Abstract
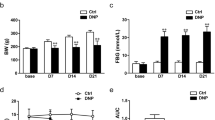
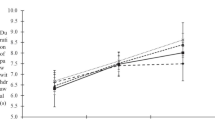
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) accounts for more than 90% of all cases of diabetes mellitus (DM). Diabetic neuropathic pain (DNP) is a common complication of T2DM. Sinomenine is a natural bioactive component extracted from the Sinomenium acutum and has anti-inflammatory effects. The aim of our study was to investigate the effects of sinomenine on DNP mediated by the P2X3 receptor in dorsal root ganglia (DRG). The mechanical withdrawal threshold (MWT) and thermal withdrawal latency (TWL) in T2DM rats were lower than those of control rats. MWT and TWL in T2DM rats treated with sinomenine were higher compared with those in T2DM rats. The expression levels of the P2X3 protein and mRNA in T2DM rat DRG were higher compared with those of the control, while those in T2DM rats treated with sinomenine were significantly lower compared with those of the T2DM rats. Sinomenine significantly inhibited P2X3 agonist ATP-activated currents in HEK293 cells transfected with the P2X3 receptor. Sinomenine decreased the phosphorylation and activation of P38MAPK in T2DM DRG. Therefore, sinomenine treatment may suppress the up-regulated expression and activation of the P2X3 receptor and relieve the hyperalgesia potentiated by the activation of P38MAPK in T2DM rats.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Toth C, Lander J, Wiebe S (2009) The prevalence and impact of chronic pain with neuropathic pain symptoms in the general population. Pain Med 10(5):918–929. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4637.2009.00655.x
Colvin LA, Dougherty PM (2015) Peripheral neuropathic pain: signs, symptoms, mechanisms, and causes: are they linked? Br J Anaesth 114(3):361–363. doi:10.1093/bja/aeu323
Treede RD, Jensen TS, Campbell JN, Cruccu G, Dostrovsky JO, Griffin JW, Hansson P, Hughes R, Nurmikko T, Serra J (2008) Neuropathic pain: redefinition and a grading system for clinical and research purposes. Neurology 70(18):1630–1635. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000282763.29778.59
Ma RC, Chan JC (2013) Type 2 diabetes in east Asians: similarities and differences with populations in Europe and the United States. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1281:64–91. doi:10.1111/nyas.12098
Whiting DR, Guariguata L, Weil C, Shaw J (2011) IDF diabetes atlas: global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2011 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 94(3):311–321. doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2011.10.029
Schreiber AK, Nones CF, Reis RC, Chichorro JG, Cunha JM (2015) Diabetic neuropathic pain: physiopathology and treatment. World J Diabetes 6(3):432–444. doi:10.4239/wjd.v6.i3.432
Xu Y, Wang L, He J, Bi Y, Li M, Wang T, Wang L, Jiang Y, Dai M, Lu J, Xu M, Li Y, Hu N, Li J, Mi S, Chen CS, Li G, Mu Y, Zhao J, Kong L, Chen J, Lai S, Wang W, Zhao W, Ning G (2013) Prevalence and control of diabetes in Chinese adults. JAMA 310(9):948–959. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.168118
Tesfaye S, Selvarajah D (2012) Advances in the epidemiology, pathogenesis and management of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 28(Suppl 1):8–14. doi:10.1002/dmrr.2239
Yoo M, Sharma N, Pasnoor M, Kluding PM (2013) Painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: presentations, mechanisms, and exercise therapy. J Diabetes Metab Suppl. doi:10.4172/2155-6156.S10-005
Davies M, Brophy S, Williams R, Taylor A (2006) The prevalence, severity, and impact of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 29(7):1518–1522. doi:10.2337/dc05-2228
Morales-Vidal S, Morgan C, Mccoyd M, Hornik A (2012) Diabetic peripheral neuropathy and the management of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain. Postgrad Med 124(4):145–153. doi:10.3810/pgm.2012.07.2576
Singh R, Kishore L, Kaur N (2014) Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: current perspective and future directions. Pharmacol Res 80:21–35. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2013.12.005
