, Xia S, Bertisch HC, Branch CA, Delisi LE. Unique topology of language processing brain network: A systemslevel biomarker of schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 2012, 141: 128–136.
Hagmann P, Cammoun L, Gigandet X, Meuli R, Honey CJ, Wedeen V, et al. Mapping the structural core of human cerebral cortex. PLoS Biol 2008, 6: 1479–1493.
Crossley NA, Mechelli A, Scott J, Carletti F, Fox PT, McGuire P, et al. The hubs of the human connectome are generally implicated in the anatomy of brain disorders. Brain 2014, 137: 2382–2395.
Lynall ME, Bassett DS, Kerwin R, McKenna PJ, Kitzbichler M, Muller U, et al. Functional connectivity and brain networks in schizophrenia. J Neurosci 2010, 30: 9477–9487.
Supekar K, Menon V, Rubin D, Musen M, Greicius MD. Network analysis of intrinsic functional brain connectivity in Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS Comput Biol 2008, 4: e1000100.
Kalkstein S, Hurford I, Gur RC. Neurocognition in schizophrenia. Curr Top Behav Neurosci 2010, 4: 373–390.
Sheppard JP, Wang JP, Wong PC. Large-scale cortical network properties predict future sound-to-word learning success. J Cogn Neurosci 2012, 24: 1087–1103.
Bassett DS, Bullmore ET, Meyer-Lindenberg A, Apud JA, Weinberger DR, Coppola R. Cognitive fitness of cost-efficient brain functional networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009, 106: 11747–11752.
Velligan DI, Mahurin RK, Diamond PL, Hazleton BC, Eckert SL, Miller AL. The functional significance of symptomatology and cognitive function in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 1997, 25: 21–31.
Munoz Maniega S, Lymer GK, Bastin ME, Marjoram D, Job DE, Moorhead TW, et al. A diffusion tensor MRI study of white matter integrity in subjects at high genetic risk of schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 2008, 106: 132–139.
Peters BD, de Haan L, Dekker N, Blaas J, Becker HE, Dingemans PM, et al. White matter fibertracking in firstepisode schizophrenia, schizoaffective patients and subjects at ultra-high risk of psychosis. Neuropsychobiology 2008, 58: 19–28.
Job DE, Whalley HC, Johnstone EC, Lawrie SM. Grey matter changes over time in high risk subjects developing schizophrenia. Neuroimage 2005, 25: 1023–1030.
Harms MP, Wang L, Mamah D, Barch DM, Thompson PA, Csernansky JG. Thalamic shape abnormalities in individuals with schizophrenia and their nonpsychotic siblings. J Neurosci 2007, 27: 13835–13842.
Glahn DC, Winkler AM, Kochunov P, Almasy L, Duggirala R, Carless MA, et al. Genetic control over the resting brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010, 107: 1223–1228.
Fornito A, Zalesky A, Bassett DS, Meunier D, Ellison-Wright I, Yucel M, et al. Genetic influences on cost-efficient organization of human cortical functional networks. J Neurosci 2011, 31: 3261–3270.
Seidman LJ, Faraone SV, Goldstein JM, Goodman JM, Kremen WS, Toomey R, et al. Thalamic and amygdalahippocampal volume reductions in first-degree relatives of patients with schizophrenia: an MRI-based morphometric analysis. Biol Psychiatry 1999, 46: 941–954.
Mandl RC, Rais M, van Baal GC, van Haren NE, Cahn W, Kahn RS, et al. Altered white matter connectivity in nevermedicated patients with schizophrenia. Hum Brain Mapp 2013, 34: 2353–2365.
Steel RM, Whalley HC, Miller P, Best JJ, Johnstone EC, Lawrie SM. Structural MRI of the brain in presumed carriers of genes for schizophrenia, their affected and unaffected siblings. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2002, 72: 455–458.
McDonald C, Grech A, Toulopoulou T, Schulze K, Chapple B, Sham P, et al. Brain volumes in familial and non-familial schizophrenic probands and their unaffected relatives. Am J Med Genet 2002, 114: 616–625.
Bohlken MM, Mandl RC, Brouwer RM, van den Heuvel MP, Hedman AM, Kahn RS, et al. Heritability of structural brain network topology: a DTI study of 156 twins. Hum Brain Mapp 2014, 35: 5295–5305.
Li Y, Liu Y, Li J, Qin W, Li K, Yu C, et al. Brain anatomical network and intelligence. PLoS Comput Biol 2009, 5: e1000395.
Hasan KM, Walimuni IS, Abid H, Hahn KR. A review of diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging computational methods and software tools. Comput Biol Med 2011, 41: 1062–1072.
Mukherjee P, Chung SW, Berman JI, Hess CP, Henry RG. Diffusion tensor MR imaging and fiber tractography: technical considerations. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2008, 29: 843–852.
Oouchi H, Yamada K, Sakai K, Kizu O, Kubota T, Ito H, et al. Diffusion anisotropy measurement of brain white matter is affected by voxel size: underestimation occurs in areas with crossing fibers. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2007, 28: 1102–1106.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, H., Tian, L., Wang, Q. et al. Compromised small-world efficiency of structural brain networks in schizophrenic patients and their unaffected parents. Neurosci. Bull. 31, 275–287 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-014-1518-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-014-1518-0