Abstract
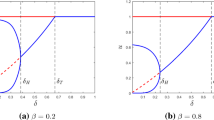
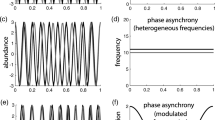
Heterogeneity in habitat plays a crucial role in the dynamics of spatially extended populations and is often ignored by both empiricists and theoreticians. A common assumption made is that spatially homogeneous systems and those with slight heterogeneity will behave similarly and, therefore, the results and data from studies of the former can be applied to the latter. Here, we test this assumption by deriving a phase model from two weakly coupled predator-prey oscillators and analyze the effect of spatial heterogeneity on the phase dynamics of this system. We find that even small heterogeneity between the two patches causes substantial changes in the phase dynamics of the system which can have dramatic effects on both population dynamics and persistence. Additionally, if the prey and predator time scales are similar, the effect of heterogeneity is much greater.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blasius, B., Stone, L., 2000. Chaos and phase synchronization in ecological systems. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 10, 2361–2380.
Blasius, B., Huppert, A., Stone, L., 1999. Complex dynamics and phase synchronization in spatially extended ecological systems. Nature 399, 354–359.
Earn, D., Rohani, P., Grenfell, B., 1998. Persistence, chaos and synchrony in ecology and epidemiology. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 265, 7–10.
Ermentrout, G., 1981. n:m phase-locking of weakly coupled oscillators. J. Math. Biol. 12, 327–342.
Ermentrout, G., 2002. Simulating, Analyzing, and Animating Dynamical Systems. SIAM, Philadelphia.
Goldwyn, E., Hastings, A., 2008. When can dispersal synchronize populations? Theor. Popul. Biol. 73, 395–402.
Grenfell, B., Bjørnstad, O., Kappey, J., 2001. Travelling waves and spatial hierarchies in measles epidemics. Nature 414, 716–723.
Hassell, M., May, R., 1974. Aggregation in predators and insect parasites and its effect on stability. J. Anim. Ecol. 43, 567–594.
Hastings, A., 1997. Population Biology: Concepts and Models. Springer, New York.
Hastings, A., 2001. Transient dynamics and persistence of ecological systems. Ecol. Lett. 4, 215–220.
Holyoak, M., 2000. Habitat patch arrangement and metapopulation persistence of predators and prey. Am. Nat. 156, 378–389.
Hugueny, B., 2006. Spatial synchrony in population fluctuations: extending the Moran theorem to cope with spatially heterogeneous dynamics. Oikos 115, 3–14.
Izhikevich, E., 2000. Phase equations for relaxation oscillators. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 60, 1789–1805.
Jansen, V., 2001. The dynamics of two diffusively coupled predator-prey populations. Theor. Popul. Biol. 59, 119–131.
Kendall, B., Fox, G., 1998. Spatial synchrony, environmental heterogeneity, and population dynamics: analysis of the coupled logistic map. Theor. Popul. Biol. 54, 11–37.
Kuramoto, Y., 1984. Chemical Oscillations, Waves, and Turbulence. Springer, Berlin.
Liebhold, A., Koenig, W., Bjørnstad, O., 2004. Spatial synchrony in population dynamics. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 35, 467–490.
Liebhold, A., Johnson, D., Bjørnstad, O., 2006. Geographic variation in density-dependent dynamics impacts the synchronizing effect of dispersal and regional stochasticity. Popul. Ecol. 48, 131–138.
Malkin, I., 1949. Methods of Poincare and Liapunov in Theory of Non-Linear Oscillations. Gostexizdat, Moscow.
Malkin, I., 1956. Some Problems in Nonlinear Oscillation Theory. Gostexizdat, Moscow.
Moran, P., 1953. The statistical analysis of the Canadian lynx cycle. ii. Synchronization and meteorology. Aust. J. Zool. 1, 291–298.
Peltonen, M., Liebhold, A., Bjørnstad, O., Williams, D.W., 2002. Spatial synchrony in forest insect outbreaks: roles of regional stochasticity and dispersal. Ecology 83, 3120–3129.
Ranta, E., Kaitala, V., Lindström, J., Lindén, H., 1995. Synchrony in population dynamics. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 262, 113–118.
Rosenzweig, M., MacArthur, R., 1963. Graphical representation and stability conditions of predator-prey interactions. Am. Nat. 97, 209–223.
Strogatz, S., 1994. Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos: With Applications to Physics, Biology, Chemistry and Engineering. Perseus Books, Cambridge.
Winfree, A., 1967. Biological rhythms and the behavior of populations of coupled oscillators. J. Theor. Biol. 16, 15.
Winfree, A., 2001. The Geometry of Biological Time. Springer, New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goldwyn, E.E., Hastings, A. Small Heterogeneity Has Large Effects on Synchronization of Ecological Oscillators. Bull. Math. Biol. 71, 130–144 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-008-9355-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-008-9355-9