Burnstock G (2006) Purinergic P2 receptors as targets for novel analgesics. Pharmacol Ther 110(3):433–454. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2005.08.013
Burnstock G (2007) Physiology and pathophysiology of purinergic neurotransmission. Physiol Rev 87(2):659–797. doi:10.1152/physrev.00043.2006
Burnstock G (2009) Purinergic receptors and pain. Curr Pharm Des 15(15):1717–1735
Gao Y, Xu C, Liang S, Zhang A, Mu S, Wang Y, Wan F (2008) Effect of tetramethylpyrazine on primary afferent transmission mediated by P2X3 receptor in neuropathic pain states. Brain Res Bull 77(1):27–32. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2008.02.026
Liang S, Xu C, Li G, Gao Y (2010) P2X receptors and modulation of pain transmission: focus on effects of drugs and compounds used in traditional Chinese medicine. Neurochem Int 57(7):705–712. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2010.09.004
Novakovic SD, Kassotakis LC, Oglesby IB, Smith JA, Eglen RM, Ford AP, Hunter JC (1999) Immunocytochemical localization of P2X3 purinoceptors in sensory neurons in naive rats and following neuropathic injury. Pain 80(1–2):273–282
Zhang A, Gao Y, Zhong X, Xu C, Li G, Liu S, Lin J, Li X, Zhang Y, Liu H, Linag S (2010) Effect of sodium ferulate on the hyperalgesia mediated by P2X3 receptor in the neuropathic pain rats. Brain Res 1313:215–221. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2009.11.067
Burnstock G, Novak I (2013) Purinergic signalling and diabetes. Purinergic Signal 9(3):307–324. doi:10.1007/s11302-013-9359-2
Peng H, Zou L, Xie J, Hong W, Bing W, Zhu G, Lv Q, Xi Z, Liu S, Li G (2016) LncRNA NONRATT021972 siRNA decreases diabetic neuropathic pain mediated by the P2X 3 receptor in dorsal root ganglia. Mol Neurobiol :1–13
Wang S, Xu H, Zou L, Xie J, Wu H, Wu B, Yi Z, Lv Q, Zhang X, Ying M, Liu S, Li G, Gao Y, Xu C, Zhang C, Xue Y, Liang S (2016) LncRNA uc.48+ is involved in diabetic neuropathic pain mediated by the P2X3 receptor in the dorsal root ganglia. Purinergic Signal 12(1):139–148. doi:10.1007/s11302-015-9488-x
Xu GY, Li G, Liu N, Huang LY (2011) Mechanisms underlying purinergic P2X3 receptor-mediated mechanical allodynia induced in diabetic rats. Mol Pain 7:60. doi:10.1186/1744-8069-7-60
Gao T, Hao J, Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z, Wang DQ, XJ X (2013) Analgesic effect of sinomenine in rodents after inflammation and nerve injury. Eur J Pharmacol 721(1–3):5–11. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.09.062
Gao T, Shi T, Wang DQ, Wiesenfeld Z (2014) Repeated sinomenine administration alleviates chronic neuropathic pain-like behaviours in rodents without producing tolerance. Scandinavian Journal of Pain 5(4):249–255
Lagerström MC (2015) Sinomenine is a promising analgesic and anti-hyperalgesic for pain and hypersensitivity in rheumatoid arthritis. Scandinavian Journal of Pain 7:15–16
Pertovaara A (2014) Sinomenine against neuropathic pain hypersensitivity. Scandinavian Journal of Pain 5(4):248
Zhu Q, Sun Y, Zhu J, Fang T, Zhang W, Li JX (2014) Antinociceptive effects of sinomenine in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Sci Rep 4:7270. doi:10.1038/srep07270
Wang AL, Li Z, Yuan M, Yu AC, Zhu X, Tso MO (2007) Sinomenine inhibits activation of rat retinal microglia induced by advanced glycation end products. Int Immunopharmacol 7(12):1552–1558. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2007.07.030
Yin Q, Xia Y, Wang G (2016) Sinomenine alleviates high glucose-induced renal glomerular endothelial hyperpermeability by inhibiting the activation of RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 477(4):881–886. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.06.152
Islam MS (2013) Animal models of diabetic neuropathy: progress since 1960s. J Diabetes Res 2013:149452. doi:10.1155/2013/149452
Li G, Xu H, Zhu S, Xu W, Qin S, Liu S, Tu G, Peng H, Qiu S, Yu S, Zhu Q, Fan B, Zheng C, Li G, Liang S (2013) Effects of neferine on CCL5 and CCR5 expression in SCG of type 2 diabetic rats. Brain Res Bull 90:79–87. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2012.10.002
