Abstract
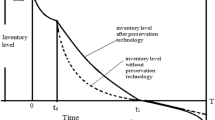
This paper deals with a stochastic deteriorating item inventory model with preservation technology and trade-credit finance. The planning horizon of many seasonal or fashionable items stochastically varies to some extent. On the other side, the demand of such items increases in initial phase followed by a constant. This type of demand pattern can be modeled as ramp-type demand. Deterioration of such products is a characteristic, which can be reduced by making the investment on latest equipment and technology. Consumption of such items within shelf life prevents to deterioration, which can be achieved by bulk sale. In order to stimulate the selling, trade-credit policy is also considered here. In these regards, this study examines the joint effect of preservation technology investment and trade-credit policy, wherein shortage is allowed and mixture of partial backlog and lost sales. Six cases may arise depending upon three parameters of time \(\mu \) (demand increases up to \(\mu \)), T (when on-hand inventory reaches to zero) and M (trade-credit period). The mathematical models are mainly categorized in two cases: (i) \(~\mu \le M\) and (ii) \(~\mu > M\). The model is illustrated through numerical experiments, sensitivity analysis, and graphical representation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hill R M 1995 Inventory models for increasing demand followed by level demand. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 46(10): 1250–1259
De A, Mamanduru V K R, Gunasekaran A, Subramanian N, and Tiwari M K 2016 Composite particle algorithm for sustainable integrated dynamic ship routing and scheduling optimization. Comput. Ind. Eng. 96: 201–215
De A, Kumar S K, Gunasekaran A and Tiwari M K 2017 Sustainable maritime inventory routing problem with time window constraints. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 61: 77–95
Giri B C, Jalan A K and Chaudhuri K S 2003 Economic order quantity model with Weibull deterioration distribution, shortage and ramp-type demand. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 34(4): 237–243
Manna S and Chaudhuri K S 2006 An EOQ model with ramp-type demand rate, time dependent deterioration rate, unit production cost and shortages. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 171(2): 577–566
Deng P S, Lin Robert H J and Chu P 2007 A note on the inventory models for deteriorating items with ramp-type demand rate . Eur. J. Oper. Res. 178(1): 112–120
Panda S, Senapati S and Basu M 2008 Optimal replenishment policy for perishable seasonal products in a season with ramp-type time dependent demand. Comput. Ind. Eng. 54(2): 301–314
Skouri K, Konstantaras I, Papachristos S and Teng J-T 2011 Supply chain models for deteriorating products with ramp-type demand rate under permissible delay in payments. Expert Syst. Appl. 38(12): 14861–14869
Kumar R S, De S K and Goswami A 2012 Fuzzy EOQ models with ramp-type demand rate, partial backlogging and time dependent deterioration rate. Int. J. Math. Oper. Res. 4(5): 473–502
Kumar R S, Tiwari M K and Goswami A 2016 Two-echelon fuzzy stochastic supply chain for the manufacturerbuyer integrated productioninventory system. J. Intell. Manuf. 27(4): 875–888
Kumar S and Singh A K 2016 Optimal time policy for deteriorating items of two-warehouse inventory system with time and stock dependent demand and partial backlogging. Sadhana 41(5): 541–548
Kumar S, Singh A K and Patel M K 2016 Optimization of Weibull deteriorating items inventory model under the effect of price and time dependent demand with partial backlogging. Sadhana 41(9): 977–984
Wu J, Skouri K, Teng J-T and Hu Y 2016 Two inventory systems with trapezoidal-type demand rate and time-dependent deterioration and backlogging. Expert Syst. Appl. 46: 367–379
Dye C-Y and Hsieh T-P 2012 An optimal replenishment policy for deteriorating items with effective investment in preservation technology. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 218(1): 106–112
Ho J C, Solis A O and Chang Y-L 2007 An evaluation of lot-sizing heuristics for deteriorating inventory in material requirements planning systems. Comput. Oper. Res. 34(9): 2562–2575
Ouyang L-Y, Wu K-S and Yang C-T 2006 A study on an inventory model for non-instantaneous deteriorating items with permissible delay in payments. Comput. Ind. Eng. 51(4): 637–651
