Abstract
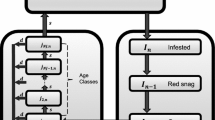
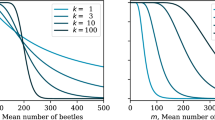
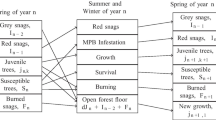
A vigor-structured model for mountain pine beetle outbreak dynamics within a forest stand is proposed and analyzed. This model explicitly tracks the changing vigor structure in the stand. All model parameters, other than beetle vigor preference, were determined by fitting model components to empirical data. An abrupt threshold for tree mortality to beetle densities allows for model simplification. Based on initial beetle density, model outcomes vary from decimation of the entire stand in a single year, to inability of the beetles to infect any trees. An intermediate outcome involves an initial infestation which subsequently dies out before the entire stand is killed. A model extension is proposed for dynamics of beetle aggregation. This involves a stochastic formulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bentz, B.J., Logan, J.A., Amman, G.D., 1991. Temperature-dependent development of mountain pine-beetle (coleoptera, scolytidae) and simulation of its phenology. Can. Entomol. 123, 1083–1094.
Berryman, A.A., 1979. Dynamics of bark beetle populations: Analysis of dispersal and redistribution. Bull. Lociete Entomol. Suisse 52, 227–234.
Berryman, A.A., Stenseth, N.C., Wollkind, D.J., 1984. Metastability of forest ecosystems infested by bark beetles. Res. Popul. Ecol. 26, 13–29.
Burnell, D.G., 1997. A dispersal-aggregation model for mountain pine beetle in lodgepole pine stands. Res. Popul. Ecol. 19, 99–106.
Caswell, H., Nisbet, R.M., de Roos, A.M., Tuljapurkar, S., 1997. Structured-population models: many methods, a few basic concepts. In: Tuljapurkar, S., Caswell, H. (Eds.), Structured-population Models in Marine, Terrestrial, and Freshwater Systems. Chapman and Hall, London
Cole, W.E., McGregor, M.D., 1983. Estimating the rate and amount of tree loss from mountain pine beetle infestations. Technical Report Res. Pap. INT-318, U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Intermountain Forest and Range Experiment Station
Gurney, W.S.C., Nisbet, R.M., 1998. Ecological Dynamics. Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Hassell, M.P., 1978. The Dynamics of Arthropod Predator-Prey Systems. Princeton Monographs in Population Biology. Princeton University Press, Princeton.
He, F., 2006. Observations of mountain pine beetle infestations of lodgepole pine stands in southern British Columbia. Unpublished
Logan, J.A., Powell, J.A., 2001. Ghost forests, global warming, and the mountain pine beetle. Am. Entomol. 47, 160–173.
Logan, J.A., White, P., Bentz, B.J., Powell, J.A., 1998. Model analysis of spatial patterns in mountain pine beetle outbreaks. Theor. Popul. Biol. 53, 236–255.
Logan, J.A., Regniere, R., Powell, J.A., 2003. Assessing the impacts of global warming on forest pest dynamics. Front. Ecol. Environ. 1, 130–137.
Moeck, H.A., Simmons, C.S., 1991. Primary attraction of mountain pine beetle Dendroctonous ponderosae Hopk. (Coloeptera: Scolytidae), to bolts of lodgepole pine. Can. Entomol. 123, 299–304.
Mulock, P., Christiansen, E., 1986. The threshold of successful attack by Ips Typographus on Picea abies: a field experiment. For. Ecol. Manag. 14, 125–132.
Nelson, W.A., Potapov, A., Lewis, M.A., Hundsdorfer, A.E., He, F., 2008. Balancing ecological complexity in predictive models: a reassessment of risk models in the mountain pine beetle system. J. Appl. Ecol. 45, 248–257.
Powell, J.A., Logan, J.A., Bentz, B.J., 1996. Local projections for a global model for mountain pine beetle attacks. J. Theor. Biol. 179, 243–260.
Powell, J.A., Kennedy, B., White, P., Bentz, B.J., Logan, J.A., Roberts, D., 2000. Mathematical elements of attack risk analysis for mountain pine beetles. J. Theor. Biol. 204, 601–620.
Raffa, K.F., Berryman, A.A., 1983. The role of host plant-resistance in the colonization behavior and ecology of bark beetles Coleoptera, Scolytidae. Ecol. Monogr. 53, 27–49.
Raffa, K.F., Berryman, A.A., 1986. A mechanistic computer-model of mountain pine-beetle populations interacting with lodgepole pine stands and its implications for forest managers. For. Sci. 32, 789–805.
Safranyik, L., Carroll, A., 2006. The biology and epidemiology of the mountain pine beetle in lodgepole pine forests. In L. Safranyik, B. Wilson (Eds.) The Mountain Pine Beetle: A Synthesis of Its Biology and Management in Lodgepole Pine, Natural Resources Canada, Canadian Forest Service.
Stancioiu, P.T., O’Hara, K.L., 2006. Leaf area and growth efficiency of regeneration in mixed species, multiaged forests of the Romanian Carpathians. For. Ecol. Manag. 222, 55–66.
Wallin, K.F., Raffa, K.F., 2004. Feedback between individual host selection behavior and population dynamics in an eruptive herbivore. Ecol. Monogr. 74, 101–116.
Waring, R.H., Pitman, G.B., 1985. Modifying lodgepole pine stands to change susceptibility to mountain pine beetle attack. Ecology 66, 889–897.
White, P., Powell, J., 1997. Phase transition from environmental to dynamic determinism in mountain pine beetle attack. Bull. Math. Biol. 59, 609–643.
White, P., Powell, J., 1998. Spatial invasion of pine beetles into lodgepole forests: a numerical approach. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 20, 164–184.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lewis, M.A., Nelson, W. & Xu, C. A Structured Threshold Model for Mountain Pine Beetle Outbreak. Bull. Math. Biol. 72, 565–589 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-009-9461-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-009-9461-3