Abstract
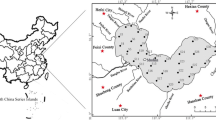
Surface sediment samples were collected at 21 offshore sites in western Xiamen Bay, Southeast China. Total concentrations of Li, V, Cr, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Sr, Mn, Pb, Ba, Fe, and Ti were determined by inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry; Hg was determined by atomic fluorescence spectrometry. A modified BCR sequential extraction procedure was used to extract fractions of the above elements. Concentrations of Pb, Cr, and Hg at most sites met the primary standard criteria of Marine Sediment Quality except site S12 for Pb and S7 for Cr, while concentrations of Zn at 17 sites and Cu at seven sites exceeded the criteria. The mean concentration of Hg was three times higher than the background, with a possible source being the Jiulong River. Fe, Ti, Ba, Co, V, and Li dominated the residual phase, mainly from terrestrial input. Ni, Cr, Pb, and Hg in the non-residual phase varied largely between sites. Sr, Mn, Cu, and Zn were mainly in the non-residual fraction. Most sites showed considerable ecological risk; exceptions were site S7 (very high) and sites S10, S11, and S14 (moderate). Cu showed moderate-to-high pollution and Pb exhibited no-to-low pollution, while other metals had a non-pollution status according to their ratios of secondary phase to primary phase (RSP). Results of two assessment methods showed moderate pollution and a very high ecological risk for Cu, Zn, Ni, and Cr at site S7, which might be due to the local sewage treatment plant.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apeti DA, Hartwell IS (2015) Baseline assessment of heavy metal concentrations in surficial sediment from Kachemak Bay, Alaska. Environ Monit Assess 187:4106
Bindler R, Yu RL, Hansson S, Claßen N, Karlsson J (2012) Mining, metallurgy and the historical origin of mercury pollution in lakes and watercourses in Central Sweden. Environ Sci Technol 46:7984–7991
Chen JS, Dong L, Deng BS, Wan LB, Wang M, Xiong ZL (1987a) Modeling study on copper partitioning in sediments, a case study of Poyang Lake. Acta Sci Circumst 7:140–149
Chen S, Xu AY, Luo BK (1987b) Distribution and sources of hevay metals in sediments from the Xiamen Harbour. J Oceanogr Taiwan Strait 6:139–145
China State Bureau of Technical Supervision (2002) GB18668-2002 marine sediment quality. Standards Press of China, Beijing
Davutluoglu OI, Seckın G, Kalat DG, Yılmaz T, Ersu CB (2010) Speciation and implications of heavy metal content in surface sediments of Akyatan Lagoon-Turkey. Desalination 260:199–210
Fernandes HM (1997) Heavy metal distribution in sediments and ecological risk assessment: the role of diagenetic processes in reducing metal toxicity in bottom sediments. Environ Pollut 97:317–325
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China (AQSIQ) (2002) The People’s Republic of China National Standards GB 18668-2002 Marine Sediment Quality. 10 pp (in Chinese)
Guo TZ, DeLaune RD, Patrck WH Jr (1997) The influence of sediment redox chemistry on chemically active forms of arsenic, cadmium, chromium, and zinc in estuarine sediment. Environ Int 23:305–316
Guo FX, Lv SH, Teng DQ, Jiang T, Jiao ZP (2011) Distribution patterns and evaluation on potential ecological risk of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Yellow Sea. J Anhui Agric Sci 39(9212–9216):9313
Håkanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control of sediment ecological approach. Water Res 14:975–1000
He C, Gao LM, Liu YL, Ning GX, Zhang CL, Wen H, Guan Y, Niu SP (2010) Total amount of heavy metals in sediments and speciation analysis in Huainan Nihe River. Environ Chem 29:766–767
Hu GR, Yu RL, Chen LP, Zhang JQ, Tu XL (2011) Evaluation of pollution of heavy metals in Luoyangjiang inter-tidal sediments, Quanzhou Bay. J Mineral Petrol 31:109–115
Kumar RN, Solanki R, Kumar JI (2013) Seasonal variation in heavy metal contamination in water and sediments of river Sabarmati and Kharicut canal at Ahmedabad, Gujarat. Environ Monit Assess 185:359–368