Hsu P H, Wee H M and Teng H M 2010 Preservation technology investment for deteriorating inventory. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 124(2): 388–394
Zauberman G, Ronen R, Akerman M and Fuchs Y 1989 Low pH treatment protects litchi fruit color. Symp. Trop. Fruit Int. Trade 269: 309–314
Tsao Y-C and Sheen G-J 2008 Dynamic pricing, promotion and replenishment policies for a deteriorating item under permissible delay in payments. Comput. Oper. Res. 35(11): 3562–3580
Geetha K V and Uthayakumar R 2010 Economic design of an inventory policy for non-instantaneous deteriorating items under permissible delay in payments. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 233(10): 2492–2505
Lee Y-P and Day C-Y 2012 An inventory model for deteriorating items under stock-dependent demand and controllable deterioration rate. Comput. Ind. Eng. 63(2): 474–482
Hsieh T-P and Dye C-Y 2013 A production-inventory model incorporating the effect of preservation technology investment when demand is fluctuating with time. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 239: 25–36
Dye C-Y 2013 The effect of preservation technology investment on a non-instantaneous deteriorating inventory model. Omega 41(5): 872–880
Mishra U, Cárdenas-Barrón L E, Tiwari S, Shaikh A A and Treviño-Garza G 2017 An inventory model under price and stock dependent demand for controllable deterioration rate with shortages and preservation technology investment. Ann. Oper. Res. 254(1–2): 165–190
Zhang J, Liu G, Zhang Q and Bai Z 2015 Coordinating a supply chain for deteriorating items with a revenue sharing and cooperative investment contract. Omega 56: 37–49
Liu G, Zhang J and Tang W 2015 Joint dynamic pricing and investment strategy for perishable foods with price-quality dependent demand. Ann. Oper. Res. 226(1): 397–416
Zhang J, Wei Q, Zhang Q and Tang W 2016 Pricing, service and preservation technology investments policy for deteriorating items under common resource constraints. Comput. Ind. Eng. 95: 1–9
Goyal S K 1985 Economic order quantity under conditions of permissible delay in payments. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 36(4): 335–338
Aggarwal P S and Jaggi K C 1995 Ordering policies of deteriorating items under permissible delay in payments. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 46(5): 658–662
Chang C-T, Ouyang L-Y and Teng J-T 2003 An EOQ model for deteriorating items under supplier credits linked to ordering quantity. Appl. Math. Model. 27(12): 983–996
Ouyang L-Y, Teng J-T, Goyal S K and Yang C-T 2009 An economic order quantity model for deteriorating items with partially permissible delay in payments linked to order quantity. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 194(2): 418–431
Dye C-Y and Hsieh T-P 2013 A particle swarm optimization for solving lot-sizing problem with fluctuating demand and preservation technology cost under trade-credit. J. Glob. Optim. 55(3): 655–679
Yang C-T, Dye C-Y and Ding J-F 2015 Optimal dynamic trade-credit and preservation technology allocation for a deteriorating inventory model. Comput. Ind. Eng. 87: 356–369
Chen S-C and Teng J-T 2015 Inventory and credit decisions for time-varying deteriorating items with up-stream and down-stream trade-credit financing by discounted cash flow analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 243(2): 566–575
Tiwari S, Cárdenas-Barrón L E, Khanna A and Jaggi C K 2016 Impact of trade-credit and inflation on retailer’s ordering policies for non-instantaneous deteriorating items in a two-warehouse environment. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 176: 154–169
Tsao Y-C 2016 Joint location, inventory, and preservation decisions for non-instantaneous deterioration items under delay in payments. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 47(3): 572–585
Acknowledgements
We express our gratefulness to the editor and the learned reviewers for their important and valuable remarks and proposals, which has led to a significant ameliorate in an earlier version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohanty, D.J., Kumar, R.S. & Goswami, A. Trade-credit modeling for deteriorating item inventory system with preservation technology under random planning horizon. Sādhanā 43, 45 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-018-0807-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-018-0807-0