Abstract
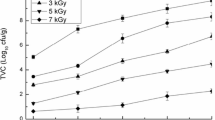
The effect of electron beam irradiation and high-pressure treatment on the characteristics of cold-smoked salmon during refrigerated storage at 5 °C was investigated. Irradiation at 1–4 kGy and high-pressure treatments at 450 MPa for 5–25 min reduced total viable counts and delayed microbial growth. Irradiation induced a slight decrease in redness (a*), whereas high-pressure treatment resulted in a brighter (L*) appearance of smoked salmon. Higher values of hardness and shear strength were recorded for pressurized samples. Total biogenic amine concentration in smoked salmon held for 20 days at 5 °C was lowered by 81 % in samples irradiated at 2 kGy, and by 46 % in samples pressurized at 450 MPa for 25 min. Smoked salmon irradiated at 1 or 2 kGy had negligible sensory (appearance, odour and flavour) alterations, but lower sensory preferences in the rank order test were observed for 3 and 4 kGy samples. Pressurization for 5 min at 450 MPa induced moderate sensory changes, which were more marked after 15 or 25 min at 450 MPa. These results point to the usefulness of E-beam radiation at 1.5 kGy to assure a safe product of sensory characteristics similar to those of untreated smoked salmon.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angsupanich, K., & Ledward, D. A. (1998). High pressure treatment effects on cod (Gadus morhua) muscle. Food Chemistry, 63(1), 39–50.
Ashie, I. N. A., & Simpson, B. K. (1996). Application of high hydrostatic pressure to control enzyme related fresh seafood texture deterioration. Food Research International, 29(5–6), 569–575.
Bover-Cid, S., & Holzapfel, W. H. (1999). Improved screening procedure for biogenic amine production by lactic acid bacteria. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 53(1), 33–41.
Cabeza, M. C., Cambero, I., de la Hoz, L., & Ordóñez, J. A. (2007). Optimization of E-beam irradiation treatment to eliminate Listeria monocytogenes from ready-to-eat (RTE) cooked ham. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 8(2), 299–305.
Cabeza, M. C., de la Hoz, L., Velasco, R., Cambero, M. I., & Ordóñez, J. A. (2009). Safety and quality of ready-to-eat dry fermented sausages subjected to E-beam irradiation. Meat Science, 83(2), 320–327.
Christensen, Z. T., Ogden, L. V., Dunn, M. L., & Eggett, D. L. (2006). Multiple comparison procedures for analysis of ranked data. Journal of Food Science, 71(2), 132–143.
Eliassen, K. A., Reistad, R., Risøen, U., & Rønning, H. F. (2002). Dietary polyamines. Food Chemistry, 78(3), 273–280.
Erkan, N., Üretener, G., Alpas, H., Selçuk, A., Özden, O., & Buzrul, S. (2011). The effect of different high pressure conditions on the quality and shelf life of cold-smoked fish. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 12(2), 104–110.
Gómez-Estaca, J., Gómez-Guillén, M., & Montero, P. (2007). High pressure on the quality and preservation of cold-smoked dolphinfish (Coryphaena hippurus) fillets. Food Chemistry, 102(4), 1250–1259.
Gómez-Estaca, J., Montero, P., Giménez, B., & Gómez-Guillén, M. C. (2007). Effect of functional edible films and high pressure processing on microbial and oxidative spoilage in cold-smoked sardine (Sardina pilchardus). Food Chemistry, 105(2), 511–520.
Halász, A., Baráth, A., Simon-Sarkadi, L., & Holzapfel, W. (1994). Biogenic amines and their production by microorganisms in food. Trends in Food Science and Technology, 5(2), 42–49.
Herrero, A. M., Ordoñez, J. A., Carmona, P., de la Hoz, L., & Cambero, M. I. (2009). Raman spectroscopy studies of electron-beam irradiated cold-smoked salmon. Food Research International, 42(1), 216–220.
Hurtado, J. L., Montero, P., Borderías, J., & Solas, M. T. (2001). High-pressure/temperature treatment effect on the characteristics of octopus (Octopus vulgaris) arm muscle. European Food Research and Technology, 213(1), 22–29.
ICMSF (International Commission on Microbiological Specifications for Foods). (1986). Microorganisms in foods 2. Sampling for microbiological analysis: principles and scientific applications (pp. 181–196). Toronto: University of Toronto Press.
ISO (International Organization for Standarization) (2004) ISO 4120: Sensory analysis–methodology–triangle test. Genéve, Switzerland.
Joanes, D. N. (1985). On a rank sum test due to Kramer. Journal of Food Science, 50(5), 1442–1444.
Jørgensen, L. V., Dalgaard, P., & Huss, H. H. (2000). Multiple compound quality index for cold-smoked salmon (Salmo salar) developed by multivariate regression of biogenic amines and pH. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 48(6), 2448–2453.
Krause, I., Bockhardt, A., Neckermann, H., Henle, T., & Klostermeyer, H. (1995). Simultaneous determination of amino acids and biogenic amines by reversed phase high-performance liquid chromatography of the dabsyl derivates. Journal of Chromatography, 715(1), 67–79.
Lakshmanan, R., & Dalgaard, P. (2004). Effects of high-pressure processing on Listeria monocytogenes, spoilage microflora and multiple compound quality indices in chilled cold-smoked salmon. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 96(2), 398–408.