Lin C, He M, Liu X, Guo W, Liu S (2013) Contamination and ecological risk assessment of toxic trace elements in the Xi River, an urban river of Shenyang city, China. Environ Monit Assess 185:4321–4332
Lin C, Liu Y, Li WQ, Sun XW, Ji WD (2014) Speciation, distribution, and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in Xiamen Bay surface sediment. Acta Oceanol Sin 33:13–21
Ma ZW, Chen K, Yuan ZW, Bi J, Huang L (2013) Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of six major Chinese freshwater lakes. J Environ Qual 42:341–350
Qian H (2001) Study of elements geochemistry of sediments in Xiamen Bay. Master Degree Thesis, Xiamem University
Qin YW, Zhang L, Zheng BH, Cao W (2012) Speciation and pollution characteristics of heavy metals in the sediment of Taihu lake. Environ Sci 33:4291–4299
Tam NFY, Wong YS (2000) Spatial variation of heavy metals in surface sediments of Hong Kong mangrove swamps. Environ Pollut 110:195–205
Vaezi AR, Karbassi AR, Fakhraee M (2015) Assessing the trace metal pollution in the sediments of Mahshahr Bay, Persian Gulf, via a novel pollution index. Environ Monit Assess 187:613
Wang LJ, Zhang CS (1999) Concentration and speciation of 27 elements in sediments and suspented refrom Guangzhou section of the Pearl River. J Basic Sci Eng 7:16–24
Wang P, Jia XX, Tu M, Wang CC (2012) Heavy metal speciation of soil sample collected from either side of a thoroughfare in Beijing and heavy metal pollution. Environ Sci Technol 35:165–172
Wang S, Hu GR, Yu RL, Yu WH, Zhou CF (2014) Pollution assessment and source analysis of heavy metals in surface sediments from Jiulong River estuary. Res Environ Sci 27:1110–1118
Xu ZQ, Ni SJ, Tuo XG, Zhang CJ (2008) Calculation of heavy metals’ toxicity coefficient in the evaluation of potential ecological risk index. Environ Sci Technol 31:112–115
Yan CZ, Li QZ, Zhang X, Li GX (2010) Mobility and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Xiamen Bay and its adjacent areas, China. Environ Earth Sci 60:1469–1479
Yang ZF, Wang Y, Shen ZY, Niu JF, Tang ZW (2009) Distribution and speciation of heavy metals in sediments from the mainstream, tributaries, and lakes of the Yangtze River catchment of Wuhan, China. J Hazard Mater 166:1186–1194
Yu RL, Wang LJ, Hu GR, Zhao YH (2008) Speciation and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in sediments from tidal reaches of the Jinjiang River. Earth Environ 36:113–118
Yu RL, Hu GR, Wang LJ (2010) Speciation and ecological risk of heavy metals in intertidal sediments of Quanzhou Bay, China. Environ Monit Assess 163:241–252
Zhang X, Man XB, Jiang HL (2015) Spatial distribution and source analysis of heavy metals in the marine sediments of Hong Kong. Environ Monit Assess 187:504
Zhao YY, Yan MC (1993) Chemical element abundances of Chinese shallow sea sediment. Sci China (Ser B) 23:1084–1090
Zhu LM, Xu JA, Wang F, Lee B (2011) An assessment of selected heavy metal contamination in the surface sediments from the South China Sea before 1998. J Geochem Explor 108:1–14
Zhu HN, Yuan XZ, Zeng GM, Jiang M, Liang J, Zhang C et al (2012) Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Xiawan Port based on modified potential ecological risk index. T Nonferr Metal Soc 22:1470–1477
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21177043, 21077036), State Key Laboratory of Environmental Geochemistry (SKLEG2013801), and Cultivation Project on 2014 Postgraduates’ Research and Innovation Capability of Huaqiao University (426). The authors express heartfelt thanks to the colleagues who participated in the sampling work. Thanks to anonymous reviewers and their constructive comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Q., Hu, G., Yu, R. et al. Distribution, fractionation, and contamination assessment of heavy metals in offshore surface sediments from western Xiamen Bay, China. Acta Geochim 35, 355–367 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-016-0101-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-016-0101-y