Srinivasan K, Ramarao P (2007) Animal models in type 2 diabetes research: an overview. Indian J Med Res 125(3):451–472
Liu S, Yu S, Xu C, Peng L, Xu H, Zhang C, Li G, Gao Y, Fan B, Zhu Q, Zheng C, Wu B, Song M, Wu Q, Liang S (2014) Puerarin alleviates aggravated sympathoexcitatory response induced by myocardial ischemia via regulating P2X3 receptor in rat superior cervical ganglia. Neurochem Int 70:39–49. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2014.03.004
Liu S, Zou L, Xie J, Xie W, Wen S, Xie Q, Gao Y, Li G, Zhang C, Xu C, Xu H, Wu B, Lv Q, Zhang X, Wang S, Xue Y, Liang S (2016) LncRNA NONRATT021972 siRNA regulates neuropathic pain behaviors in type 2 diabetic rats through the P2X7 receptor in dorsal root ganglia. Mol Brain 9:44. doi:10.1186/s13041-016-0226-2
Morris GM, Huey R, Lindstrom W, Sanner MF, Belew RK, Goodsell DS, Olson AJ (2009) AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J Comput Chem 30(16):2785–2791. doi:10.1002/jcc.21256
Trott O, Olson AJ (2010) AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J Comput Chem 31(2):455–461. doi:10.1002/jcc.21334
Mansoor SE, Lu W, Oosterheert W, Shekhar M, Tajkhorshid E, Gouaux E (2016) X-ray structures define human P2X3 receptor gating cycle and antagonist action. Nature 538(7623):66–71. doi:10.1038/nature19367
Jiang R, Taly A, Lemoine D, Martz A, Cunrath O, Grutter T (2012) Tightening of the ATP-binding sites induces the opening of P2X receptor channels. EMBO J 31(9):2134–2143. doi:10.1038/emboj.2012.75
Callaghan BC, Cheng HT, Stables CL, Smith AL, Feldman EL (2012) Diabetic neuropathy: clinical manifestations and current treatments. Lancet Neurol 11(6):521–534. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(12)70065-0
Krimon S, Araldi D, Do PF, Tambeli CH, Oliveira-Fusaro MC, Parada CA (2013) P2X3 receptors induced inflammatory nociception modulated by TRPA1, 5-HT3 and 5-HT1A receptors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 112:49–55. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2013.09.017
Burnstock G, Krugel U, Abbracchio MP, Illes P (2011) Purinergic signalling: from normal behaviour to pathological brain function. Prog Neurobiol 95(2):229–274. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2011.08.006
Chizh BA, Illes P (2001) P2X receptors and nociception. Pharmacol Rev 53(4):553–568
Jin SX, Zhuang ZY, Woolf CJ, Ji RR (2003) P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase is activated after a spinal nerve ligation in spinal cord microglia and dorsal root ganglion neurons and contributes to the generation of neuropathic pain. J Neurosci 23(10):4017–4022
Ji RR, Samad TA, Jin SX, Schmoll R, Woolf CJ (2002) P38 MAPK activation by NGF in primary sensory neurons after inflammation increases TRPV1 levels and maintains heat hyperalgesia. Neuron 36(1):57–68
Oh YC, Kang OH, Kim SB, Mun SH, Park CB, Kim YG, Kim YI, Lee YS, Han SH, Keum JH, Shin DW, Ma JY, Kwon DY (2012) Anti-inflammatory effect of sinomenine by inhibition of pro-inflammatory mediators in PMA plus A23187-stimulated HMC-1 cells. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 16(9):1184–1191
Acknowledgements
These studies were supported by grants (nos. 31560276, 81570735, 81171184, 31060139, and 81200853) from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, a grant (no. 20151BBG70250) from the Technology Pedestal and Society Development Project of Jiangxi Province, a grant (no. 20142BAB205028) from the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province, and grants (nos. GJJ13155 and GJJ14319) from the Educational Department of Jiangxi Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Shenqiang Rao and Shuangmei Liu are joint first authors
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11302-017-9560-9.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, S., Liu, S., Zou, L. et al. The effect of sinomenine in diabetic neuropathic pain mediated by the P2X3 receptor in dorsal root ganglia. Purinergic Signalling 13, 227–235 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-016-9554-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-016-9554-z