Lakshmanan, R., Miskin, D., & Piggott, J. R. (2005). Quality of vacuum packed cold-smoked salmon during refrigerated storage as affected by high-pressure processing. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 85(4), 655–661.
Lakshmanan, R., Patterson, M. F., & Piggott, J. R. (2005). Effects of high-pressure processing on proteolytic enzymes and proteins in cold-smoked salmon during refrigerated storage. Food Chemistry, 90(4), 541–548.
Marcos, B., Kerry, J. P., & Mullen, A. M. (2010). High pressure induced changes on sarcoplasmic protein fraction and quality indicators. Meat Science, 85(1), 115–120.
Matser, A. M., Stegeman, D., Kals, J., & Bartels, P. V. (2000). Effects of high pressure on colour and texture of fish. High Pressure Research, 19(1–6), 499–505.
Mbarki, R., Sadok, S., & Barkallah, I. (2008). Influence of gamma irradiation on microbiological, biochemical, and textural properties of bonito (Sarda sarda) during chilled storage. Food Science and Technology International, 14(4), 367–373.
Mckenna, D. R., Nanke, K. E., & Olson, D. G. (2003). The effects of irradiation, high hydrostatic pressure, and temperature during pressurization on the characteristics of cooked-reheated salmon and catfish fillets. Journal of Food Science, 68(1), 368–377.
Medina, M., Cabeza, M. C., Bravo, D., Cambero, I., Montiel, R., Ordóñez, J. A., Núñez, M., & Hoz, L. (2009). A comparison between E-beam irradiation and high pressure treatment for cold-smoked salmon sanitation: microbiological aspects. Food Microbiology, 26(2), 224–227.
Mendes, R., Silva, H. A., Nunes, M. L., & Abecassis Empis, J. M. (2005). Effect of low-doses irradiation and refrigeration on the microflora, sensory characteristics and biogenic amines of Atlantic horse mackerel (Trachurus trachurus). European Food Research and Tecnology, 221(3–4), 329–335.
Moini, S., Tahergorabi, R., Hosseini, S. V., Rabbani, M., Tahergorabi, Z., Feás, X., & Aflaki, F. (2009). Effect of gamma radiation on the quality and shelf-life of refrigerated rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fillets. Journal of Food Protection, 72(7), 1419–1426.
Nanke, K. E., Sebranek, J. G., & Olson, D. G. (1998). Color characteristics of irradiated vacuum-packaged pork, beef and turkey. Journal of Foood Science, 63(6), 1001–1006.
Pedrero, D. L., & Pangborn, R. M. (1989). Evaluación sensorial de alimentos: métodos analíticos. México: Alhambra Mexicana.
Ritz, M., Jugiau, F., Federighi, M., Chapleau, N., & de Lamballerie, M. (2008). Effects of high pressure, subzero temperature, and pH on survival of Listeria monocytogenes in buffer and smoked salmon. Journal of Food Protection, 71(8), 1612–1618.
Romero, R., Gázquez, D., Bagur, M. G., & Sánchez-Viñas, M. (2000). Optimization of chromatographic parameters for the determination of biogenic amines in wines by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Journal of Chromatography. A, 871(1), 75–83.
Schanda, J. (2007). Understanding the CIE system (pp. 25–78). New York: Wiley.
Sequeira-Muñoz, A., Chevalier, D., LeBail, A., Ramaswamy, H. S., & Simpson, B. K. (2006). Physicochemical changes induced in carp (Cyprinus carpio) fillets by high pressure processing at low temperature. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 7(1–2), 13–18.
Spinelli, J., Eklund, M., Stoll, N., & Miyauchi, D. (1965). Irradiation preservation of Pacific coast fish and shellfish. III. Storage life of petrale sole fillets at 33º and 42 ºF. Food Technology, 19(6), 126–130.
Stratton, J. E., Hutkins, R. W., & Taylor, S. L. (1991). Biogenic amines in cheese and other fermented foods—a review. Journal of Food Protection, 54(6), 460–470.
Su, Y. C., Duan, J. Y., & Morrissey, M. T. (2004). Electron beam irradiation for reducing Listeria monocytogenes contamination on cold-smoked salmon. Journal of Aquatic Food Product Technology, 13(1), 3–11.
Venugopal, V., Doke, S. N., & Thomas, P. (1999). Radiation processing to improve the quality of fishery products. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 39(5), 391–440.
Yagiz, Y., Kristinsson, H. G., Balaban, M. O., Welt, B. A., Raghavan, S., & Marshall, M. R. (2010). Correlation between astaxanthin amount and a* value in fresh Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) muscle during different irradiation doses. Food Chemistry, 120(1), 121–127.
Acknowledgements
This work has received financial support from projects CSD2007-00016 and AGL2007-65235-C02 (Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation) and S-0505/AGR-0314 (Comunidad de Madrid). We thank Beatriz Noval (Ionmed S.A.), Buenaventura Rodríguez and Máximo de Paz for their valuable help in treatments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Montiel, R., Cabeza, M.C., Bravo, D. et al. A Comparison Between E-Beam Irradiation and High-Pressure Treatment for Cold-Smoked Salmon Sanitation: Shelf-Life, Colour, Texture and Sensory Characteristics. Food Bioprocess Technol 6, 3177–3185 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-012-0954-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-012-0954-y